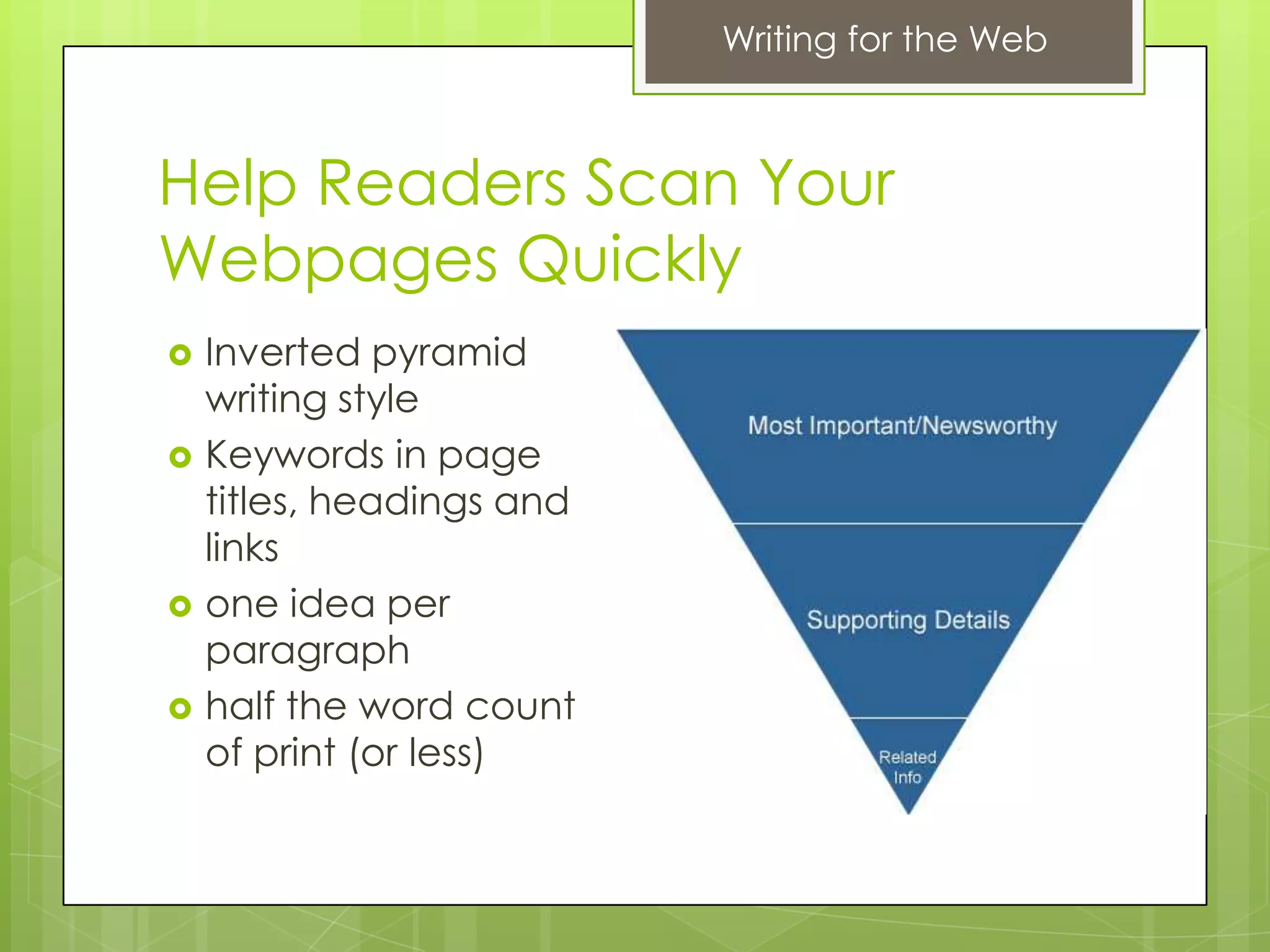
The document discusses tips for effective writing for the web. It begins with an introduction of the author and their background in web content strategy. It then contrasts print vs. web writing, noting that web writing should use shorter paragraphs and place structure in the writer's hands rather than space. The document outlines six tips for web writing: keep content concise, use headings, help readers scan quickly, use lists and formatting, use visuals strategically, and use PDFs sparingly. It emphasizes getting to the point quickly and using keywords and formatting to aid scanning.