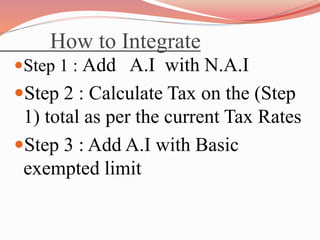
This document discusses agricultural income as defined in the Indian Income Tax Act of 1961. It defines agricultural income as income derived from agricultural sources in India. It exempts agricultural income from taxation under section 10(1) of the Act. The document outlines the various types of agricultural income, including income from cultivation, agricultural processes, sale of produce, and renting agricultural property. It also discusses the tests to determine what qualifies as agricultural income and provides examples of agricultural and non-agricultural incomes. The document concludes with an explanation of how agricultural income is integrated with non-agricultural income for taxation purposes when thresholds are exceeded.