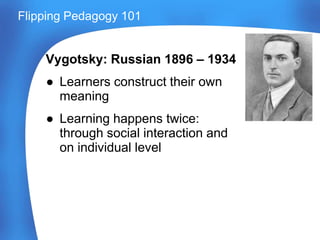
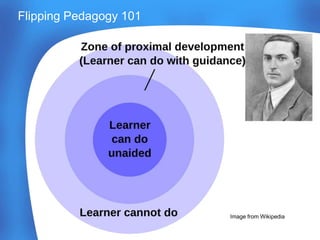
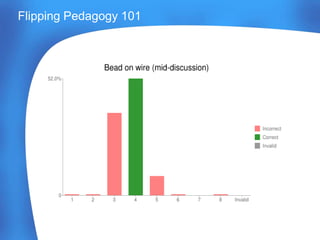
This document discusses flipping pedagogy and constructivist learning theories. It provides context on flipping pedagogy workshops and references several theorists including Piaget, Vygotsky, Posner, and Ausubel. Key constructivist concepts are explained, such as assimilation, accommodation, the zone of proximal development, and conceptual change theory. Factors that influence pedagogical decisions are outlined, including content, aims, and responsiveness to students. The document also discusses peer instruction techniques and decisions for implementing clicker questions in the classroom.