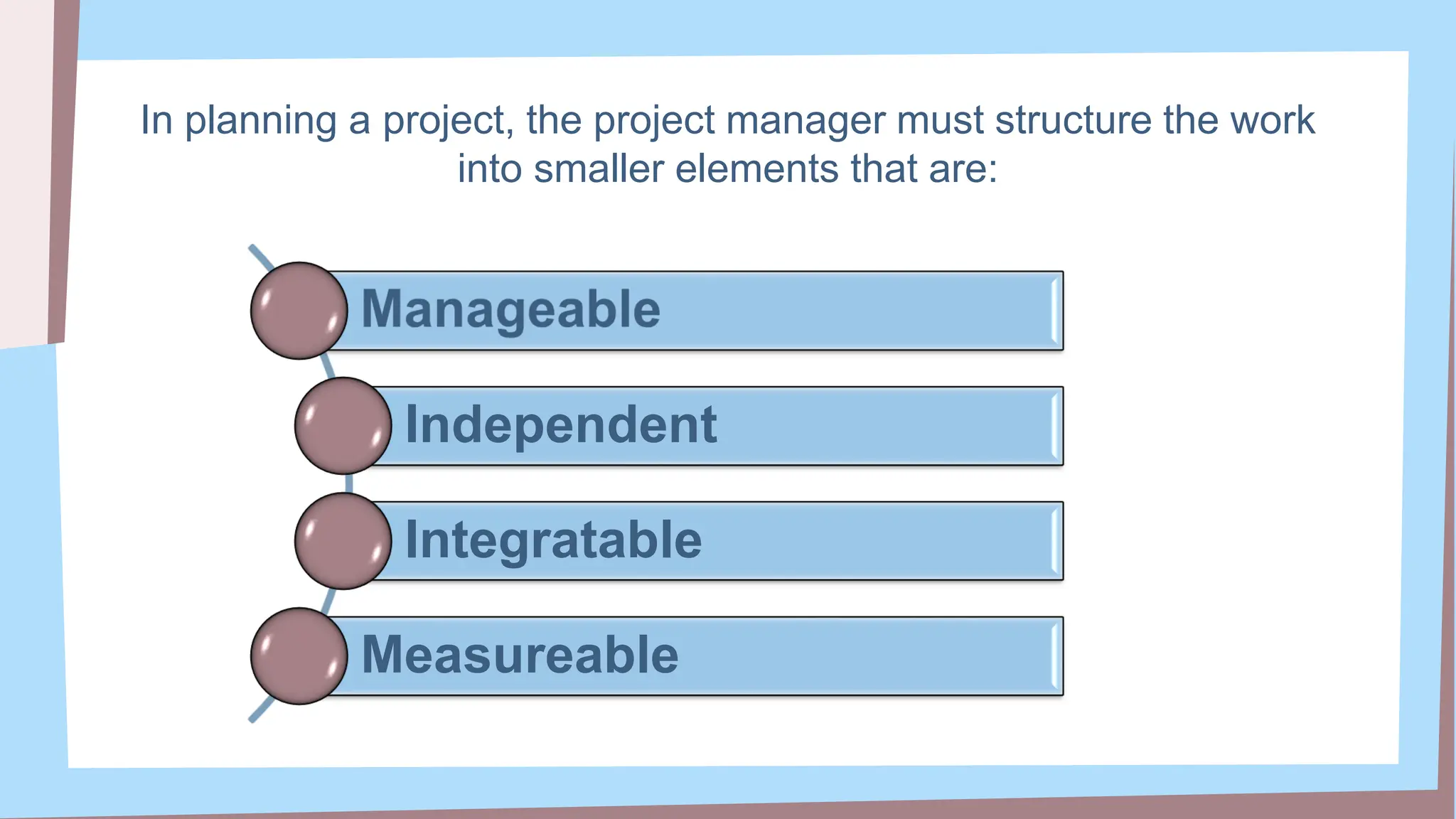
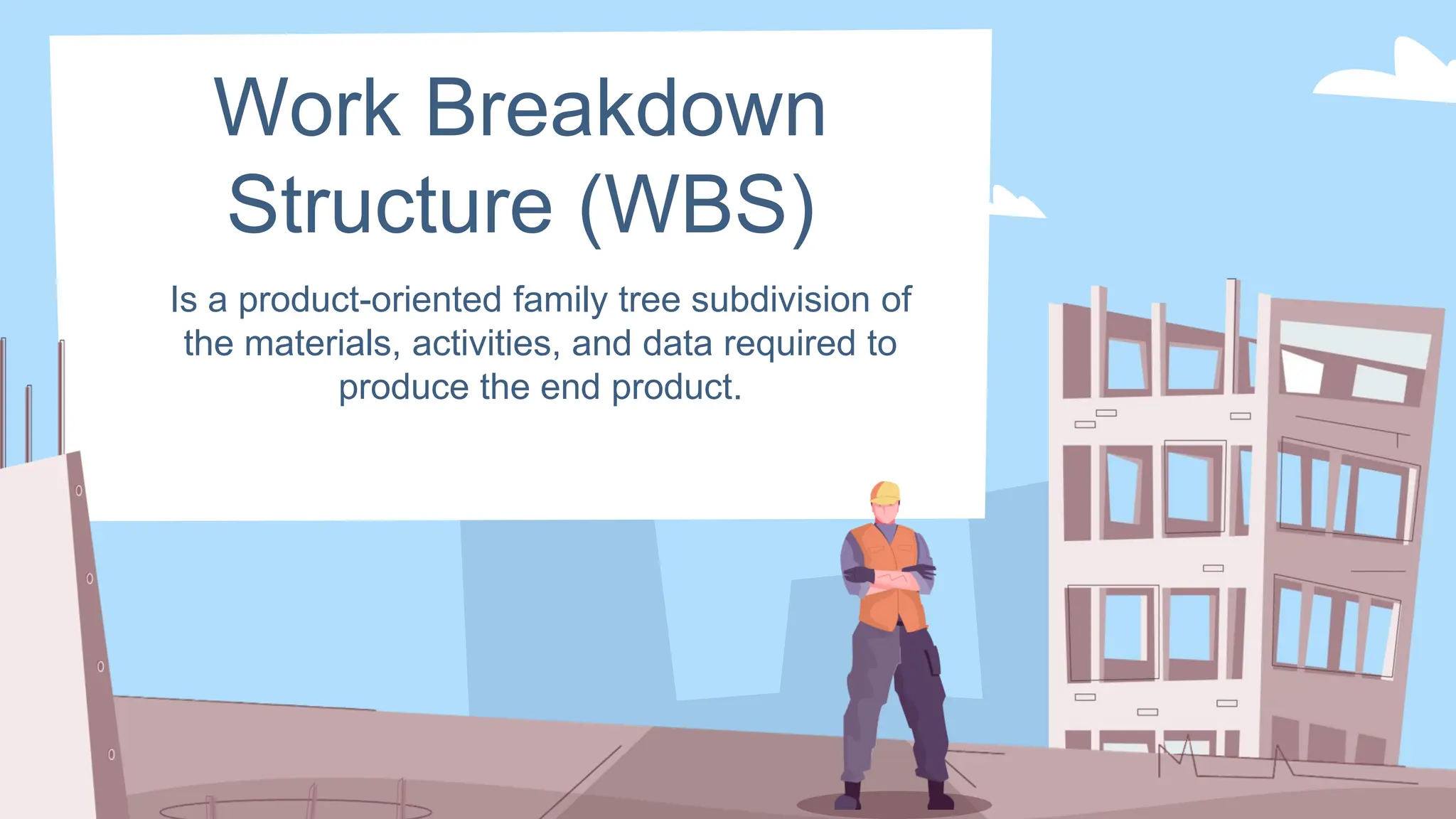
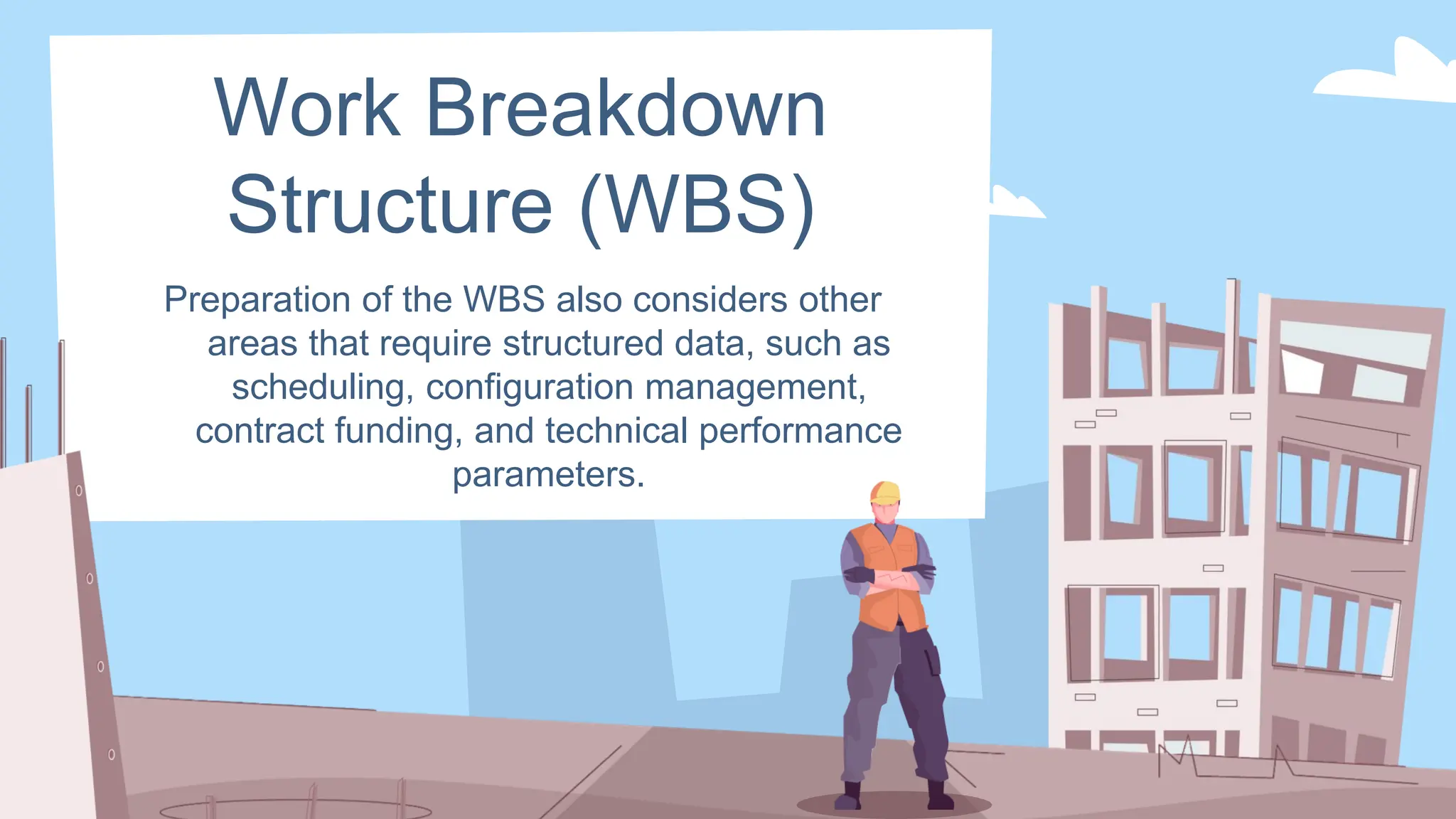
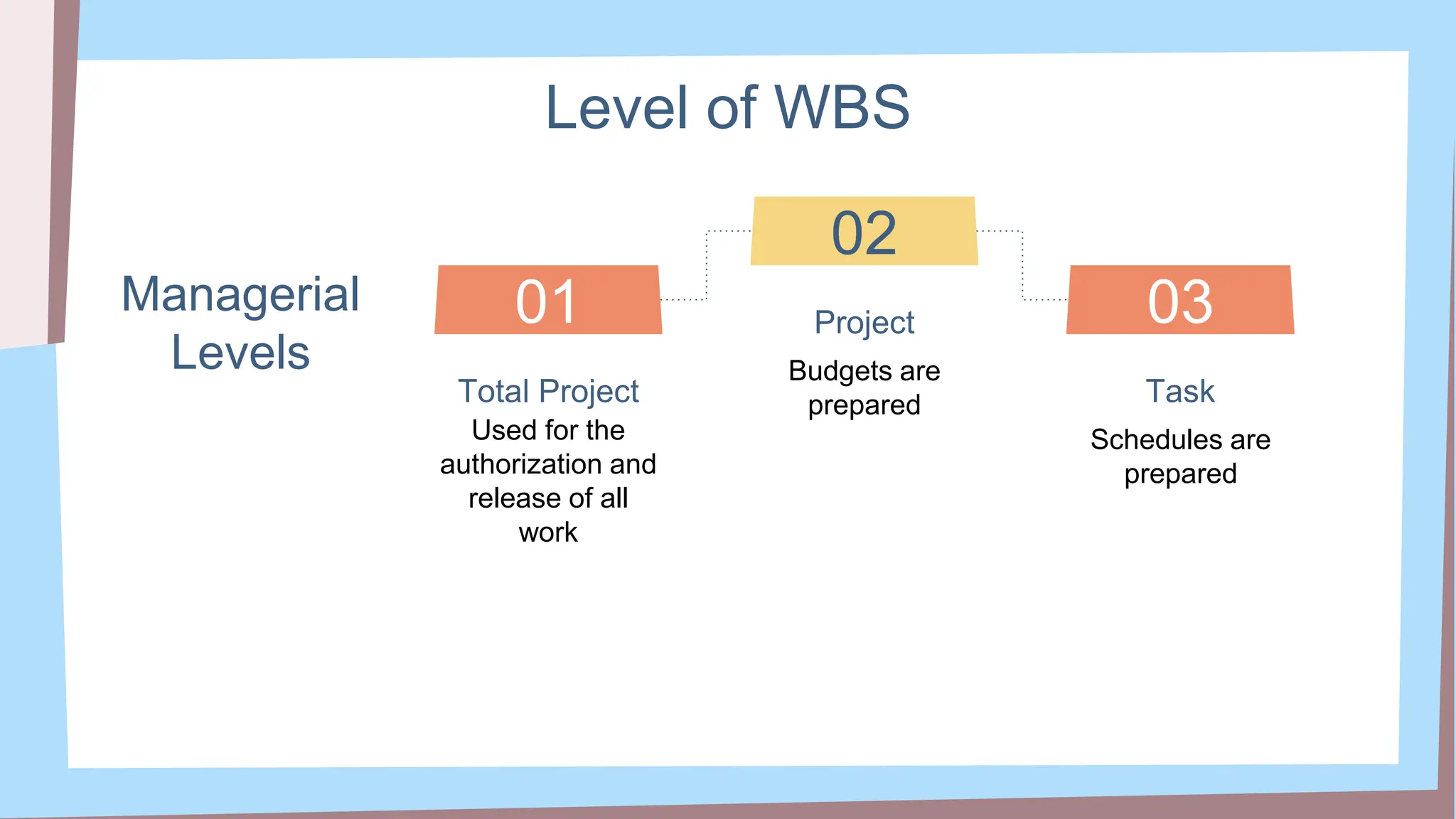
