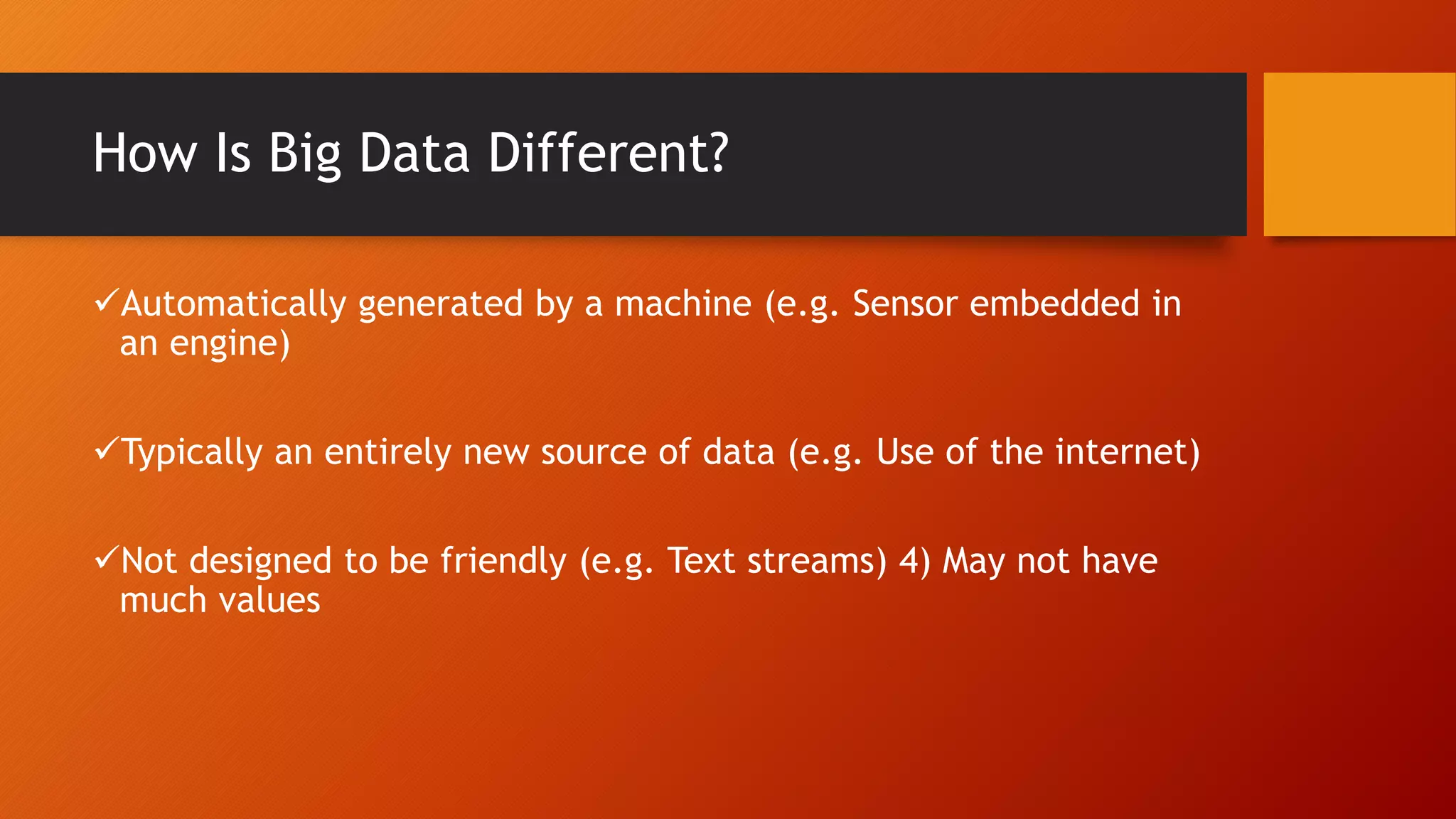
Big data refers to large datasets that are too complex for traditional data processing applications. Examples include Wikipedia which contains terabytes of text and images. Big data is characterized by being automatically generated, from new sources like the internet, and not designed for easy use. Analyzing big data can provide competitive advantages through insights from hidden patterns. Tools used for big data include distributed servers, cloud computing, distributed storage, distributed processing, and high performance databases. Data mining of big data helps businesses make better decisions by discovering patterns and relationships. Applications of big data include smarter healthcare, homeland security, traffic control, and more. Risks include being overwhelmed by data, escalating costs, and privacy issues. Big data impacts IT through new job opportunities in