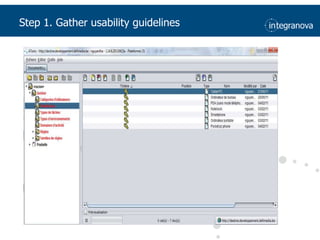
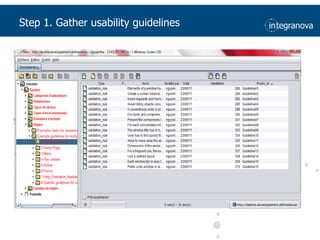
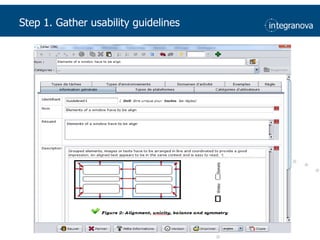
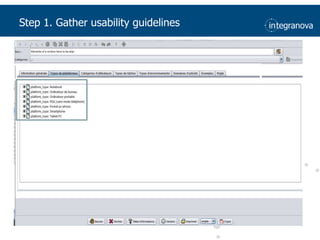
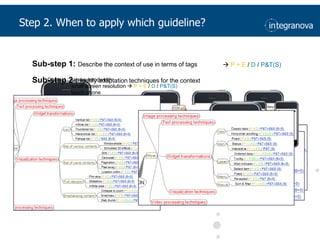
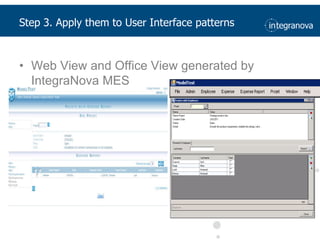
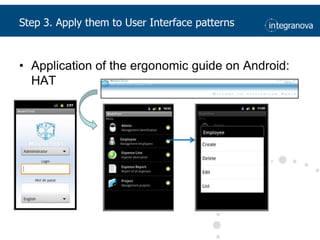
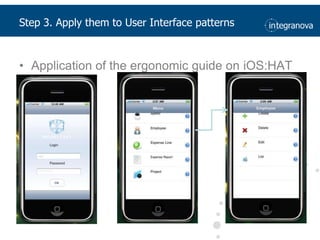
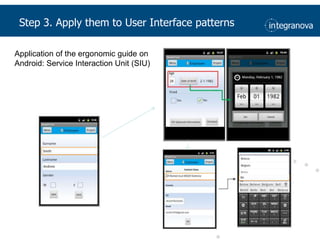
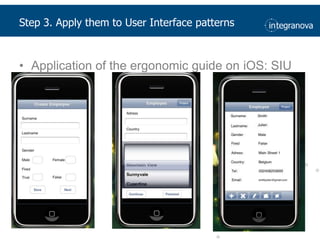
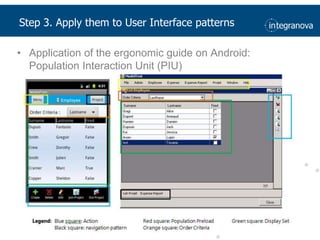
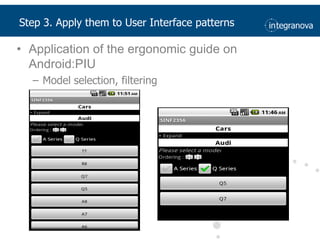
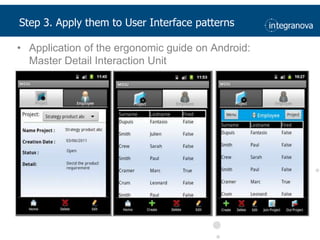
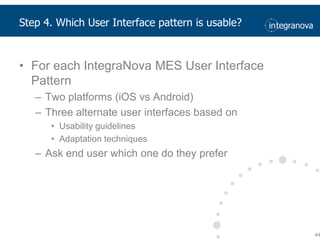
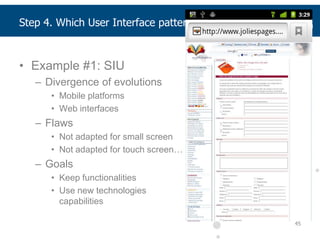
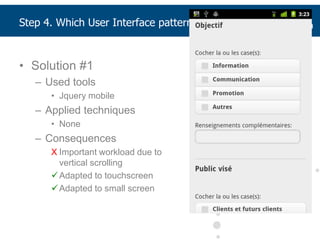
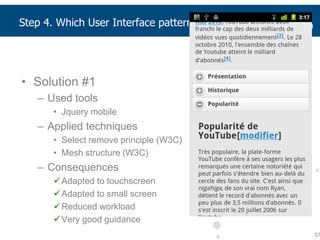
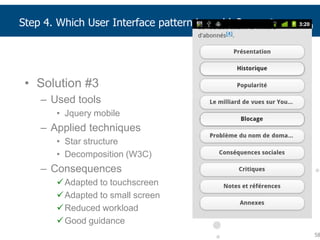
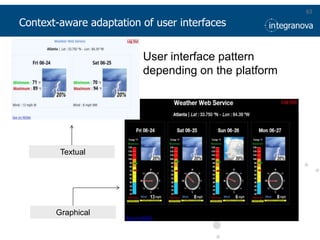
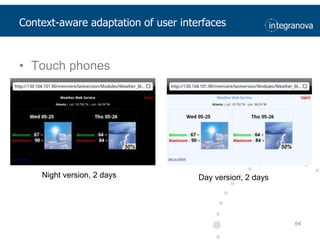
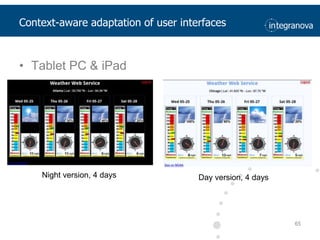
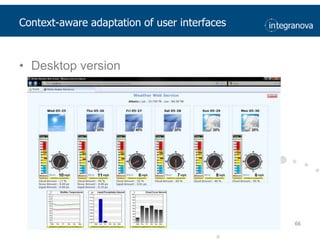
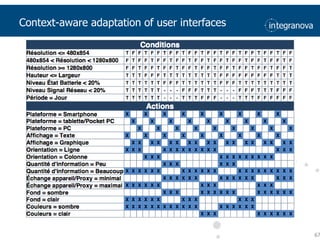
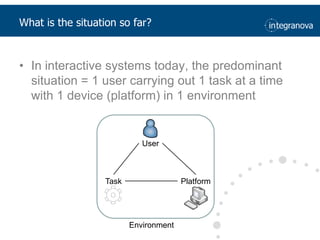
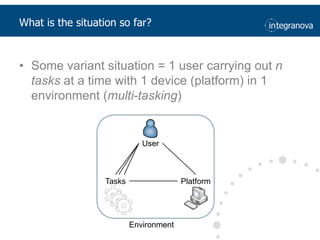
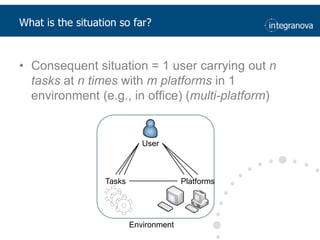
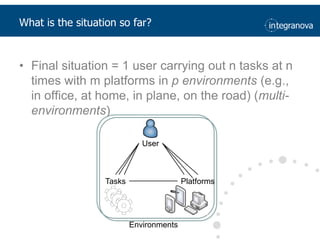
This document summarizes a presentation about adapting user interface patterns for mobile platforms. It discusses how interface patterns were traditionally designed for single devices and tasks, but now must support multiple tasks, devices, and environments as users are increasingly mobile. The presentation describes gathering usability guidelines for multiple platforms and applying them to modify existing interface patterns from an industrial system to support touch interfaces like Android and iOS. User testing was conducted to evaluate alternative pattern implementations and determine the most preferred version. The goal is to develop context-aware interface patterns that can dynamically change based on factors like device and environment.


![Why multiple monitors?DevicesideMonitor surface increases, whilepricedecreases[Harris,2002]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vanderdonckt-sab2011-110930020237-phpapp01/85/When-User-Interface-Patterns-Become-Mobile-7-320.jpg)
