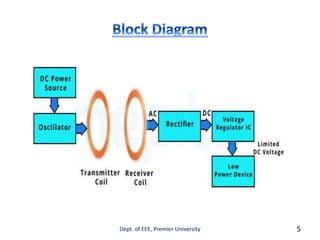
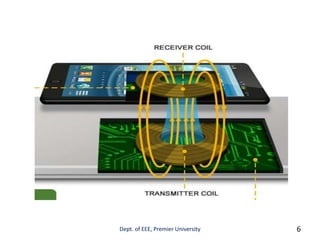
This document presents information on wireless charging technology. It discusses how wireless charging uses electromagnetic fields to transfer energy between two objects, such as a charging station and electrical device, through inductive coupling. The document provides a brief history of wireless power transmission, including Nikola Tesla proposing the concept in 1890 and MIT researchers powering a light bulb in 2007. It describes how wireless systems use inductive coupling between planar coils to transfer power from a transmitter to receiver. The document notes that wireless power systems are evolving to allow for more convenient charging of smartphones and other mobile devices without needing separate chargers.