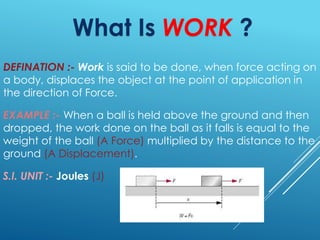
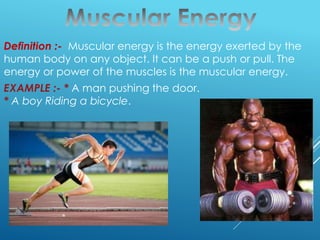
The document explains the concept of work in physics as the displacement of an object by a force, with a focus on various types of energy including kinetic, potential, heat, thermal, mechanical, muscular, sound, and chemical energy. It outlines the law of conservation of energy, which states that energy cannot be created or destroyed but can be transformed. Additionally, it defines power as the rate of doing work, providing examples and SI units for each concept discussed.