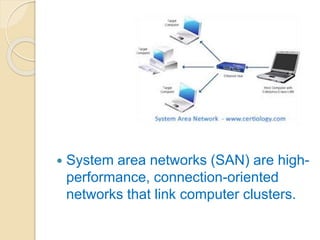
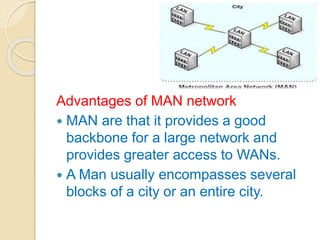
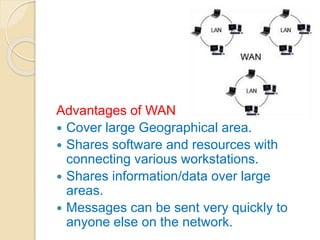
This document provides an overview of computer networks and networking. It defines what a computer network is and discusses the need for networking in terms of file sharing, hardware sharing, application sharing, and user communication. It then covers different types of networks including personal area networks, storage area networks, system area networks, local area networks, metropolitan area networks, and wide area networks. Finally, it discusses wireless networking technologies and applications of computer networks.