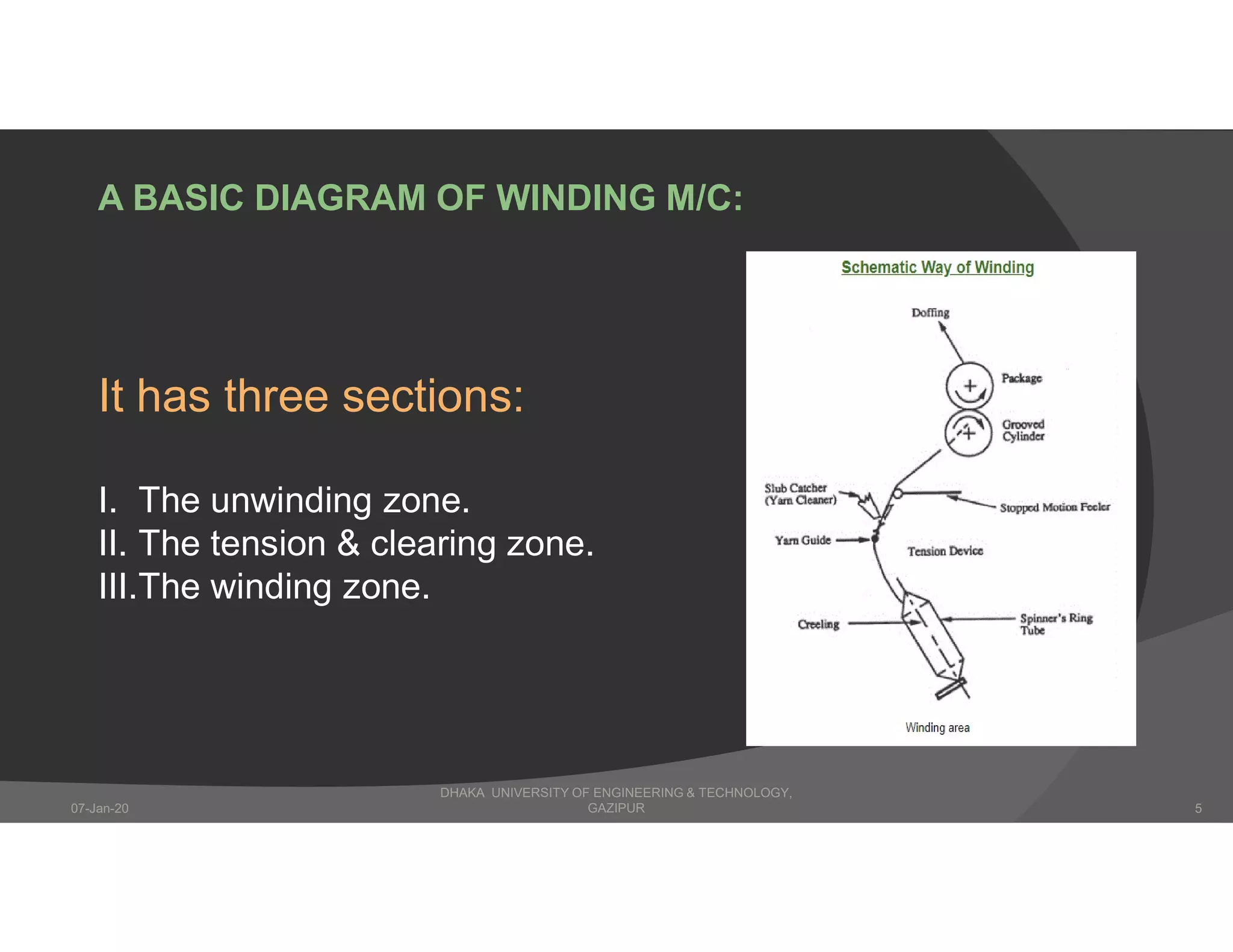
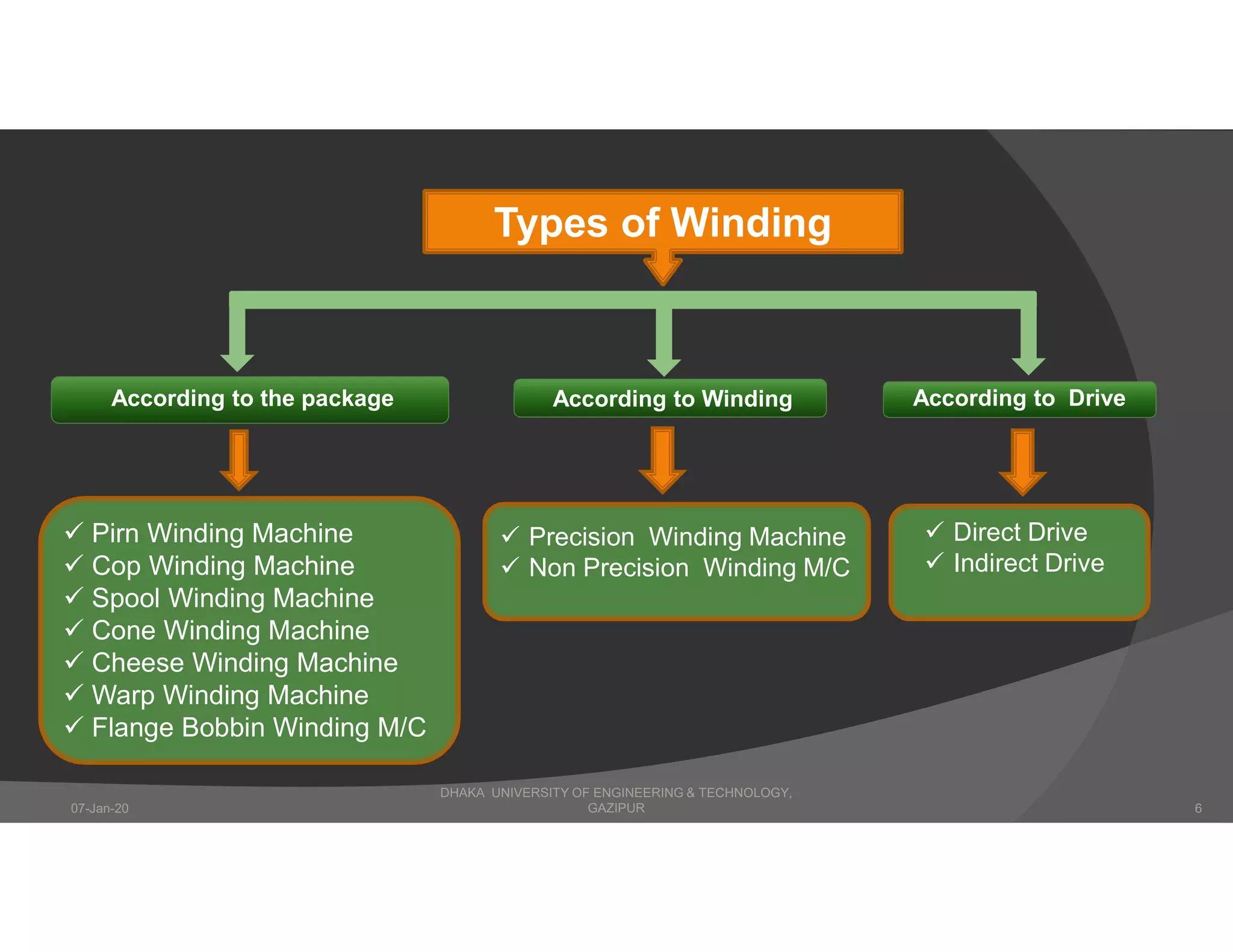
