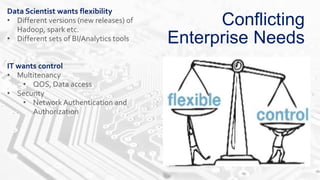
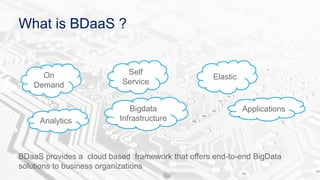
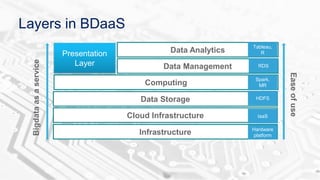
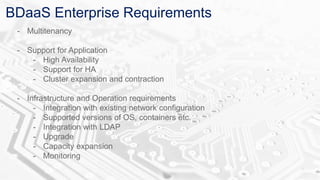
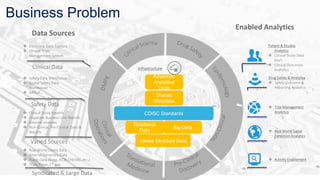
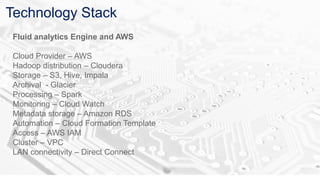
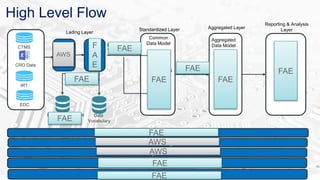
The document discusses BDAAS (Big Data as a Service), outlining its definition, challenges, enterprise requirements, and advantages, including scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. It also presents a case study from the life sciences sector, detailing the integration of various data sources and analytics for clinical studies. Key technologies include AWS and Hadoop distributions for infrastructure management and analytics processing.