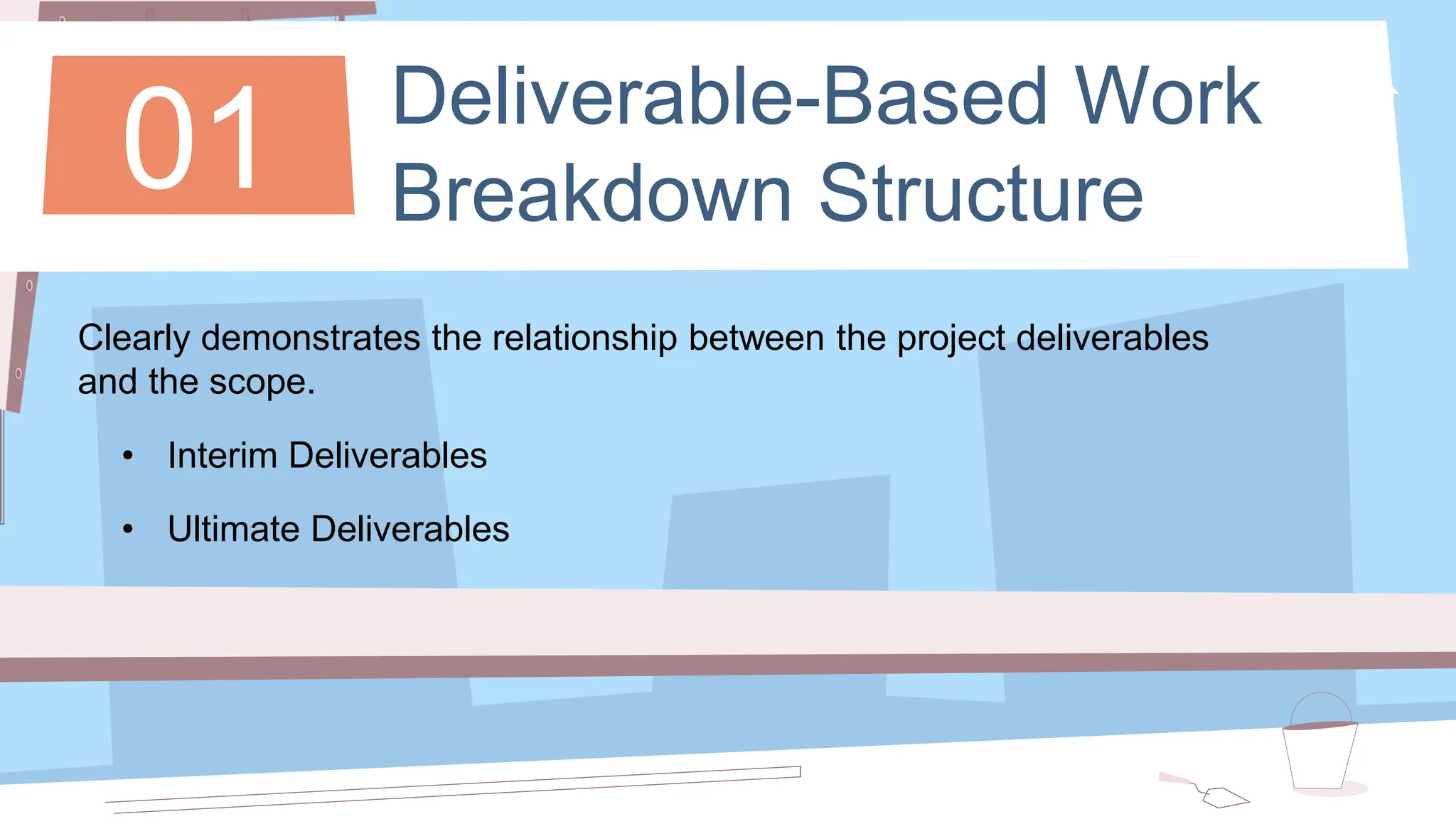
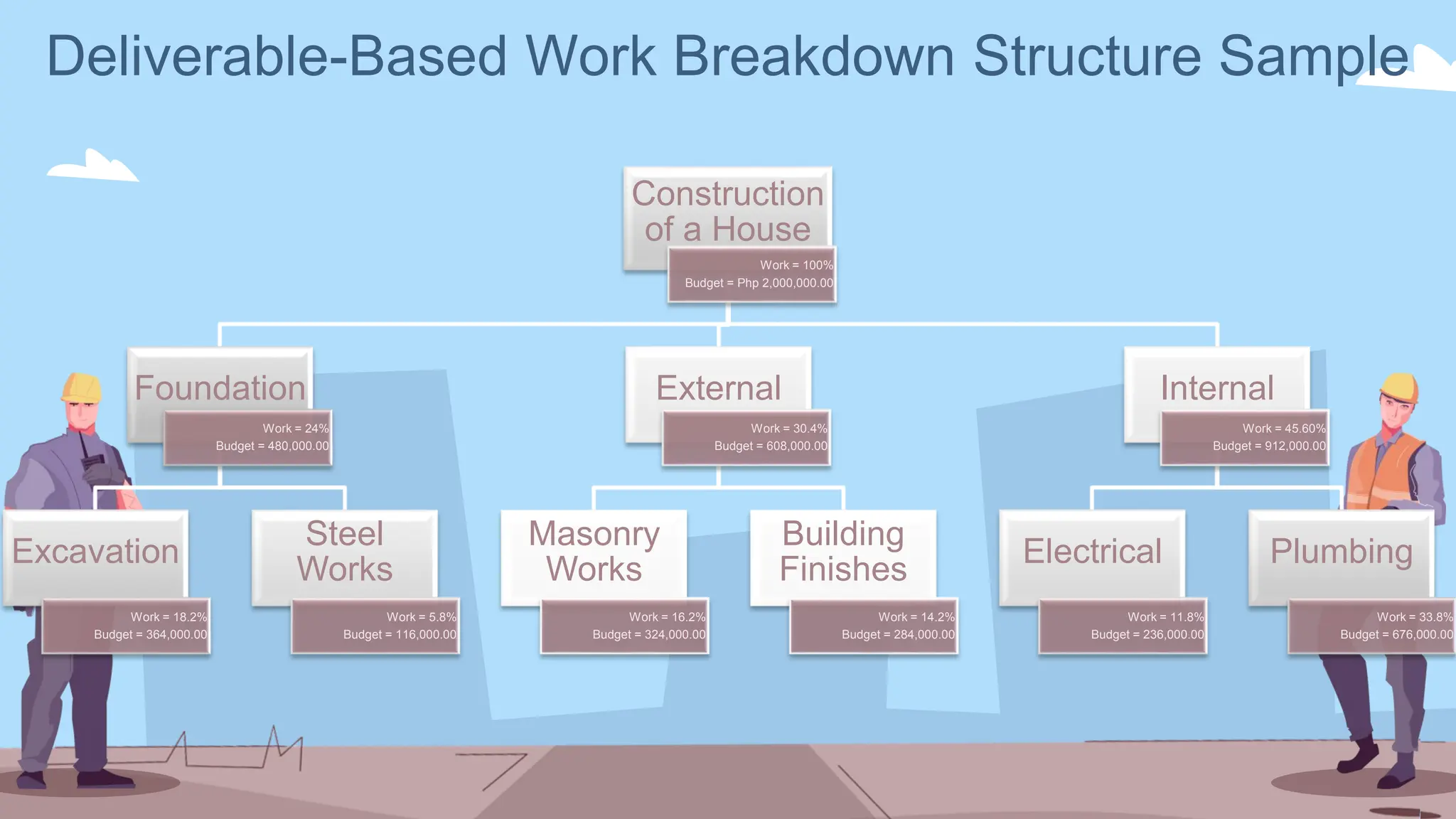
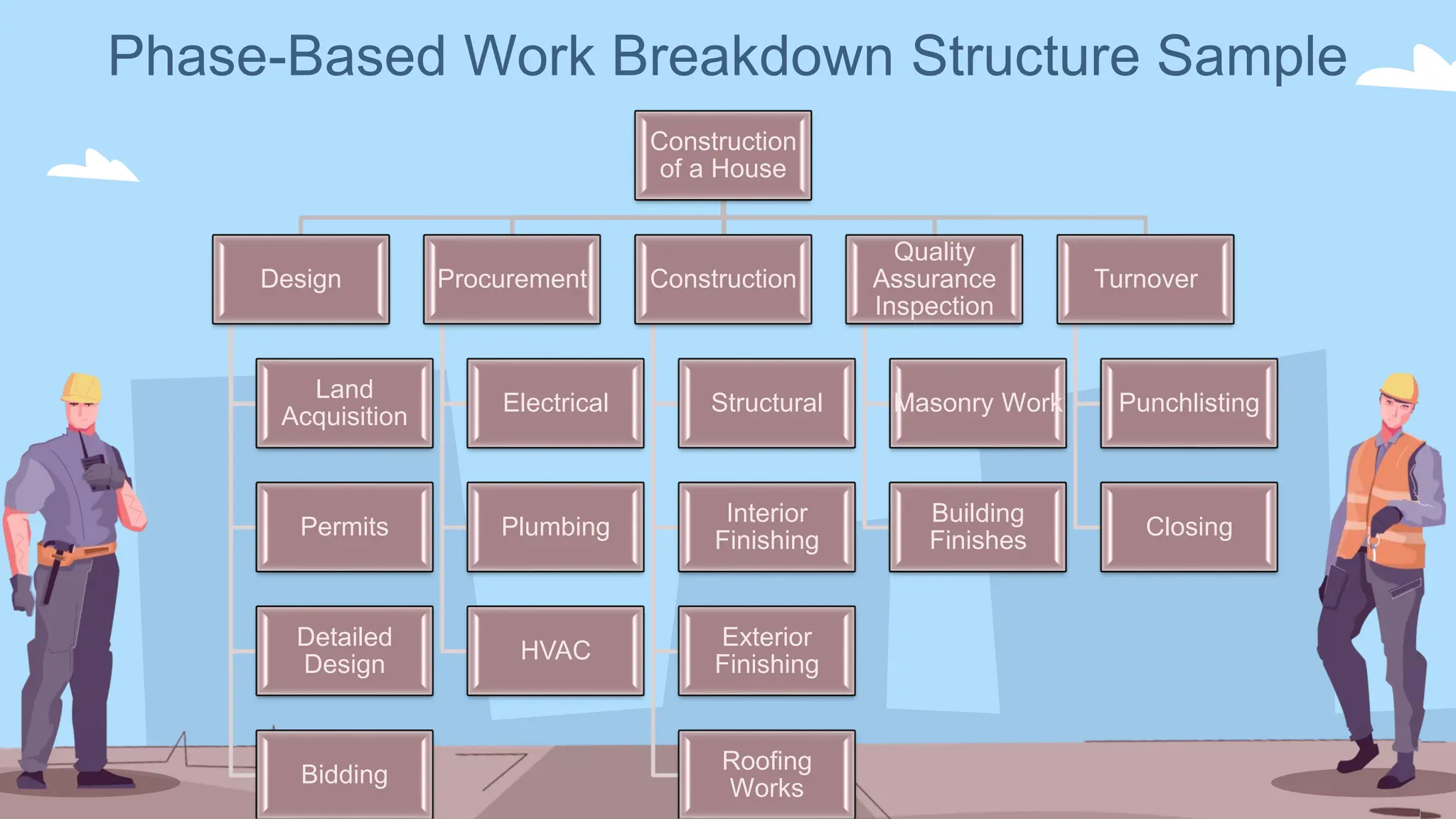