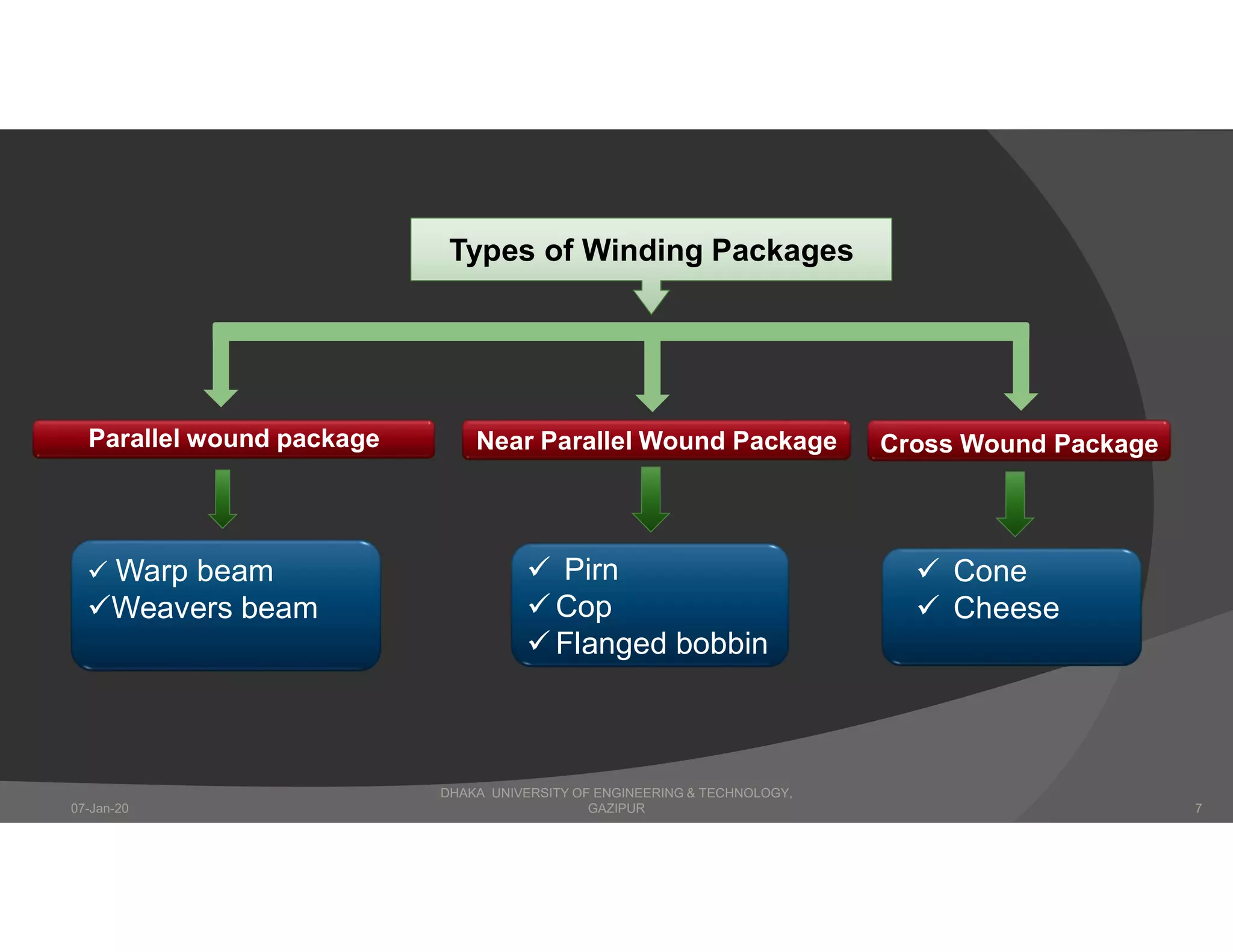
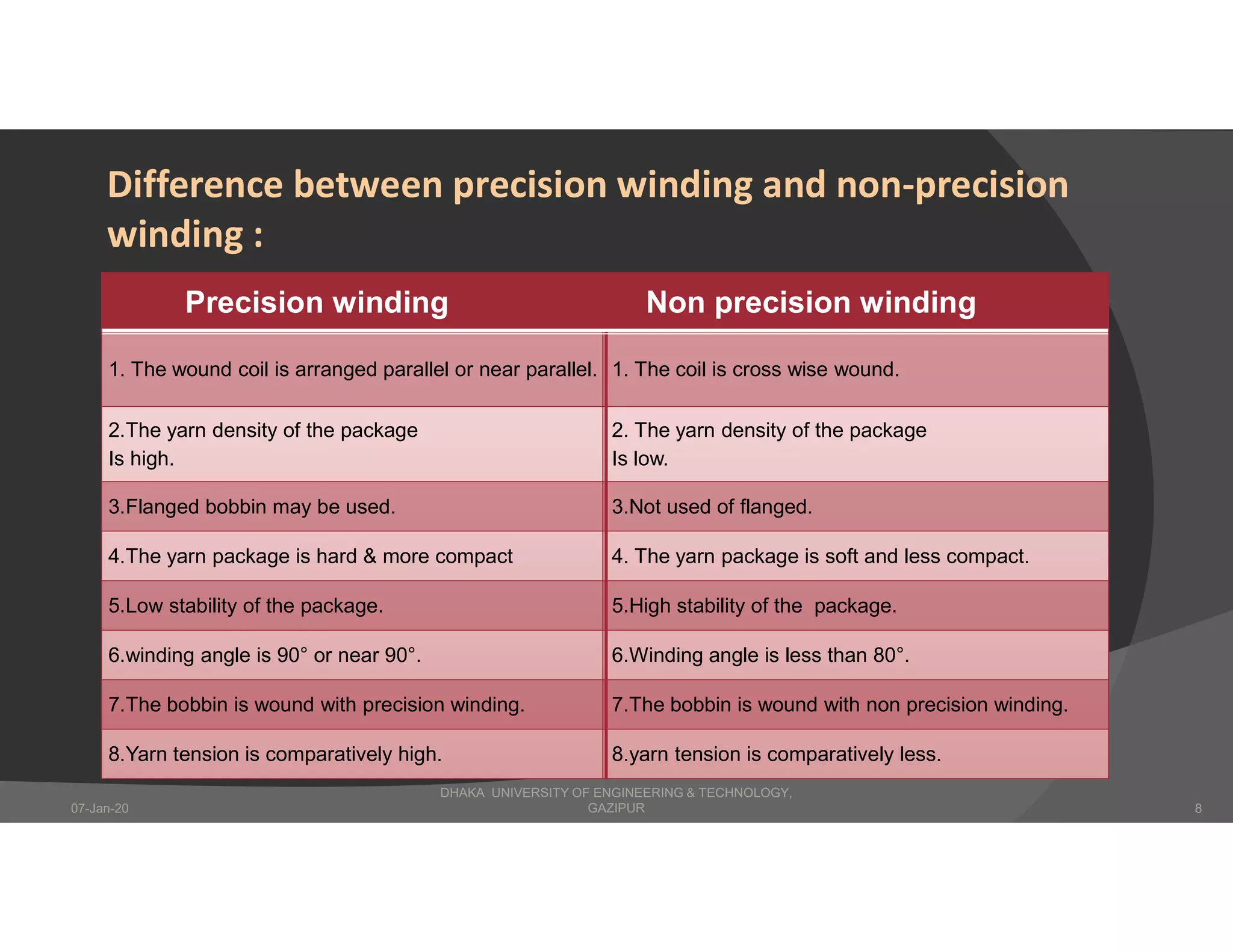
