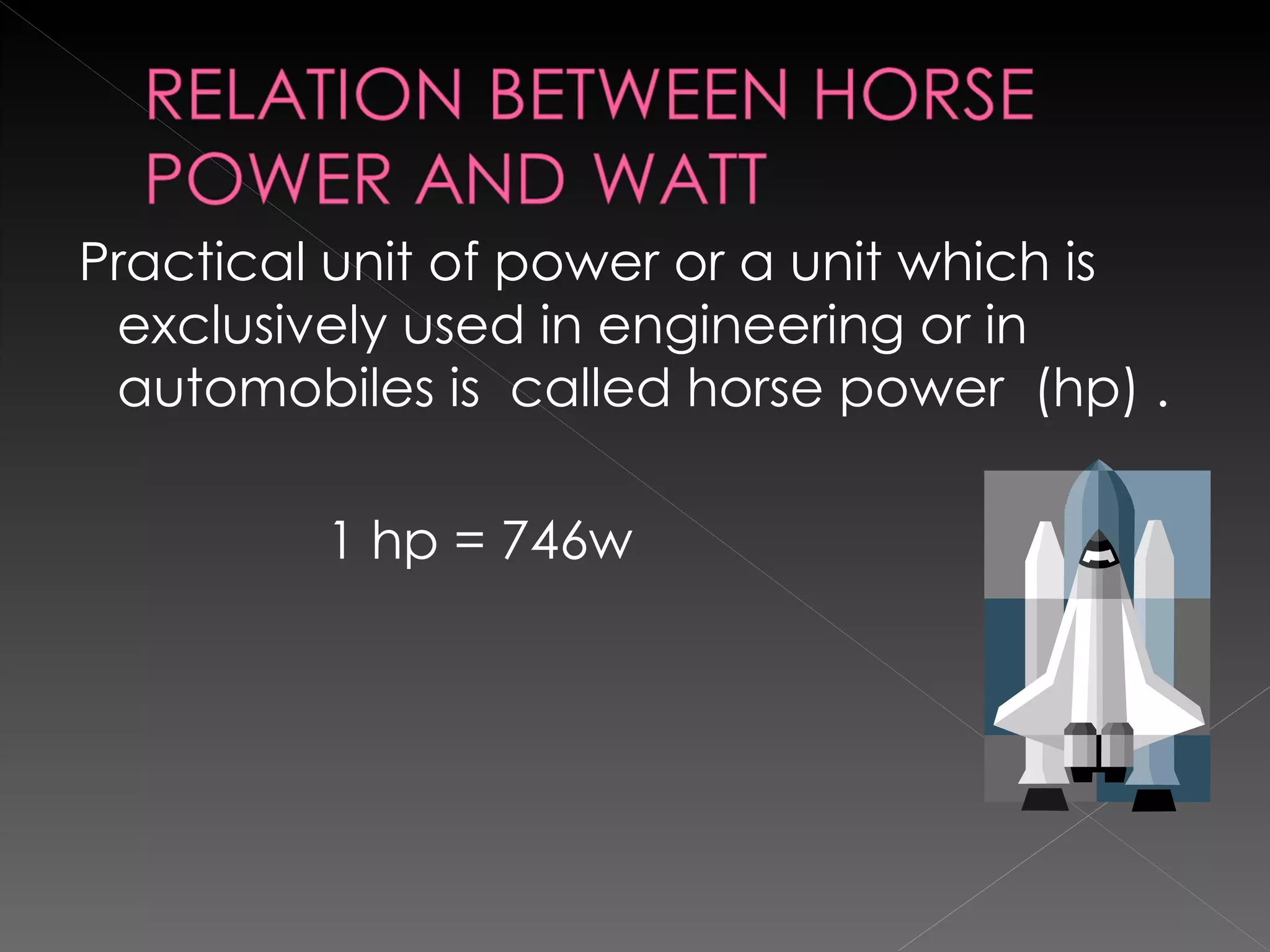
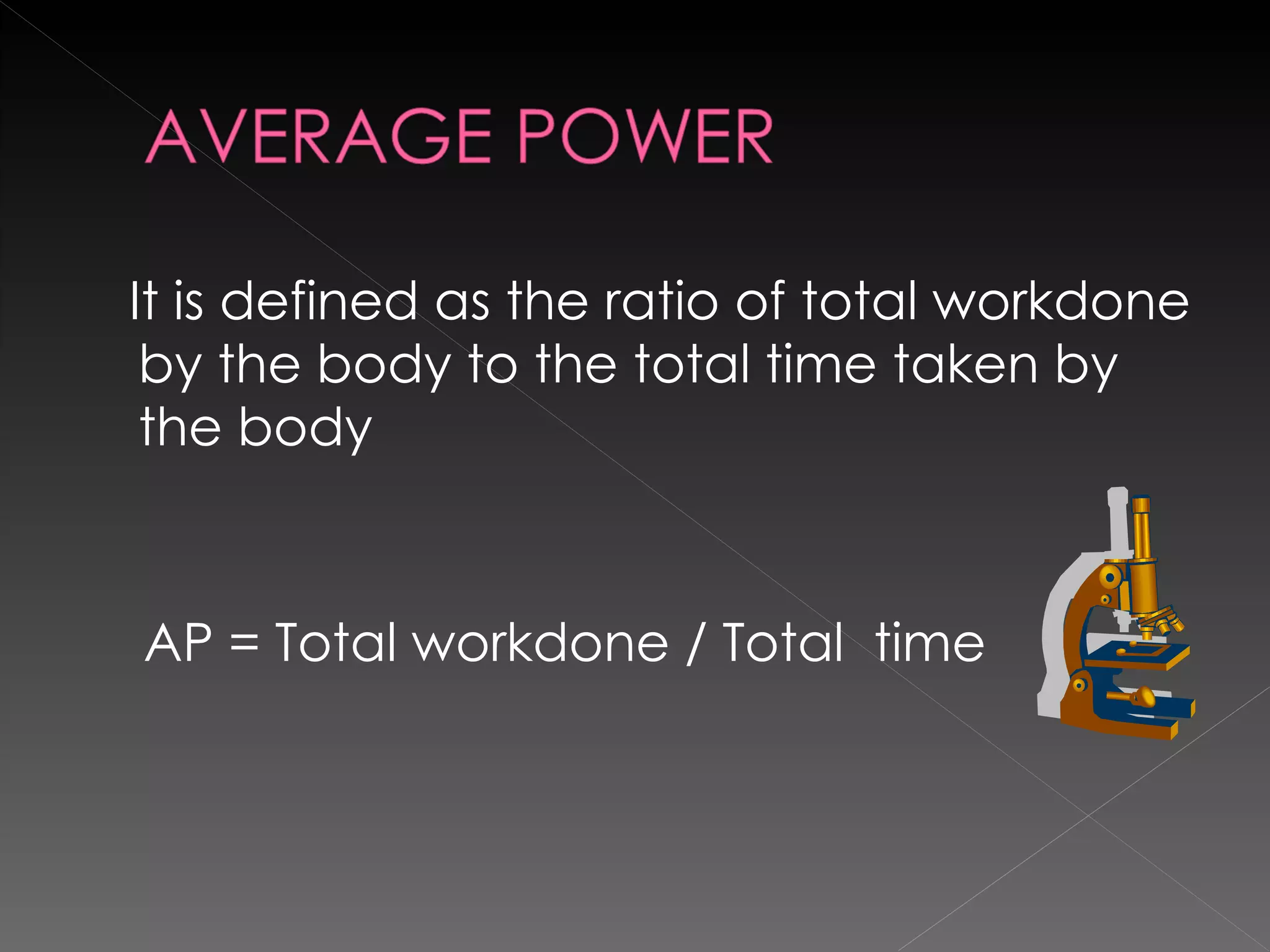
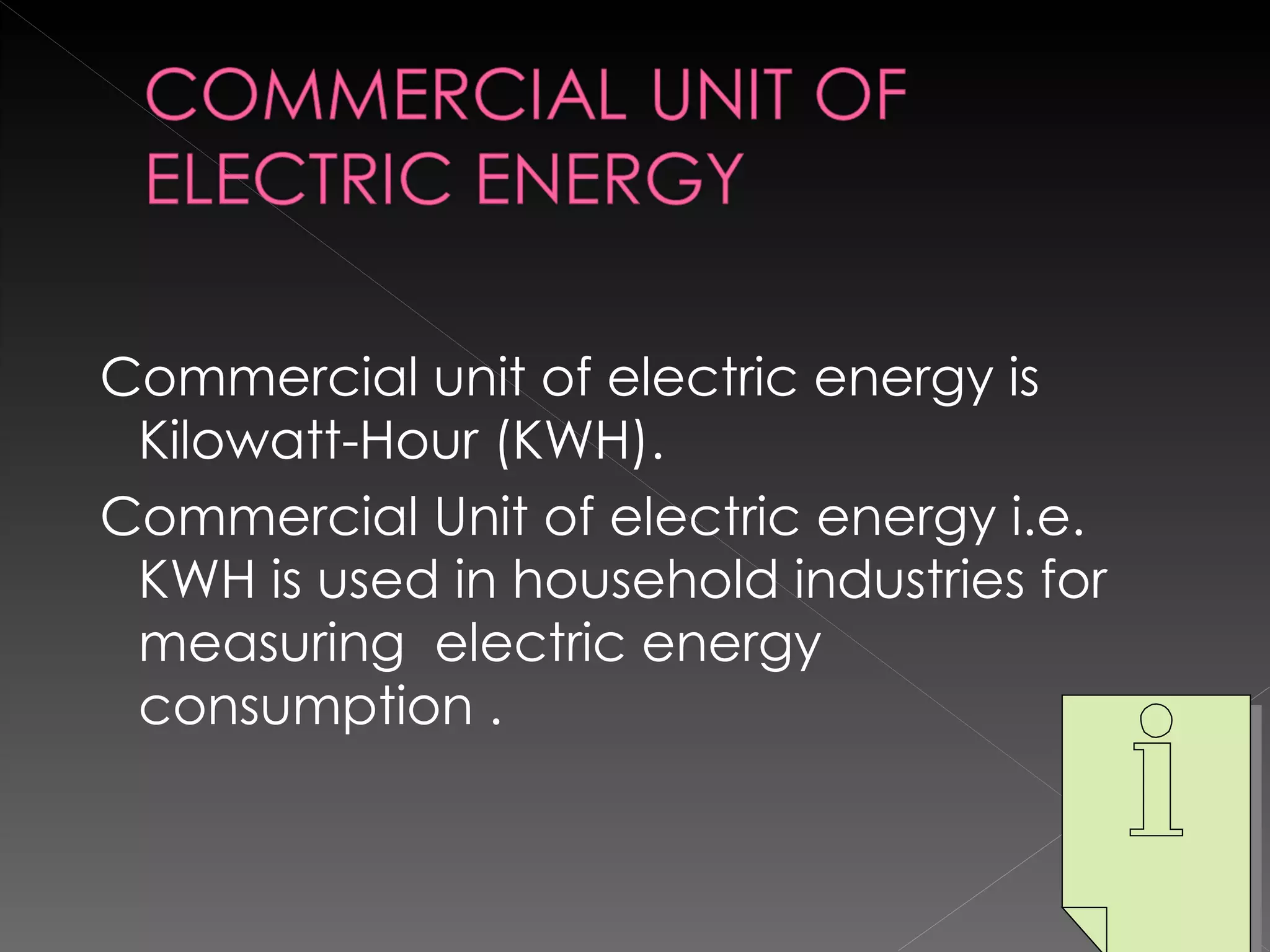
The document defines key terms related to work, energy, and power in physics. It provides the scientific definitions of work, energy, and power, outlines different types of energy, and discusses the units used to measure work, energy, and power. The key equations for work, kinetic energy, and potential energy are also presented.







