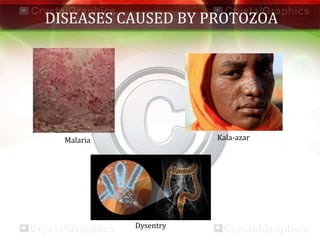
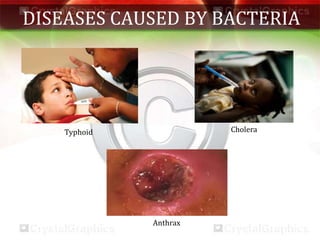
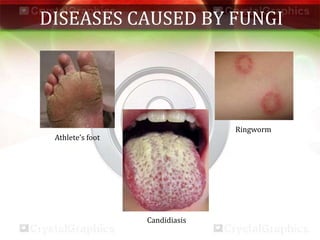
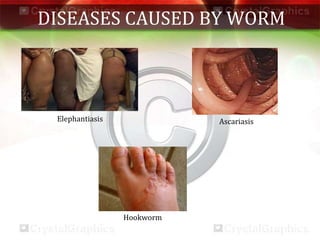
This document discusses various aspects of health and disease. It defines health as a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being. Maintaining good health requires a balanced diet, exercise, proper shelter, sleep and hygiene. Disease can be caused by intrinsic or extrinsic factors and can be acute, chronic, congenital or acquired. Infectious diseases spread via air, water, food, vectors or contact and common examples are provided. Prevention focuses on avoiding exposure and immunization, while treatment aims to reduce symptoms and kill microbes. Vaccination helps strengthen immunity against specific diseases. The main pathogens that cause infectious disease are viruses, bacteria, fungi, protozoa and worms.