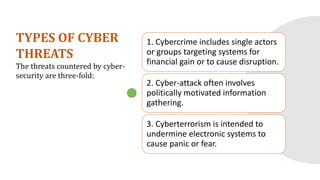
Cyber security involves protecting computers, networks, and data from malicious attacks. The document discusses how the global cyber threat is rising, with over 7 billion records exposed in data breaches in the first nine months of 2019. It also outlines frameworks and guidance from organizations like NIST and ACSC to help combat cyber threats. The types of cyber threats include cybercrime, cyber attacks, and cyberterrorism. Common methods that malicious actors use to gain control of systems include malware, SQL injection, phishing, and man-in-the-middle attacks. The document provides examples of recent cyber threats like romance scams and concludes with cyber safety tips.