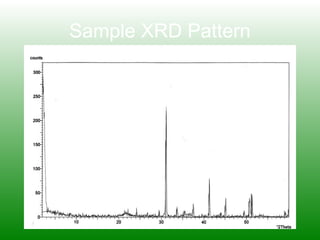
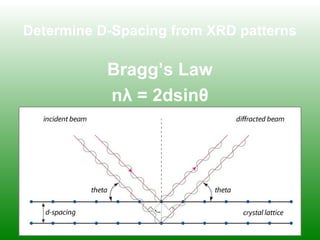
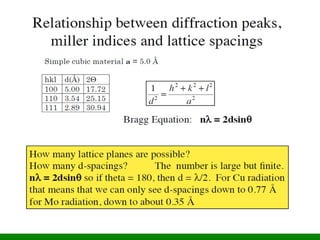
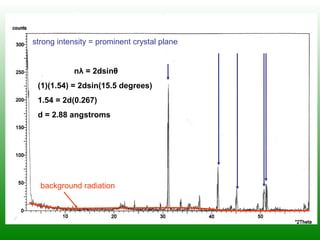
The XRD technique involves taking a powdered sample and illuminating it with x-rays of fixed wavelength. The intensity of the reflected radiation is recorded using a goniometer and analyzed to calculate the inter-atomic spacing based on reflection angle. Spacings are compared to known data to identify possible mineral matches. Samples are powdered finely and randomly oriented to give a statistical representation of all atomic planes. Problems can arise with preferentially oriented minerals like mica and clay.