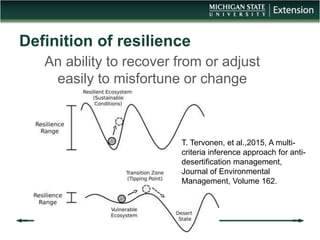
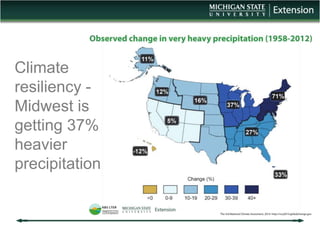
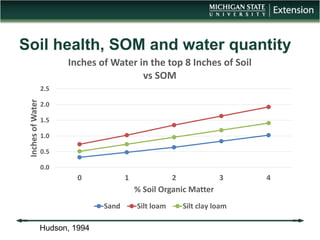
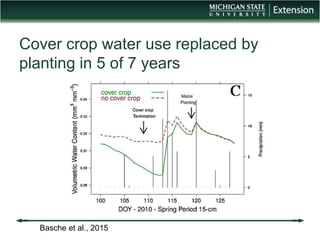
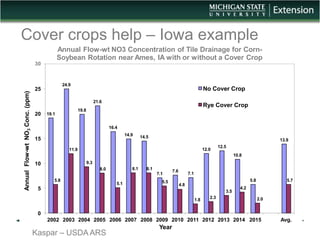
The document discusses the relationship between cover crops, soil health, and climate resilience. It defines resilience as the ability to recover from or adjust to change. Cover crops can increase resilience by building soil organic matter which acts like a sponge to absorb and store water, helping soils better withstand both drought and heavy rainfall. Studies show cover crops increase water storage in soil, conserve water, and increase water availability for crops in dry years. Cover crops also reduce nutrient loss from soils and improve water quality. In conclusion, cover crops contribute to climate resilience by improving soil health and increasing available water.