![Why multiple monitors?User sideUsersprefer more display surfaceUser’sproductivityincreasesfrom 10% to 30% (althoughsomeusabilityproblems are raised) [Harris,2002]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vanderdonckt-sab2011-110930020237-phpapp01/85/When-User-Interface-Patterns-Become-Mobile-8-320.jpg)
![Why multiple monitors?User sideUsersprefer more display surfaceUser’sproductivityincreasesfrom 10% to 30%Effects of Display Size on Task Times160140120100SmallAverage Task Time (Seconds)80Large6040200[Czerwinsky,2005]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vanderdonckt-sab2011-110930020237-phpapp01/85/When-User-Interface-Patterns-Become-Mobile-9-320.jpg)
![Why multiple monitors?User sideUsersprefer more display surfaceUser’sproductivityincreasesfrom 10% to 30%The tasks were easy to perform543Average Rating (1=Disagree, 5=Agree)210SmallLarge[Czerwinsky,2005]Display Size](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vanderdonckt-sab2011-110930020237-phpapp01/85/When-User-Interface-Patterns-Become-Mobile-10-320.jpg)
![Why multiple monitors?User sideUsersprefer more display surfaceUser’sproductivityincreasesfrom 10% to 30%[Czerwinsky,2005]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vanderdonckt-sab2011-110930020237-phpapp01/85/When-User-Interface-Patterns-Become-Mobile-11-320.jpg)
![(Amount of interactive systems)(Amount of end users)10 to 50 systemsfor 1 user10000500002 or 3 systemsfor 1 user1 system for 1 user100050001005001 system for 100 users1050[Weiser, 1998]197019801990200020102020[ForresterResearch, 2002]Why multiple platforms?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vanderdonckt-sab2011-110930020237-phpapp01/85/When-User-Interface-Patterns-Become-Mobile-12-320.jpg)

![[Pierce et al.,2004]Whichplatformsshouldbesupported?SomereasonsSales increaseCapabilitiesincrease](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vanderdonckt-sab2011-110930020237-phpapp01/85/When-User-Interface-Patterns-Become-Mobile-14-320.jpg)
![Whichplatformsshouldbesupported?Break-even point before 2014[MEE 2010]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vanderdonckt-sab2011-110930020237-phpapp01/85/When-User-Interface-Patterns-Become-Mobile-15-320.jpg)