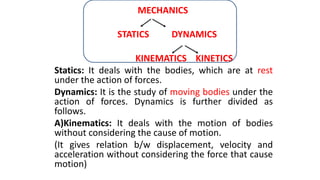
This document provides an overview of laws of motion from a 10th grade physics textbook. It discusses key topics like rest and motion, mechanics, Aristotle and Galileo's theories of force and inertia. It explains that mechanics has two branches - statics dealing with bodies at rest and dynamics dealing with moving bodies. Dynamics further divides into kinematics concerning motion without forces, and kinetics concerning motion and causes. The document outlines Galileo's proposals about inertia and uniform motion. It also previews upcoming topics on Newton's laws of motion, forces, torque, momentum and applications of mechanics principles.