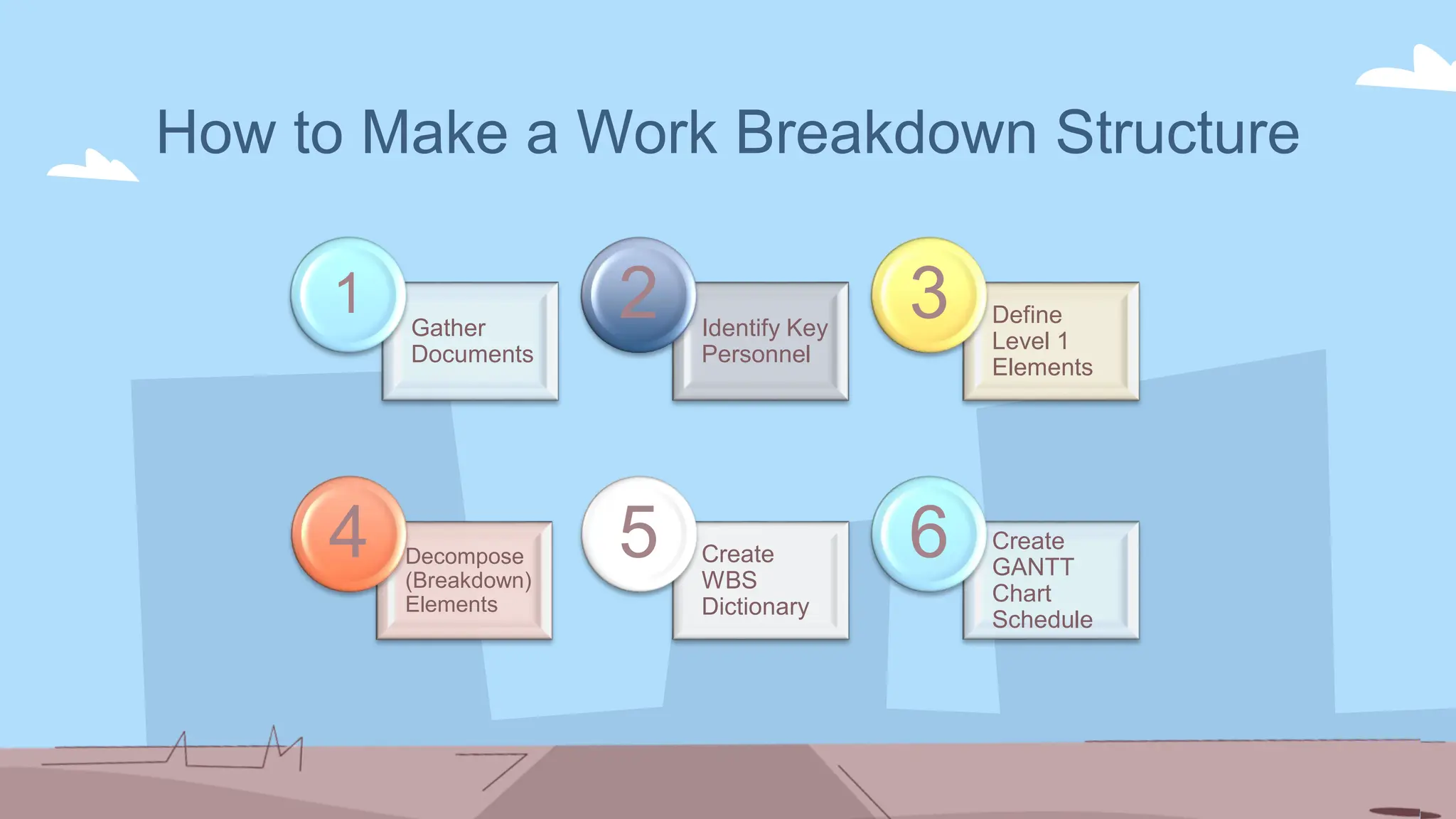
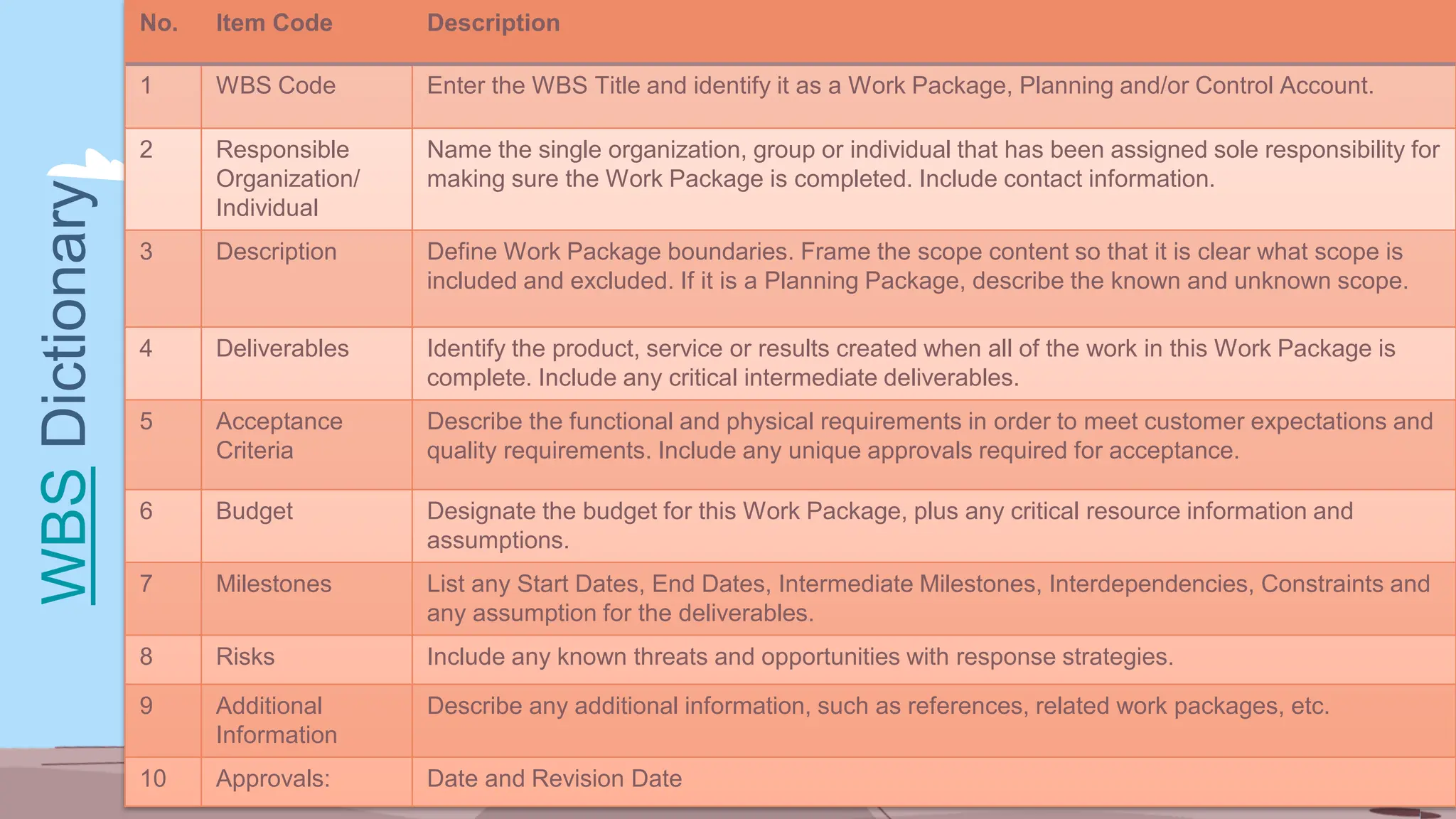
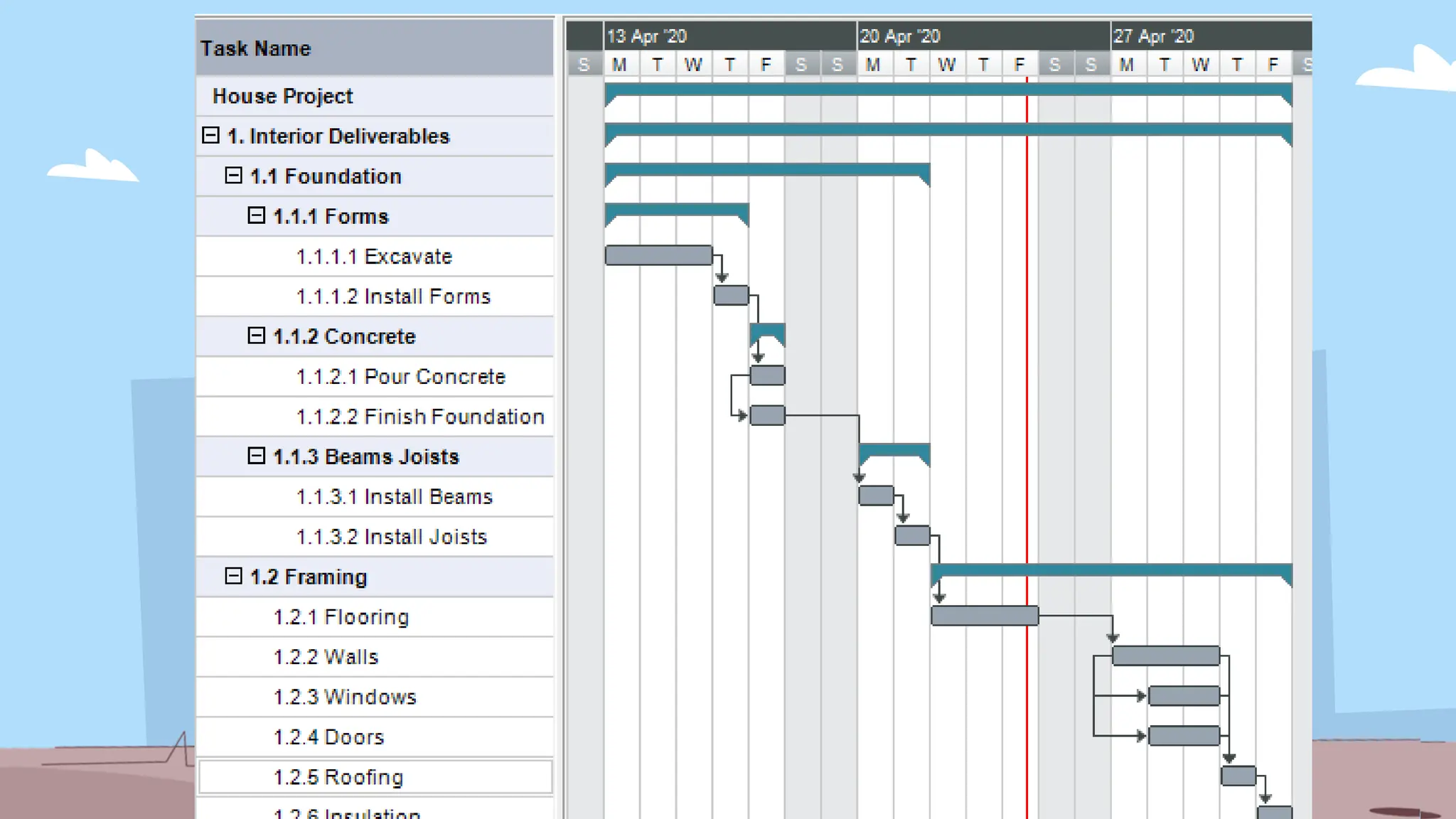
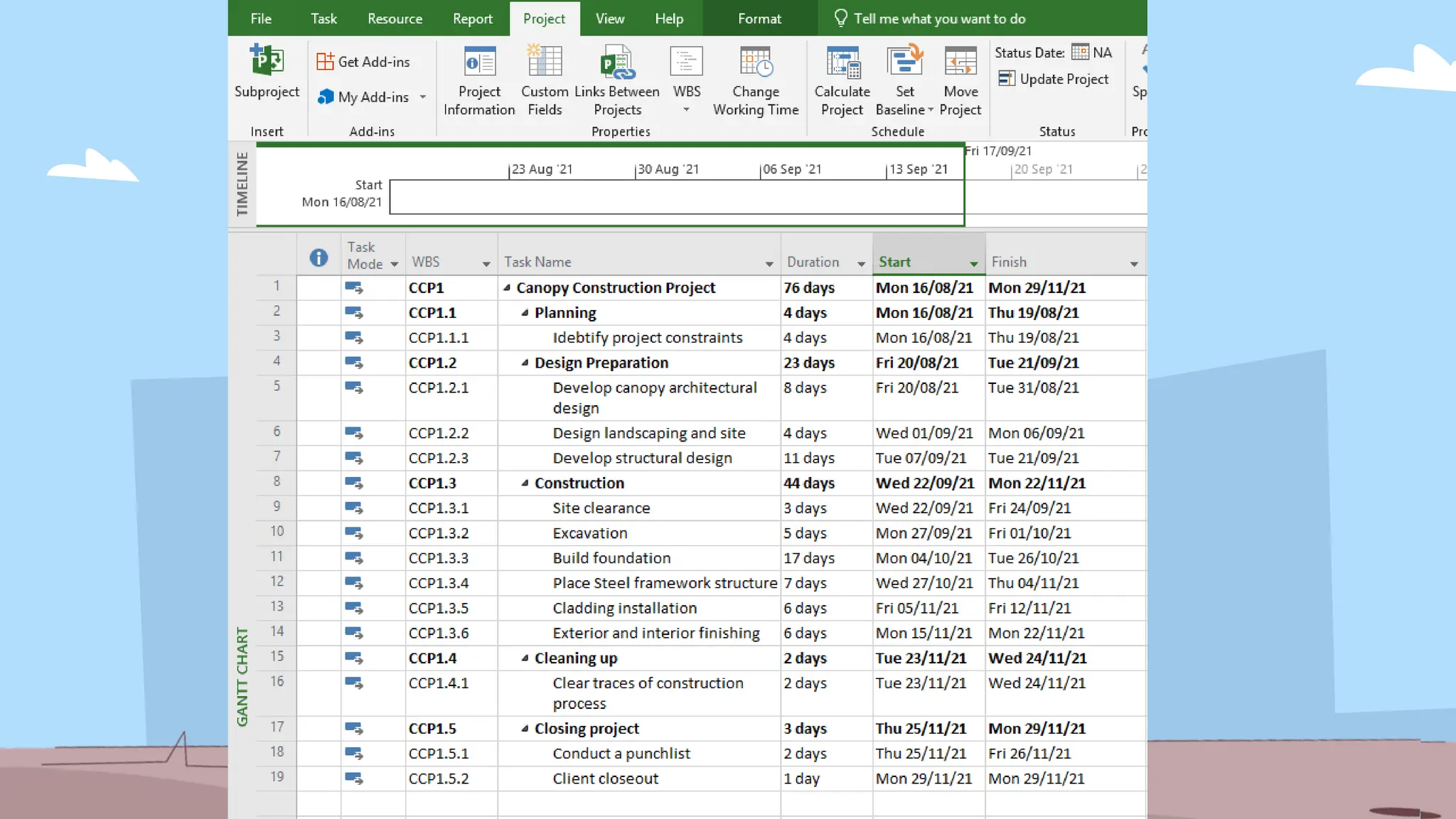
