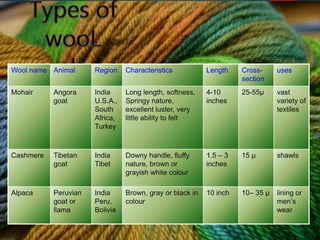
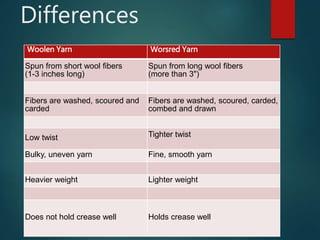
Wool comes from sheep and other animals like goats and rabbits. There are different types of wool like mohair, cashmere, and alpaca. Wool is produced through rearing sheep on farms, shearing them annually, processing the fleece through scouring, carding, combing and spinning into yarn. Wool yarn can be woolen or worsted depending on the processing method. Wool is then dyed and woven into fabrics that are used to make clothing, blankets, carpets and other products.