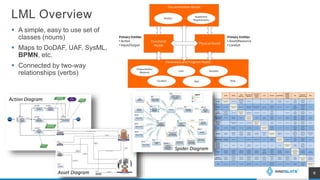
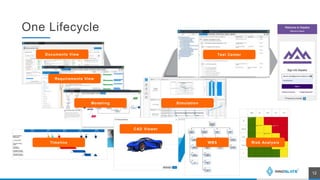
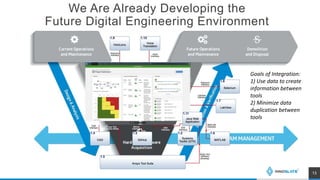
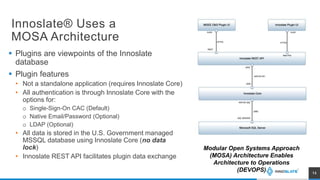
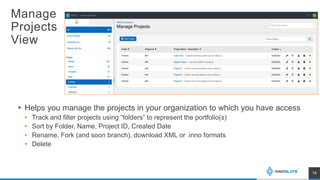
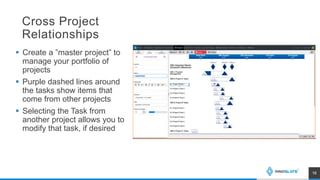
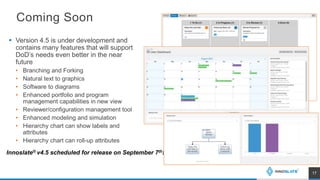
The presentation discusses an MBSE approach to portfolio management and introduces the Lifecycle Modeling Language (LML) as a tool for systems engineers to achieve strategic objectives in project management. Spec Innovations, the company behind the cloud-native software Innoslate, aims to enhance digital modernization within the defense acquisition system through improved data management and portfolio management capabilities. The upcoming release of Innoslate version 4.5 promises new features supporting the Department of Defense's needs, including enhanced visual management tools and analytical capabilities.