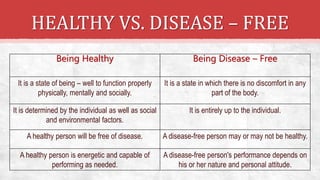
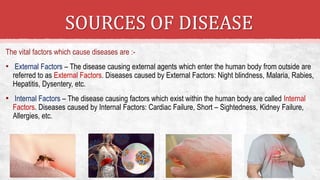
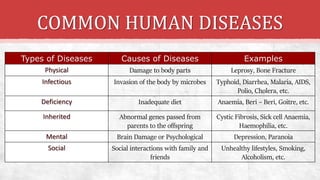
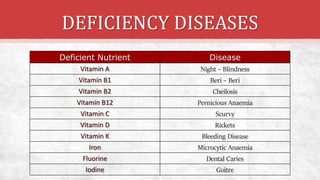
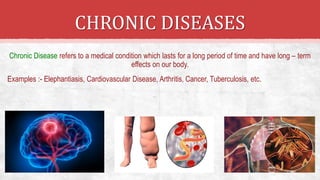
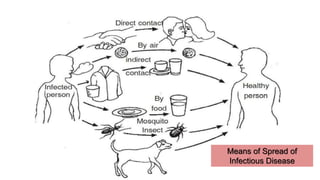
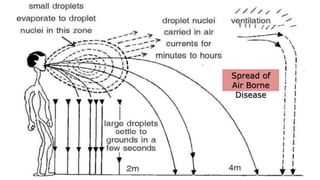
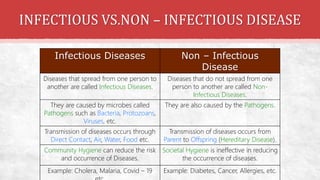
The document discusses the concept of health, distinguishing between being 'healthy' and 'disease-free', and outlines the various causes of diseases, including environmental factors, infectious agents, and genetic disabilities. It categorizes diseases into acute, chronic, infectious, and non-infectious types, and explains how diseases spread through various means such as air, water, and vectors. Additionally, it touches on disease treatment methods and the importance of vaccination to develop long-term immunity against pathogens.