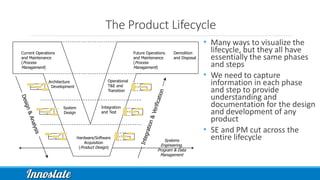
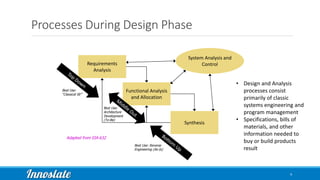
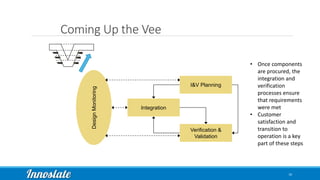
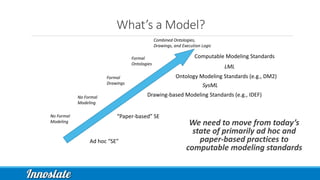
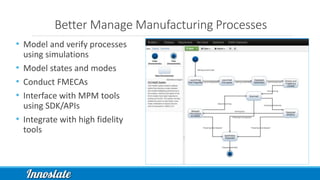
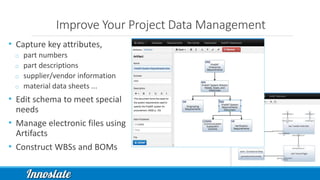
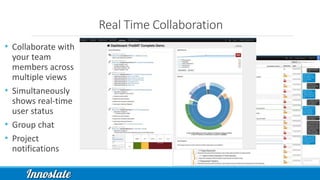
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) combines five disciplines—systems engineering, program management, product design, process management for manufacturing, and product data management—to effectively manage products throughout their lifecycle. Model-Based Systems Engineering (MBSE) offers a formalized approach utilizing modern software tools for improved data capture, analysis, and visualization across all phases of product development. Innoslate® provides a comprehensive platform to support these PLM practices, ensuring effective collaboration and management of product information.