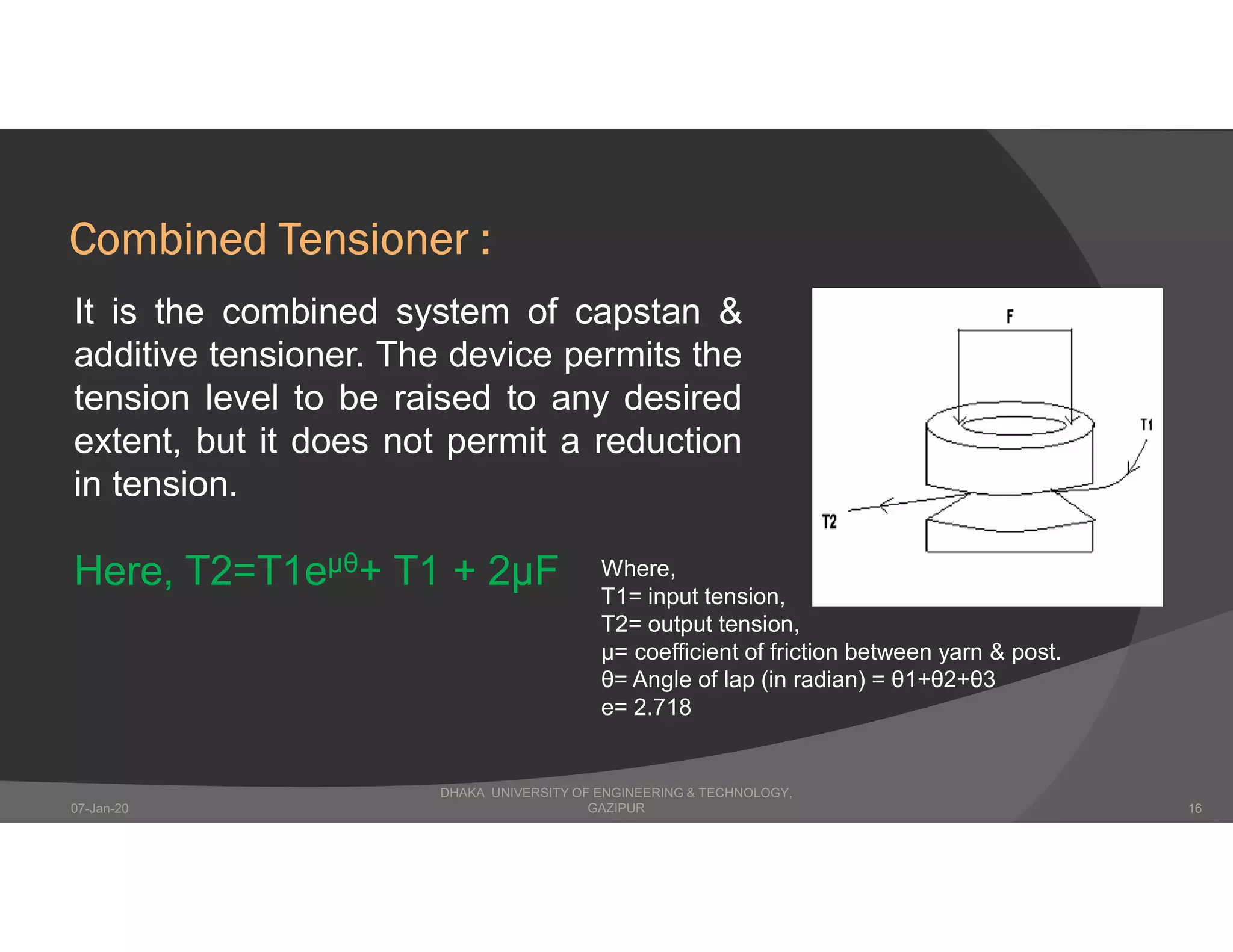
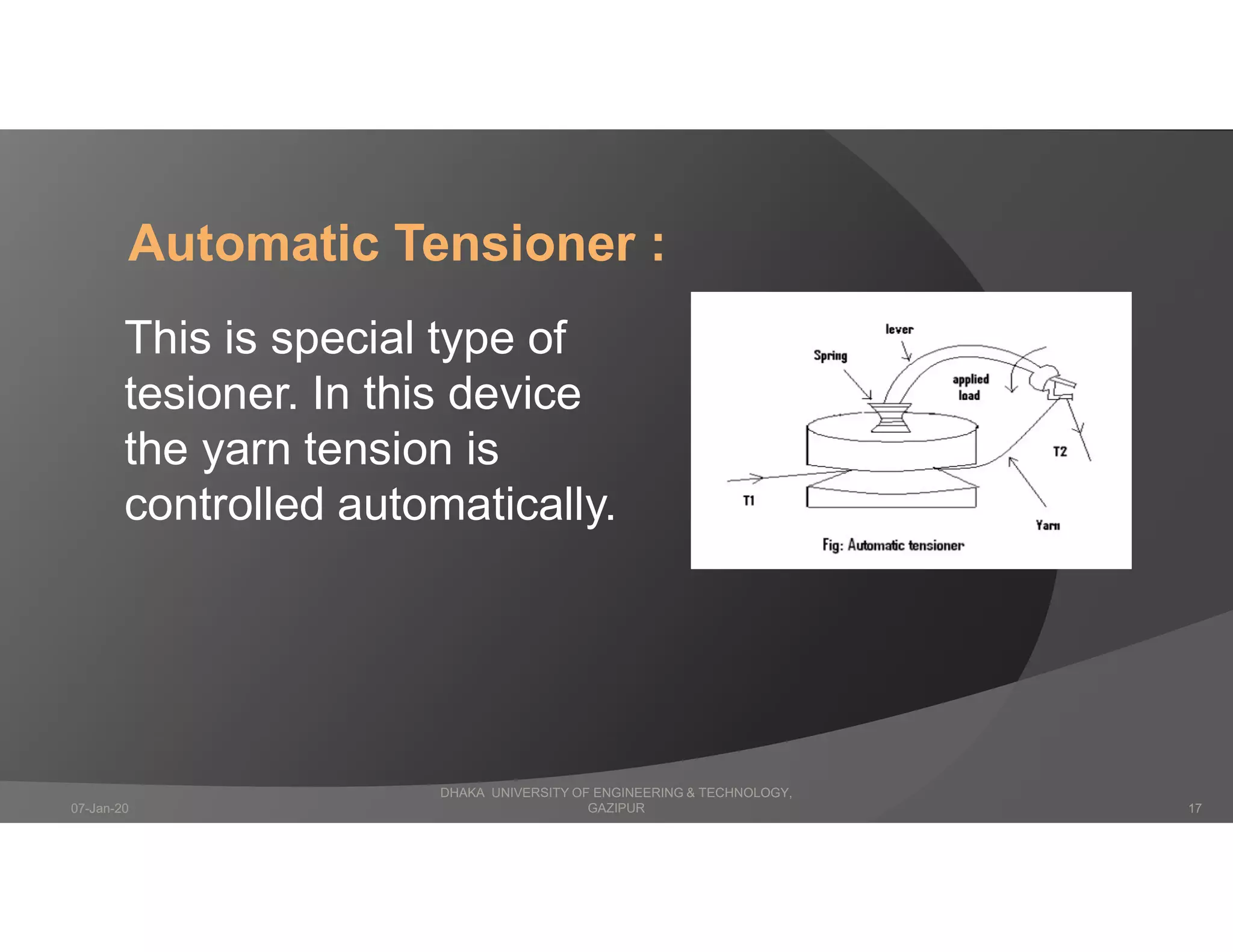
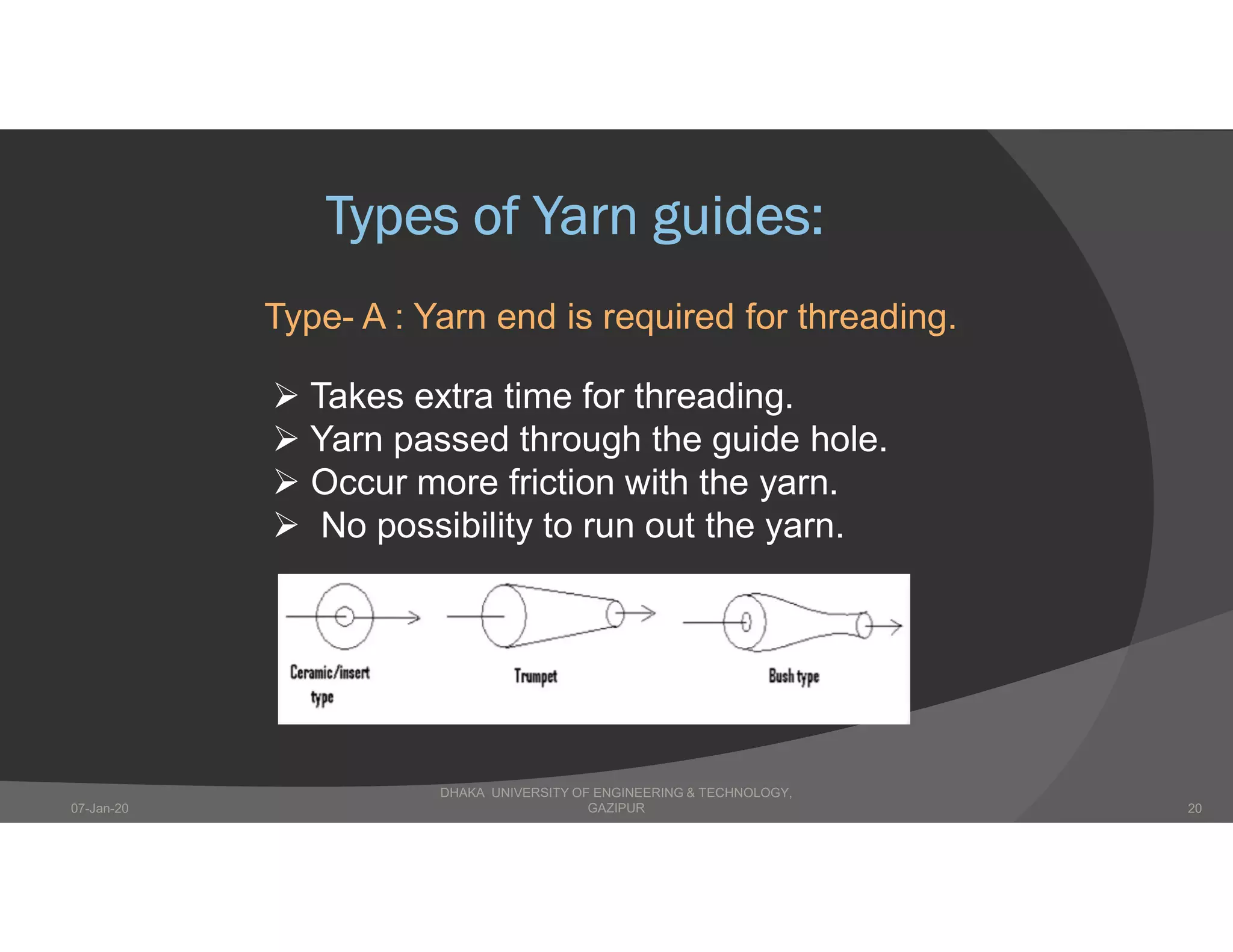
