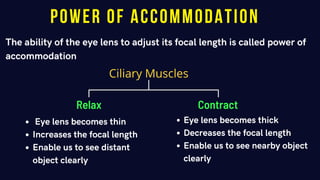
The document summarizes key aspects of the human eye and vision. It describes the structure of the eye, including the cornea, iris, pupil, lens, retina, and other parts. It explains how the iris controls the size of the pupil to regulate the amount of light entering the eye. It also discusses refractive errors like myopia and hyperopia, and how lenses are used to correct vision. Prisms and dispersion of light are described. Atmospheric effects like refraction, twinkling of stars, and why the sky appears blue are summarized.