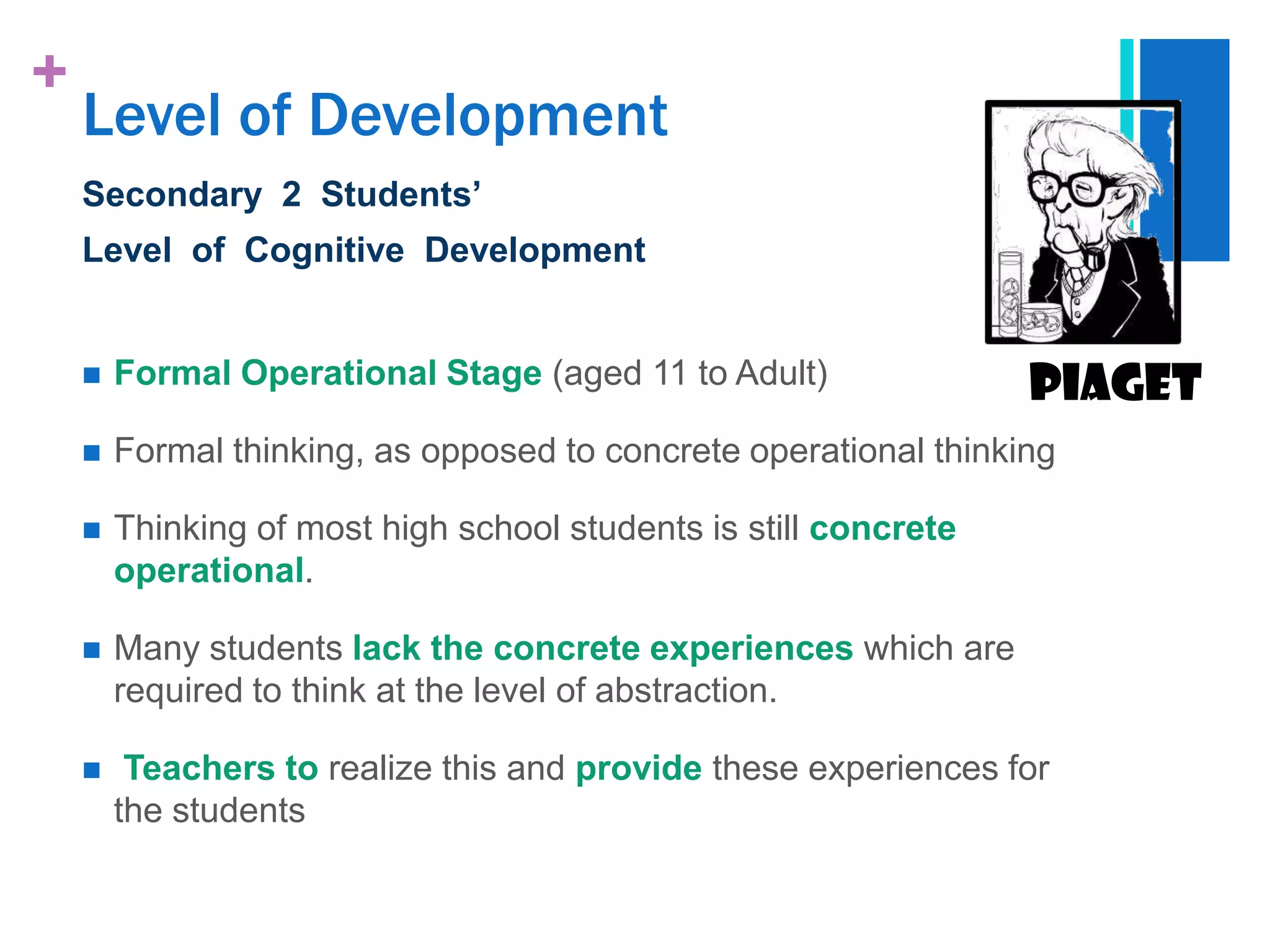
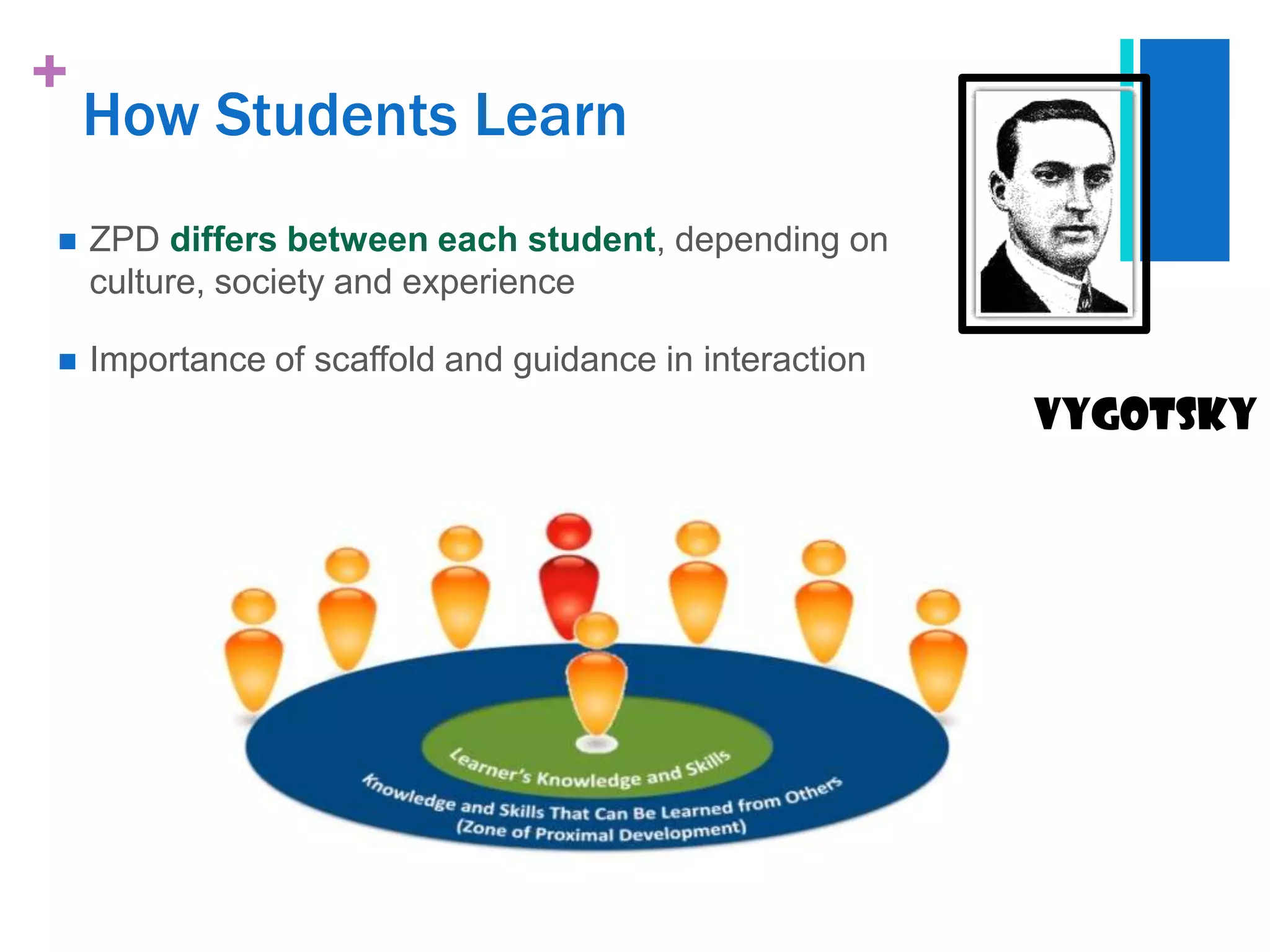
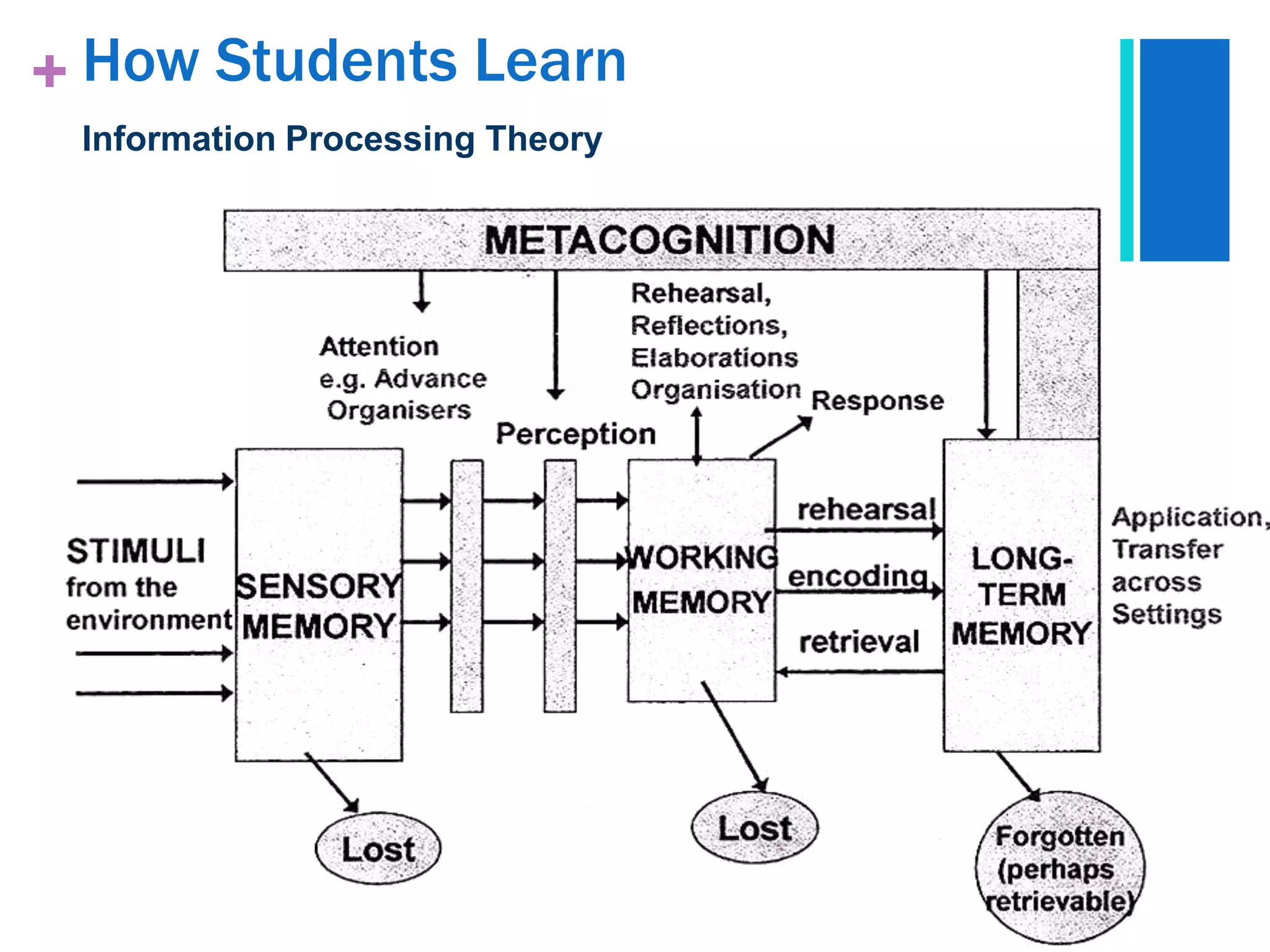
