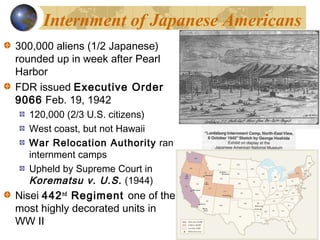
World War 2 began in 1939 after Germany invaded Poland. Germany was led by Adolf Hitler and the Nazi party, who had risen to power in 1933. Hitler aggressively expanded German territory by remilitarizing the Rhineland in 1936 and annexing Austria and the Sudetenland in 1938. In 1939, Germany formed an alliance with the Soviet Union and invaded Poland, prompting Britain and France to declare war on Germany. Germany then quickly conquered Western Europe using the new "blitzkrieg" approach of coordinated air and land attacks. The U.S. initially remained neutral through isolationist policies, but began providing aid to Britain through acts like Lend-Lease. On December 7, 1941, Japan attacked the U.