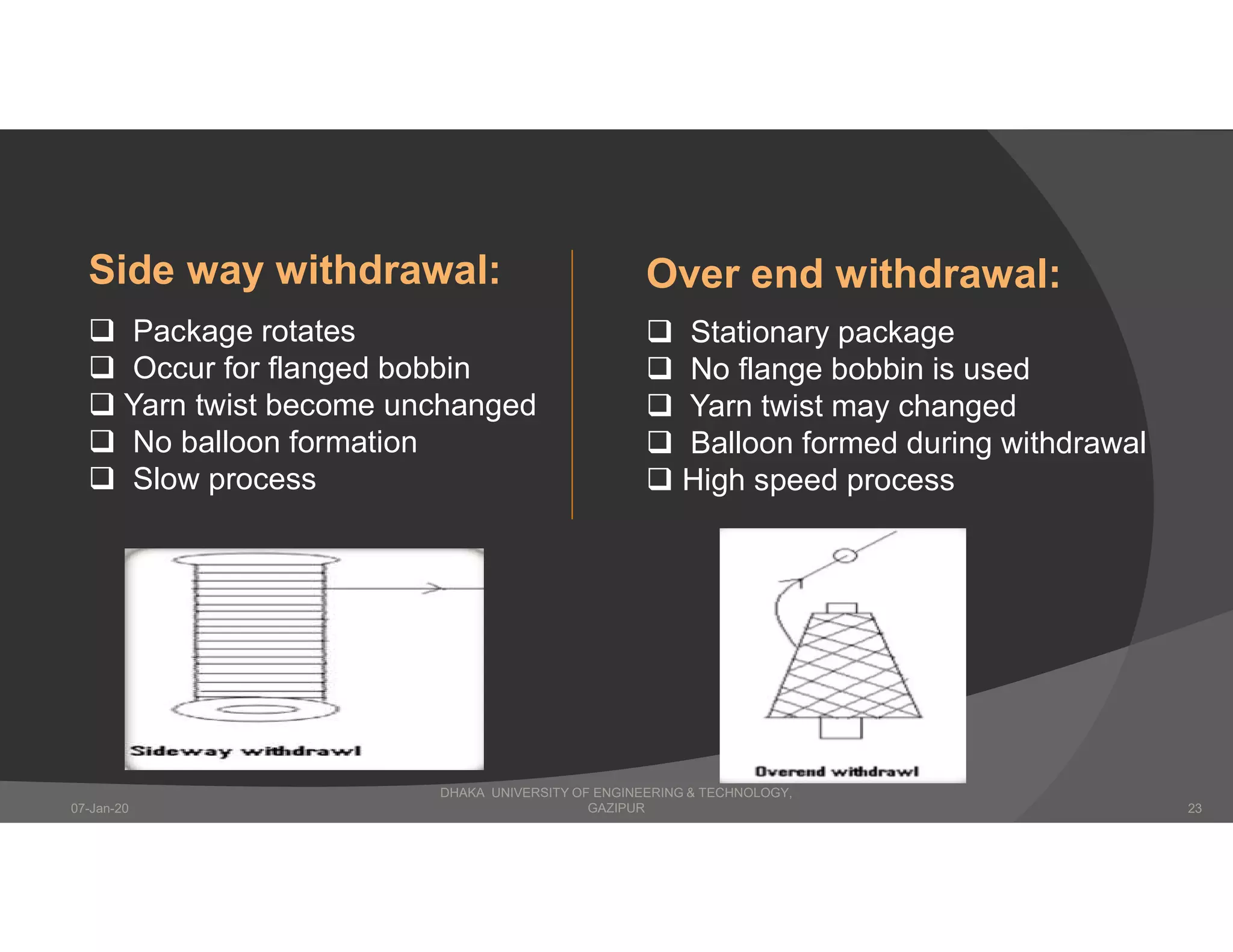
The presentation describes winding in fabric manufacturing, detailing its process, objectives, and types of machines involved. It outlines different winding techniques such as precision and non-precision winding, their respective advantages and disadvantages, and various yarn tension devices. Additionally, it covers yarn withdrawal methods, winding efficiency, and common winding faults.