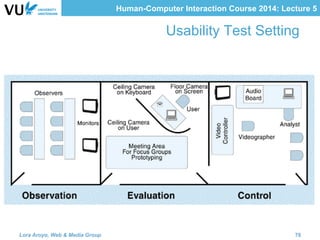
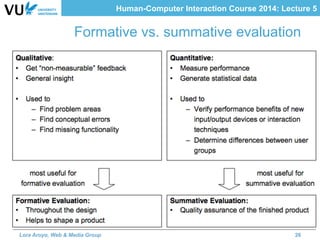
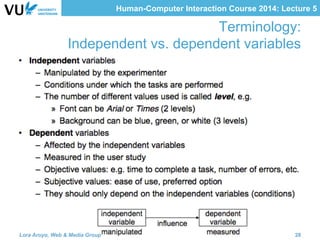
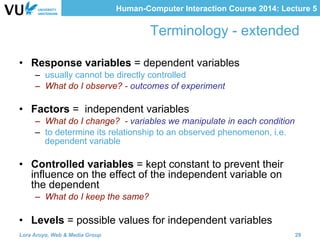
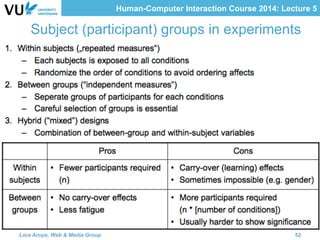
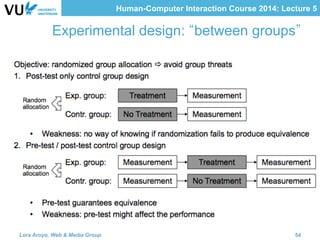
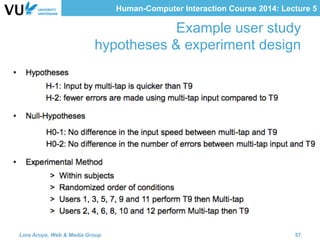
The document outlines methods for evaluating user interfaces in human-computer interaction through expert analyses and user studies. It presents various user study examples, including an iPhone texting study and a mobile learning game in medieval Amsterdam, highlighting the importance of usability testing and the evaluation of user experience. Key concepts discussed include experimental design, reliability, validity, generalizability, and the formulation of hypotheses for effective user study outcomes.























































![Human-Computer Interaction Course 2014: Lecture 5
Measuring User Preferences
• How much users like or dislike the system
– can ask them to rate on a scale of [1..5], [1..7] [1..10]
– or have them choose among statements
• best UI I ve ever… , better than average …
– hard to be sure what data will mean
• novelty of UI, feelings, not realistic setting …
• If many give you low ratings à trouble
• Can get some useful data by asking
– what they liked / disliked
– where they had trouble, best part, worst part
• redundant questions are OK
Lora Aroyo, Web & Media Group 70](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15-5-150630082020-lva1-app6892/85/Lecture-5-Human-Computer-Interaction-Course-2015-VU-University-Amsterdam-70-320.jpg)