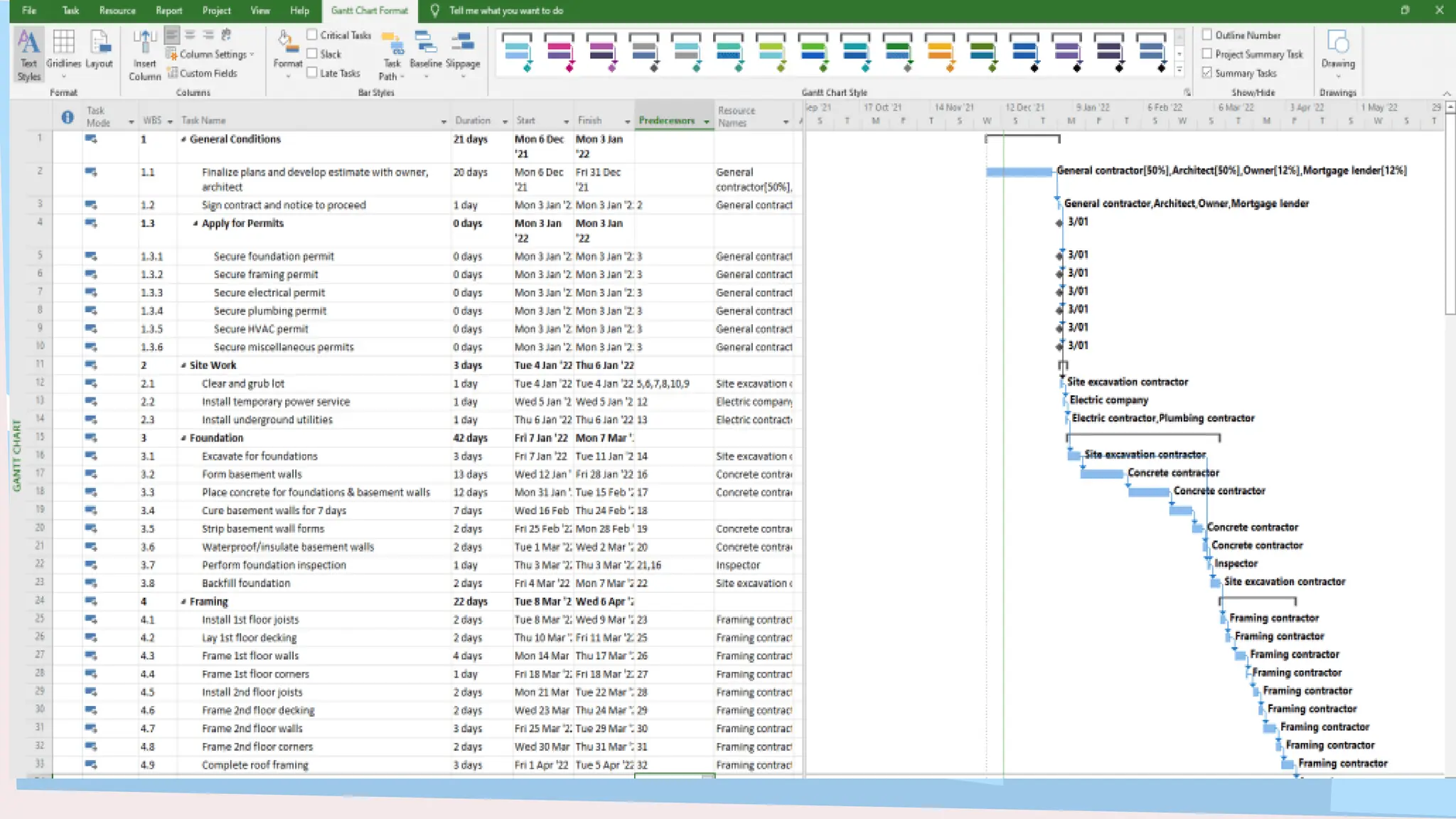
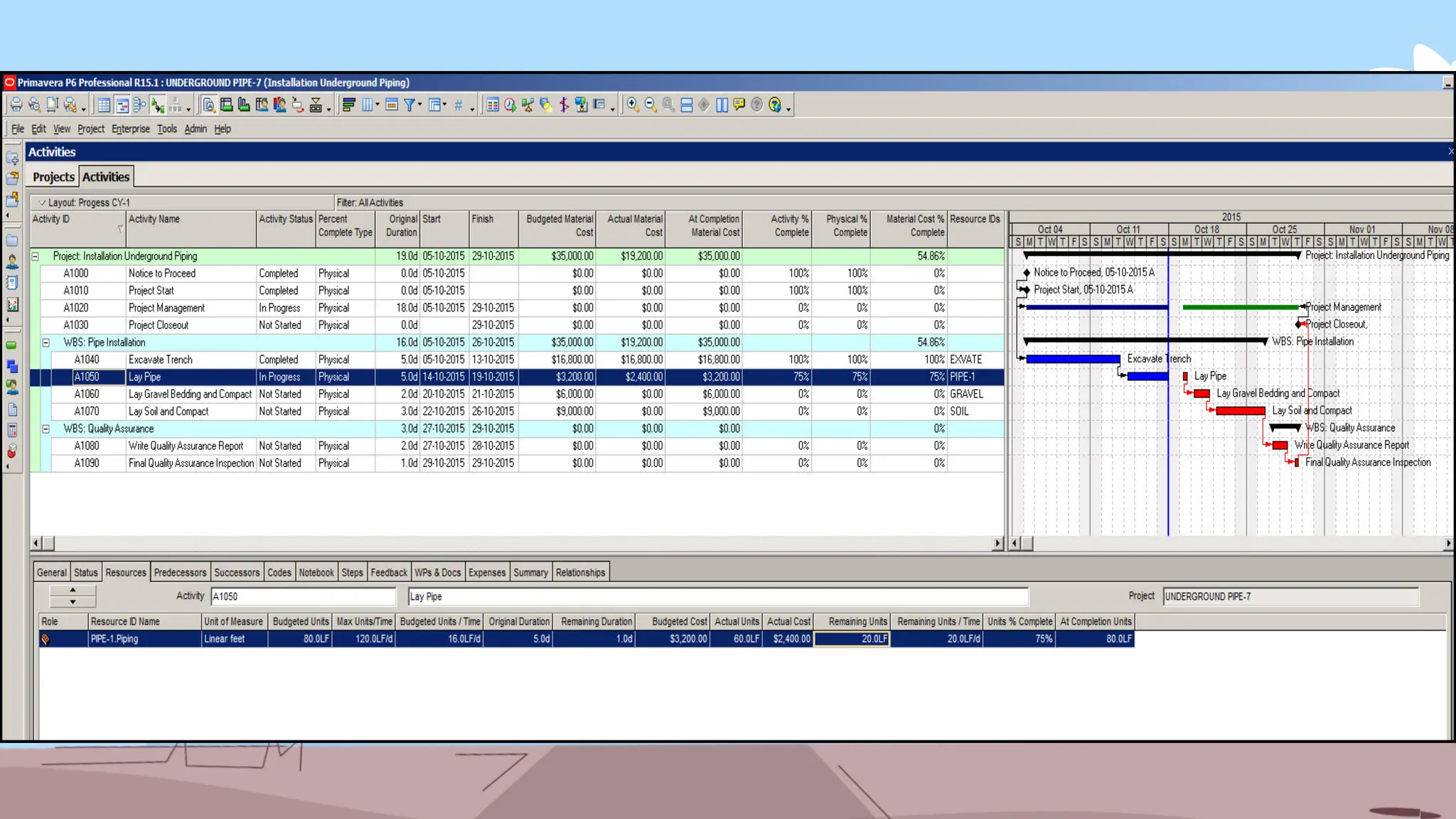
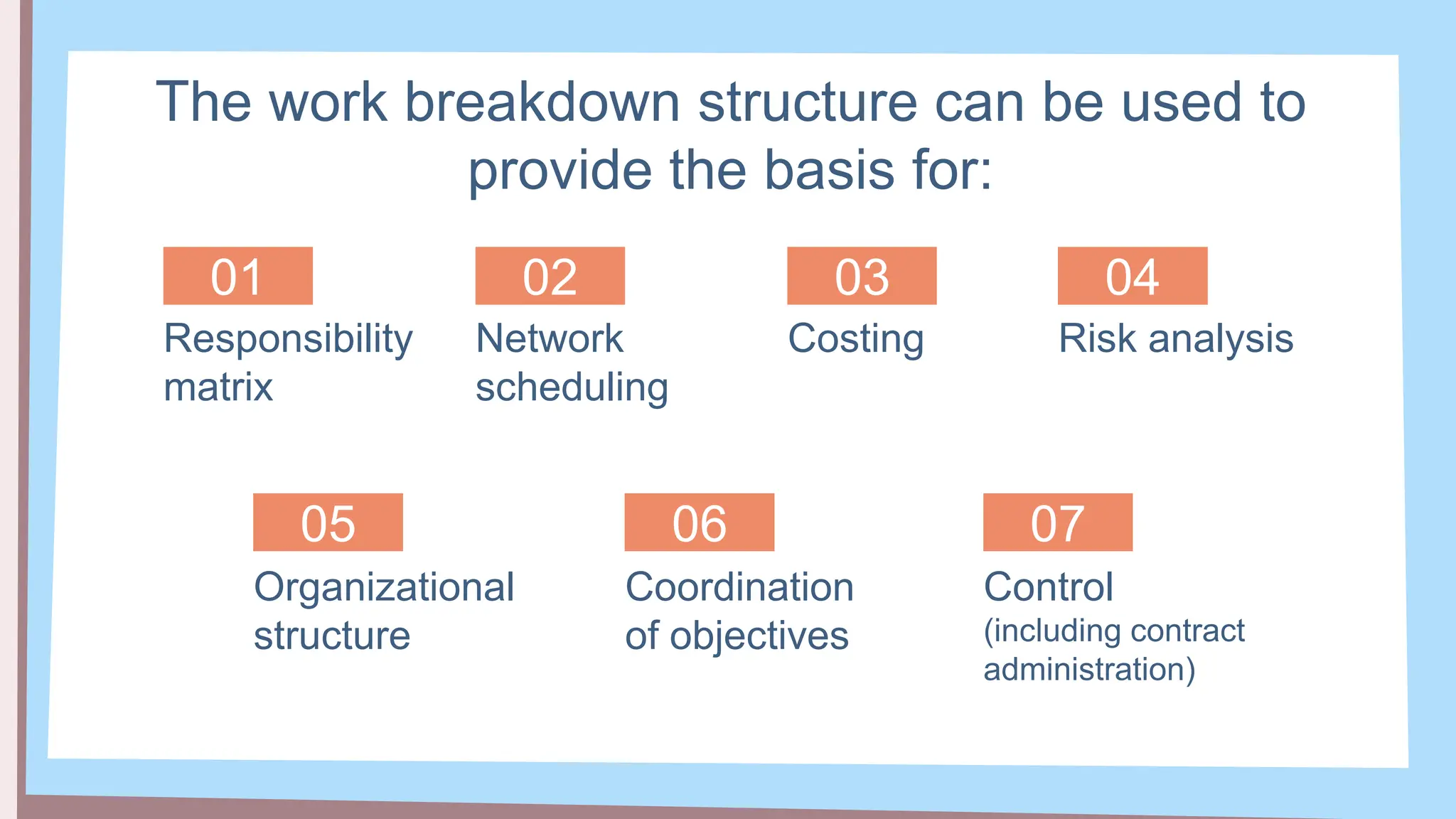
