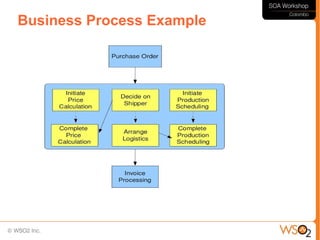
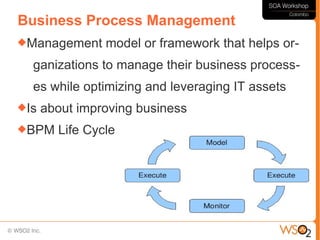
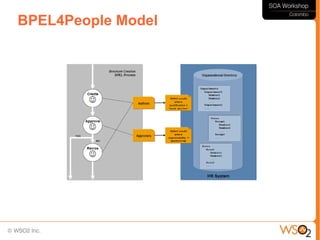
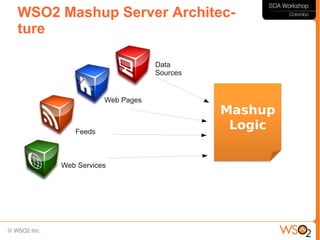
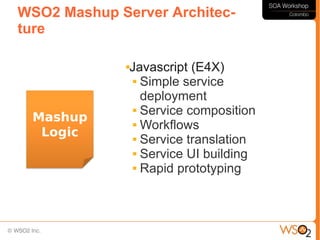
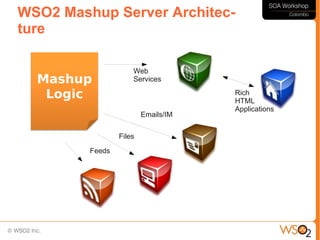
This document discusses business process management (BPM) and how it relates to service-oriented architecture (SOA) and mashups. It defines BPM as a framework that helps organizations manage and optimize their business processes while leveraging IT assets. BPM provides a bridge between business goals and IT solutions, while SOA is an architectural style for developing distributed systems. BPM needs SOA to access data and functionality across systems, and SOA needs BPM for service coordination and orchestration. The document also discusses modeling business processes, using BPEL for process composition, and when to use BPEL versus a lighter-weight mashup approach.