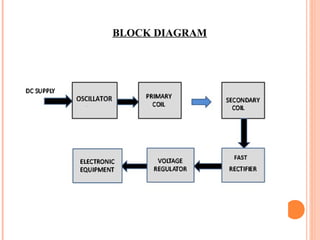
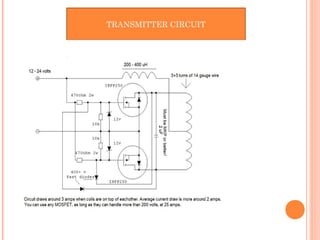
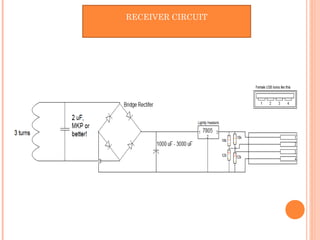
This document describes a wireless power transmission system using resonant inductive coupling. It works by transferring power wirelessly between two coils that are tuned to the same resonant frequency. When an alternating current is passed through the transmitting coil, it establishes a varying magnetic field that transfers energy to the receiving coil through inductive coupling. A capacitor is used to form a resonant circuit with the inductor to achieve greater transmission distances. Applications include wireless charging stations for devices like phones and potential use for charging electric vehicles. The system provides a more convenient alternative to wired charging but also has limitations such as power loss and short transmission range.