![CASE 1 When the direction of force and displacement are same . we know W = FScosθ (θ = 0 [in degree] ) W =FScos180 W =FS* 1 W =FS Example- when a body is dropped from a certain height.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amitsharmaandmohineeshsharma-120102075019-phpapp01/75/Amit-sharma-and-mohineesh-sharma-9-2048.jpg)









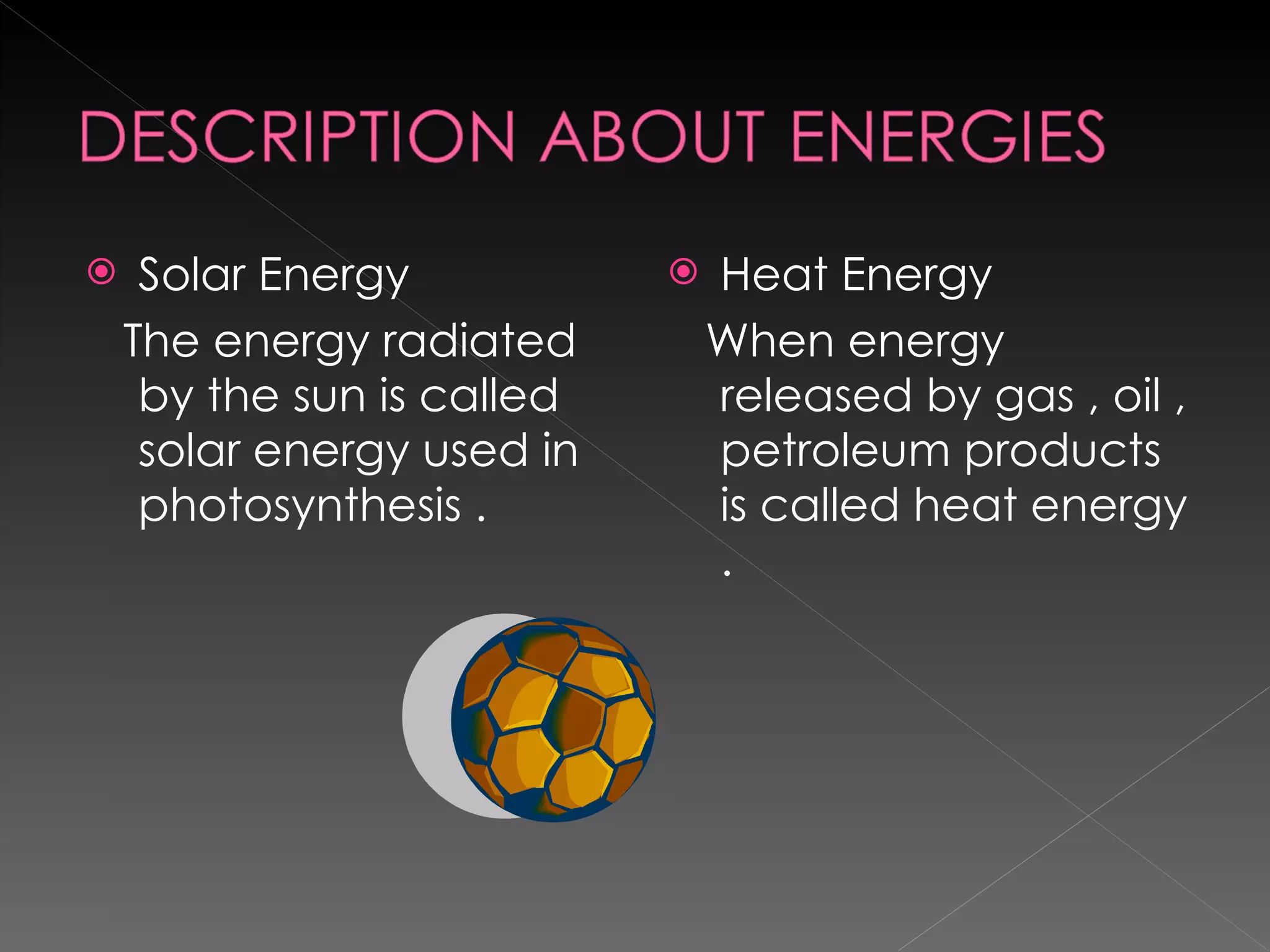




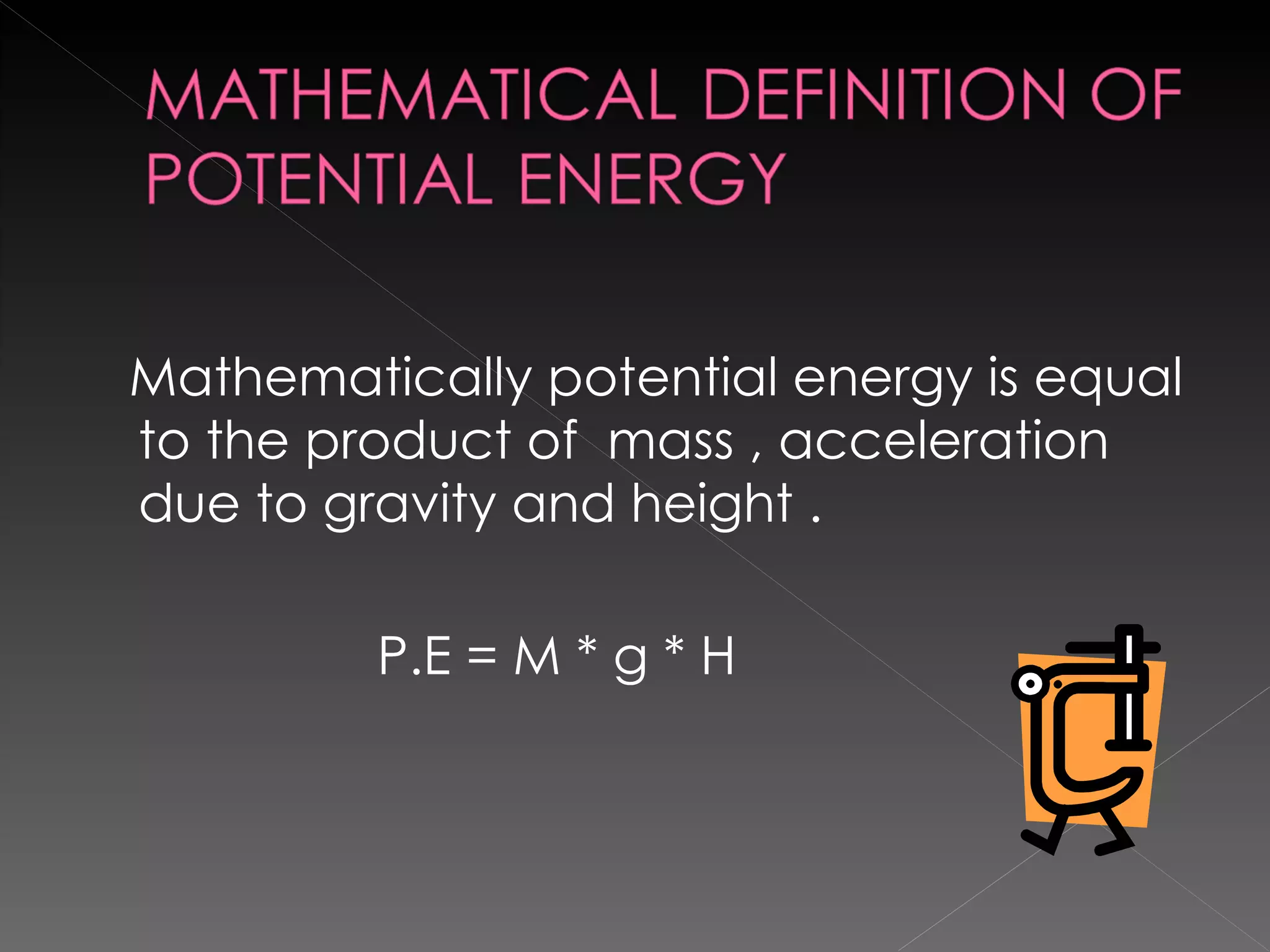



![si unit of power = si unit of wok / si unit time W = J / SI Unit of power is Watt [ W] and is named in the honor of James Watt .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amitsharmaandmohineeshsharma-120102075019-phpapp01/75/Amit-sharma-and-mohineesh-sharma-32-2048.jpg)