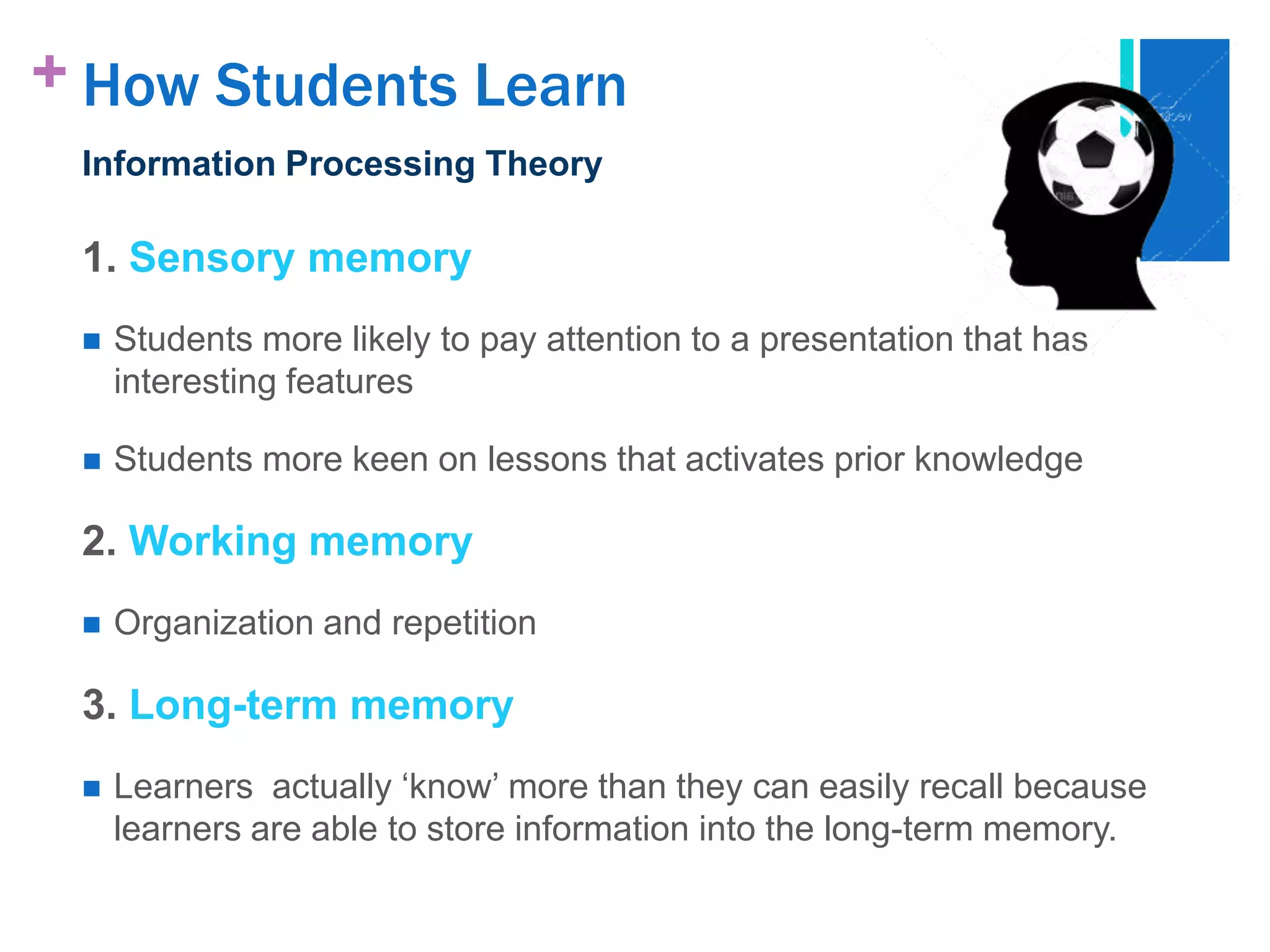
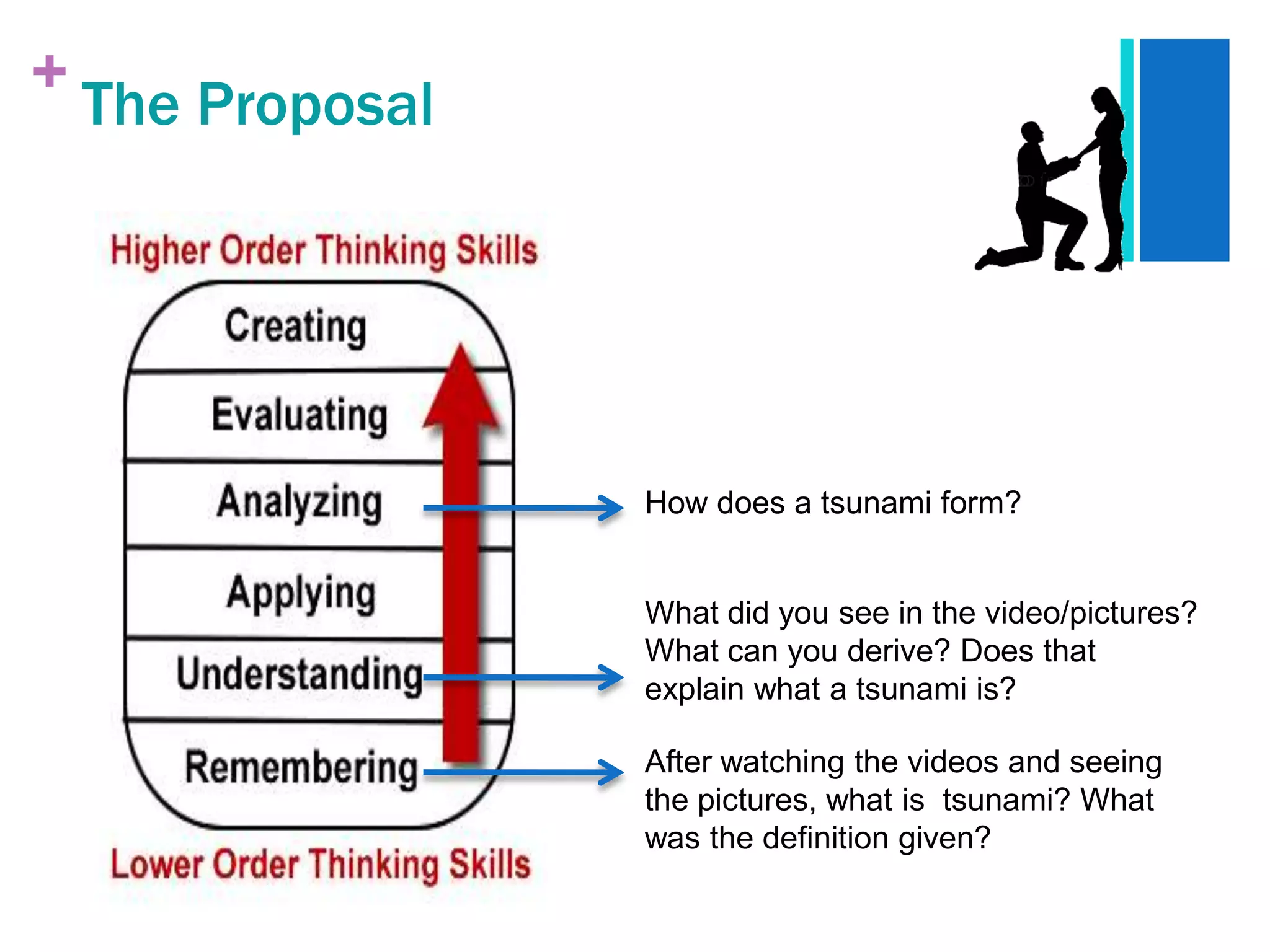
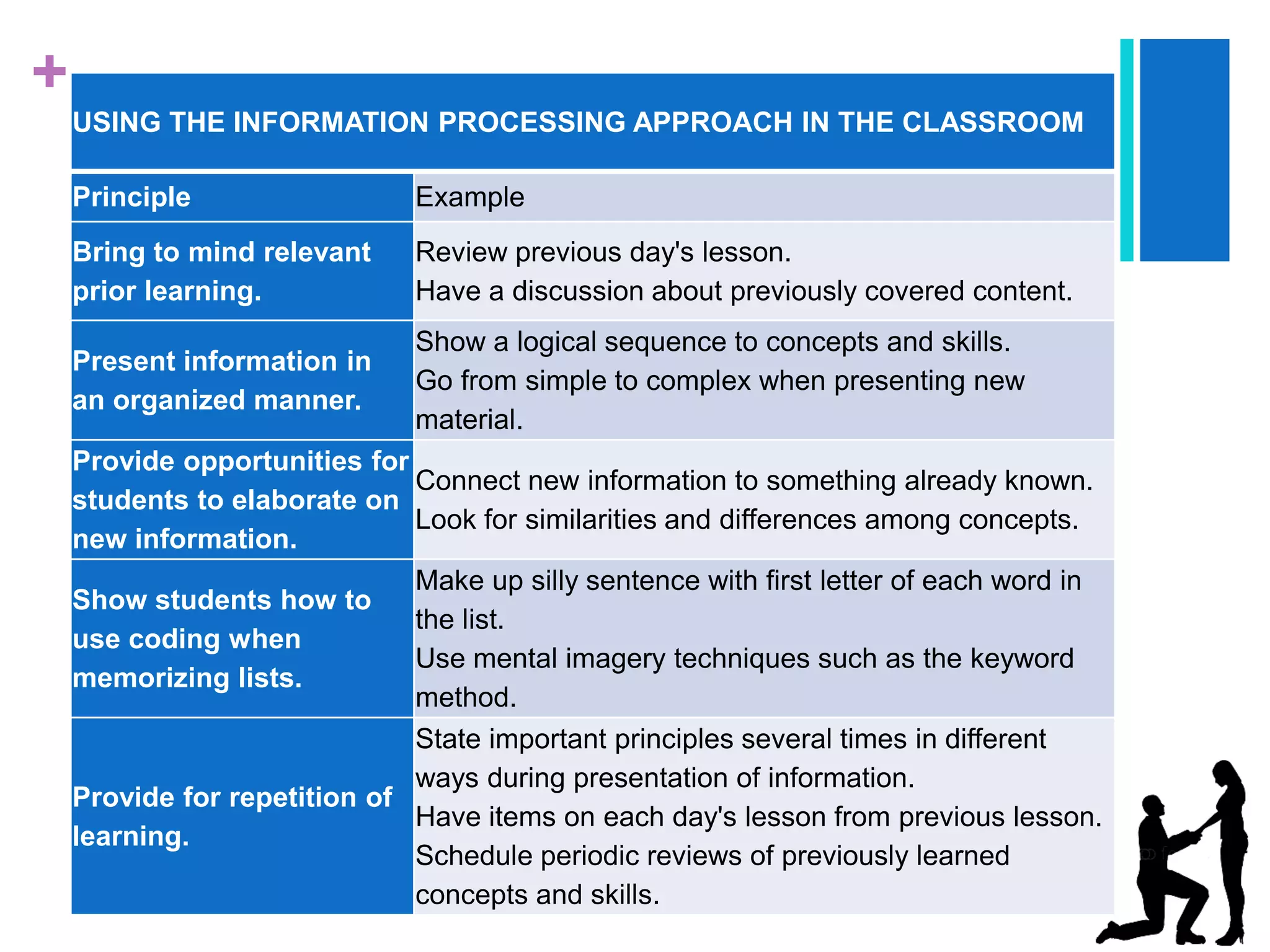
The document presents a case study analysis of a teacher, Ms. Rita, who struggled with engaging her secondary 2 students in a lesson about tsunamis due to not properly considering their cognitive development level and learning processes according to theorists like Piaget and Vygotsky. It analyzes the students' developmental level and how they learn, and proposes pedagogical strategies Ms. Rita could employ to improve her lesson planning and instruction, such as activating prior knowledge, using scaffolding techniques, and facilitating social interaction and meaning making.