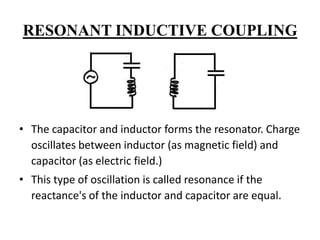
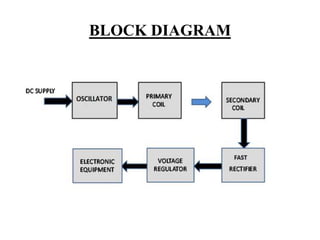
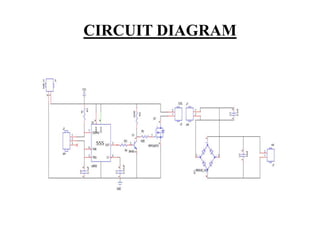
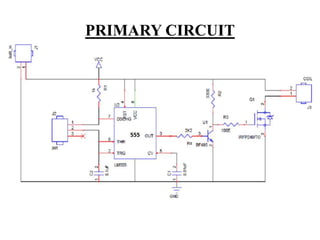
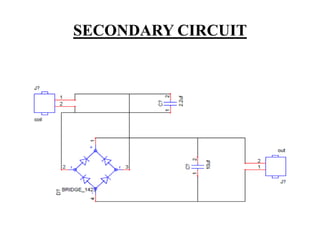
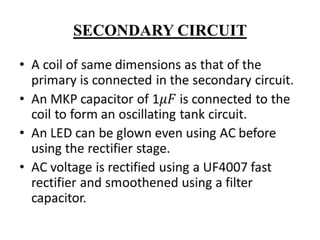
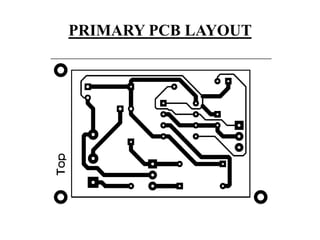
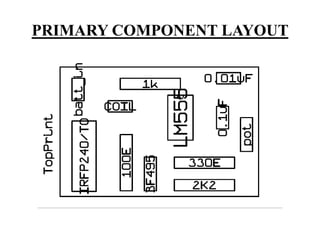
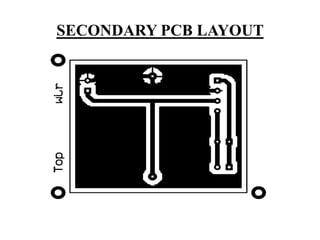
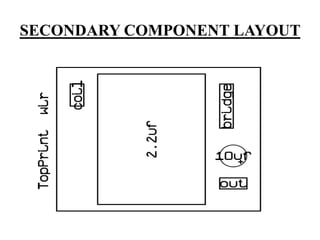
This document describes a project on wireless power transmission using resonant inductive coupling. It introduces various wireless power transmission techniques and focuses on resonant inductive coupling, which involves transferring energy between two coils that are tuned to resonate at the same frequency. The document includes circuit diagrams and layouts of the primary and secondary coils used to demonstrate resonant inductive coupling through an oscillator, resonant charging, and regulated output. It discusses applications for charging devices wirelessly and advantages like safety, efficiency and lack of interference.