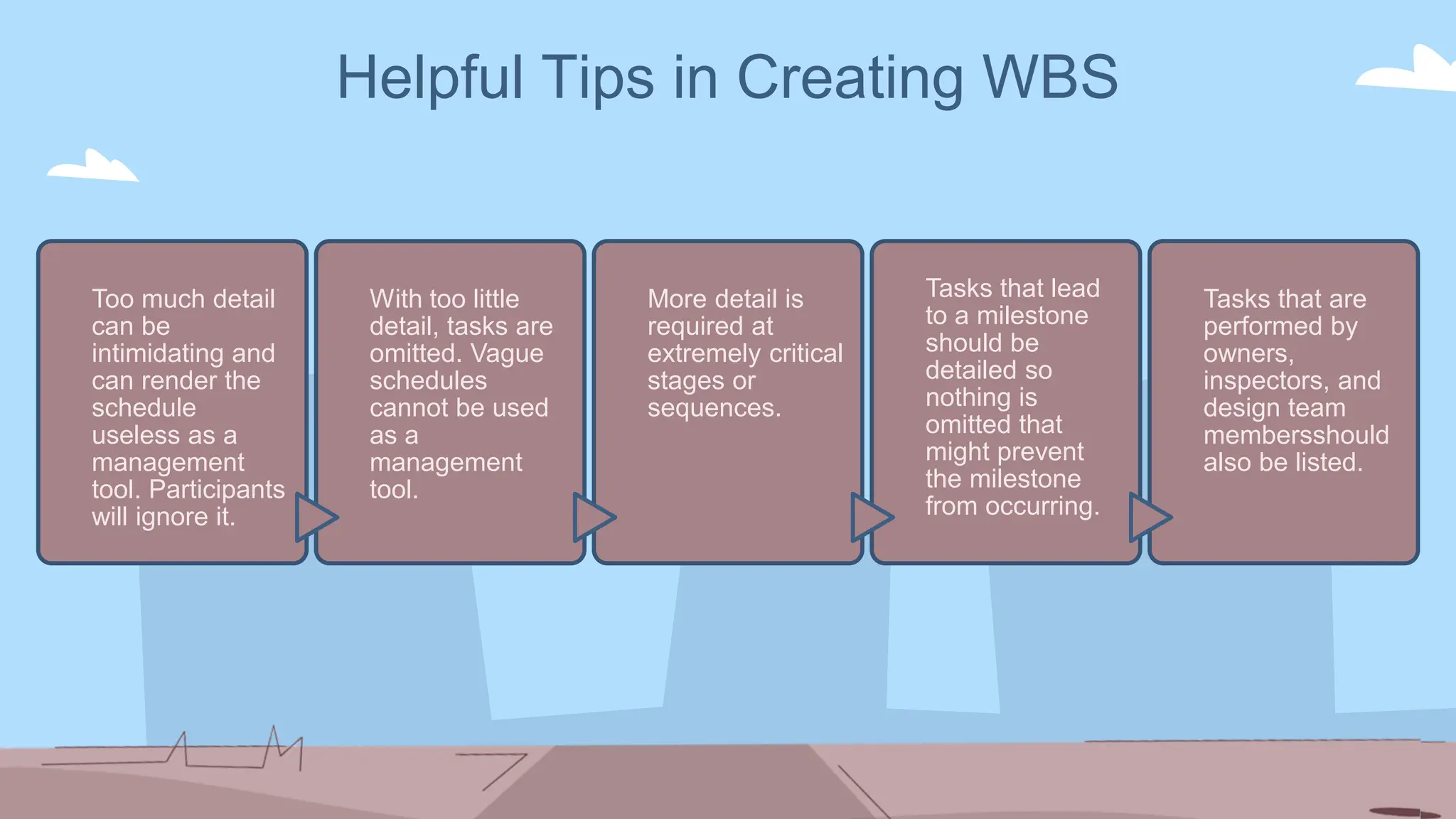
The document outlines the concept and implementation of a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) in construction cost engineering, detailing its definition, levels, and types, including deliverable-based and phase-based structures. It emphasizes the need for clear organization of project tasks into manageable components, assisting in project planning, budgeting, and performance tracking. Additionally, it provides guidelines on creating a WBS, including critical elements such as deliverables, acceptance criteria, and risk management.