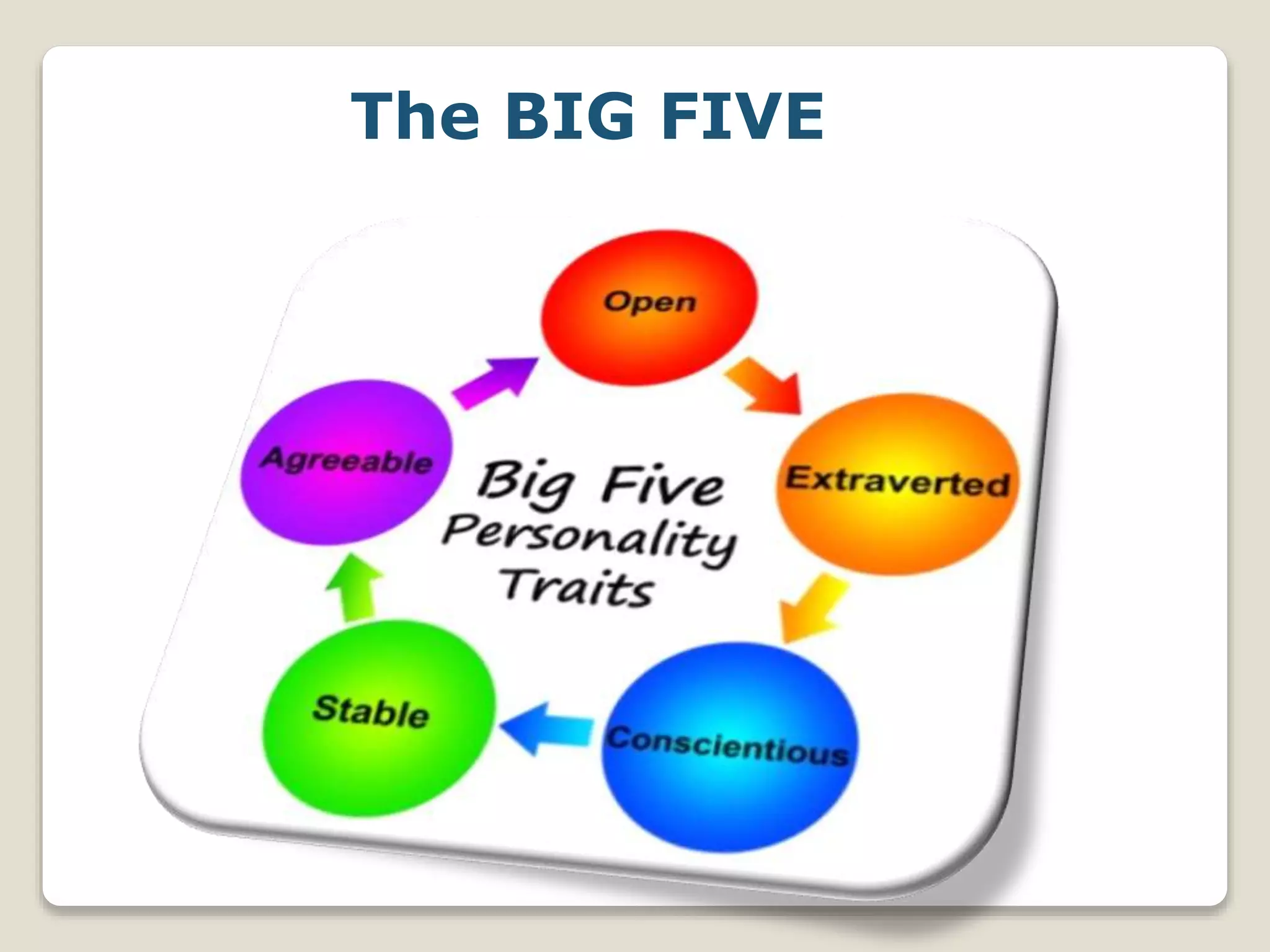
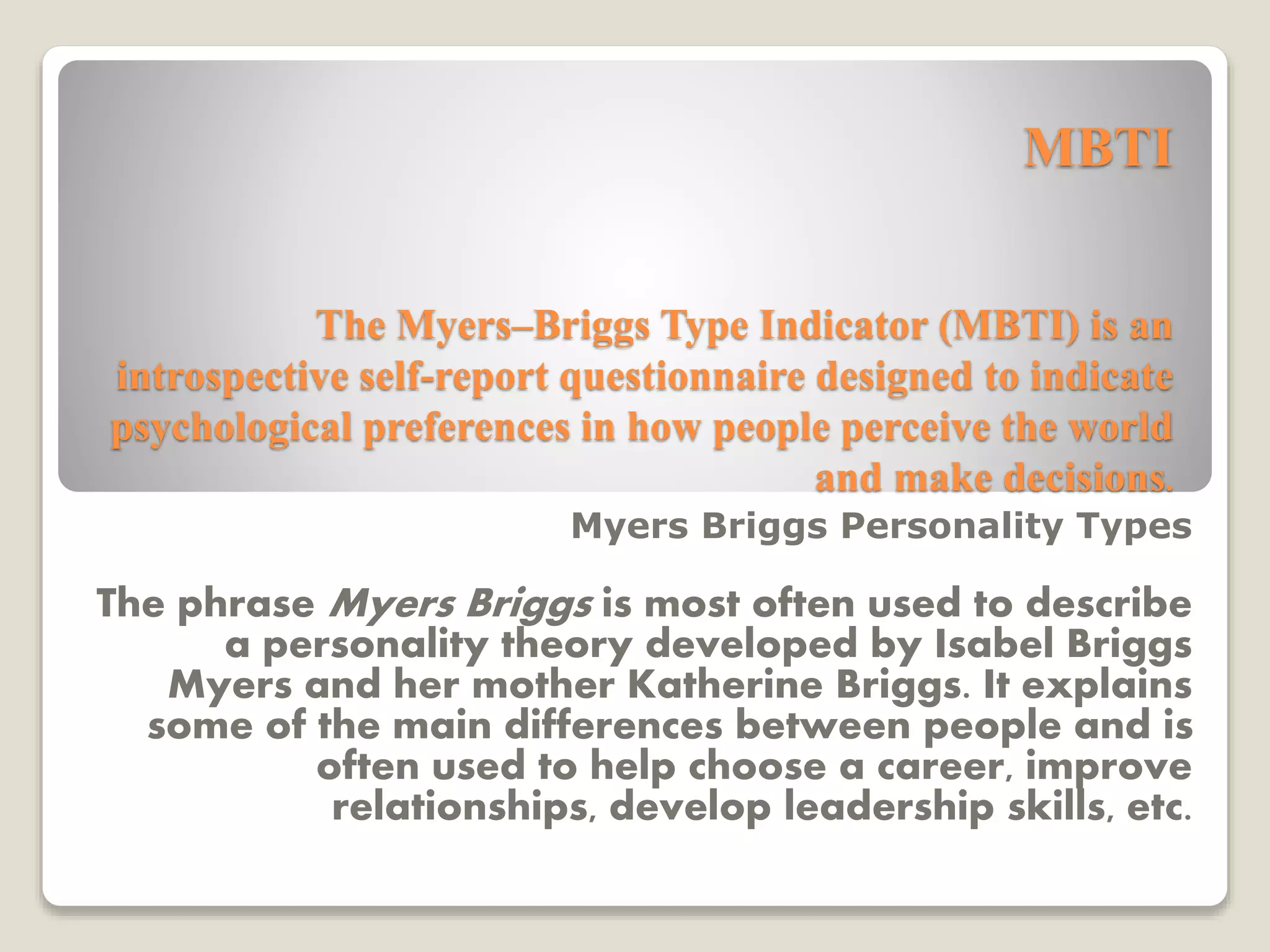
This document discusses personality and job satisfaction. It defines personality as relatively enduring patterns of behavior and thought. It outlines four perspectives on personality: psychoanalytic, trait, humanistic, and social-cognitive. It then discusses the Big Five model of personality, which describes the five broad domains of extraversion, agreeableness, conscientiousness, emotional stability, and openness to experience. The document also discusses the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator and its four dimensions: extraversion vs introversion, sensing vs intuition, thinking vs feeling, and judgment vs perception. Finally, it defines job satisfaction and outlines several theories of job satisfaction, including content, process, and situational theories. It concludes with some managerial