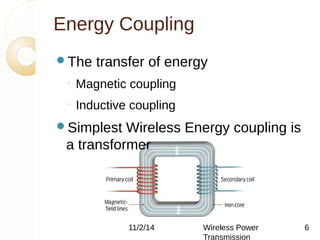
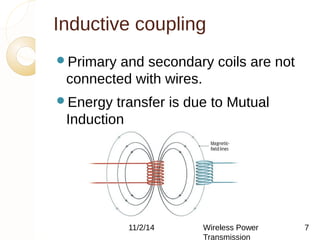
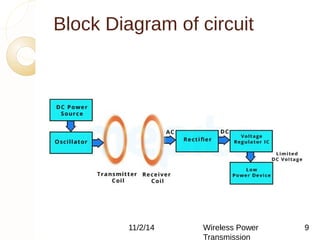
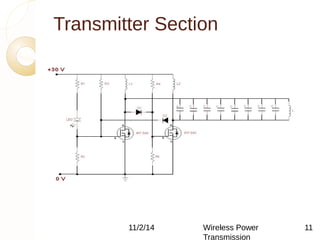
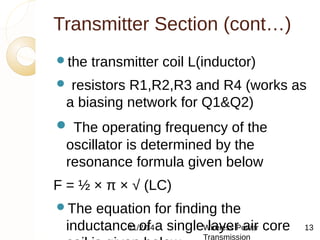
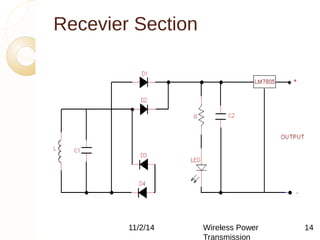
This document discusses wireless power transmission using inductive coupling. It provides an overview of wireless power transmission, including its history dating back to Nikola Tesla's experiments in the late 1890s. The document then describes inductive coupling as the simplest form of wireless energy transfer, like a transformer without wires. It includes a block diagram and explanation of a wireless charging circuit that uses inductive coupling between a transmitter coil powered by an oscillator and a receiver coil that converts the power for use. The document discusses advantages like eliminating wires but also challenges like difficulty in tuning and constraints on transmission distance.
Human: Thank you for the summary. You captured the key points effectively in 3 concise sentences as requested.