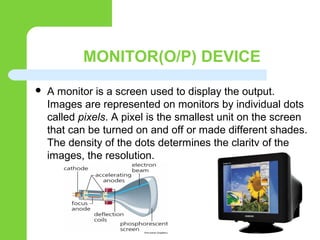
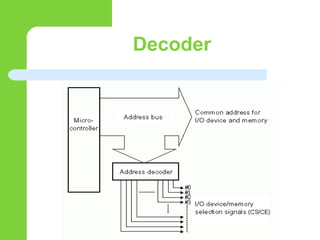
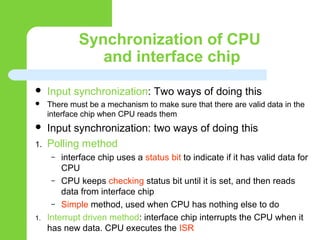
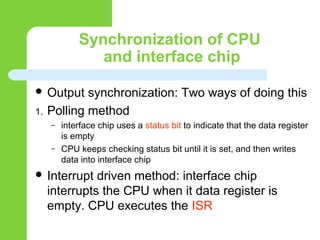
This document discusses computer peripheral devices and their functions. It defines peripheral devices as external objects that provide input and output for computers. It describes several types of input devices like keyboards, mice, scanners, and microphones that feed data into computers. It also discusses various output devices like monitors, printers, and projectors that display or print the computer's output. The document explains how interface chips and decoders help synchronize data transfer between the CPU and input/output devices.