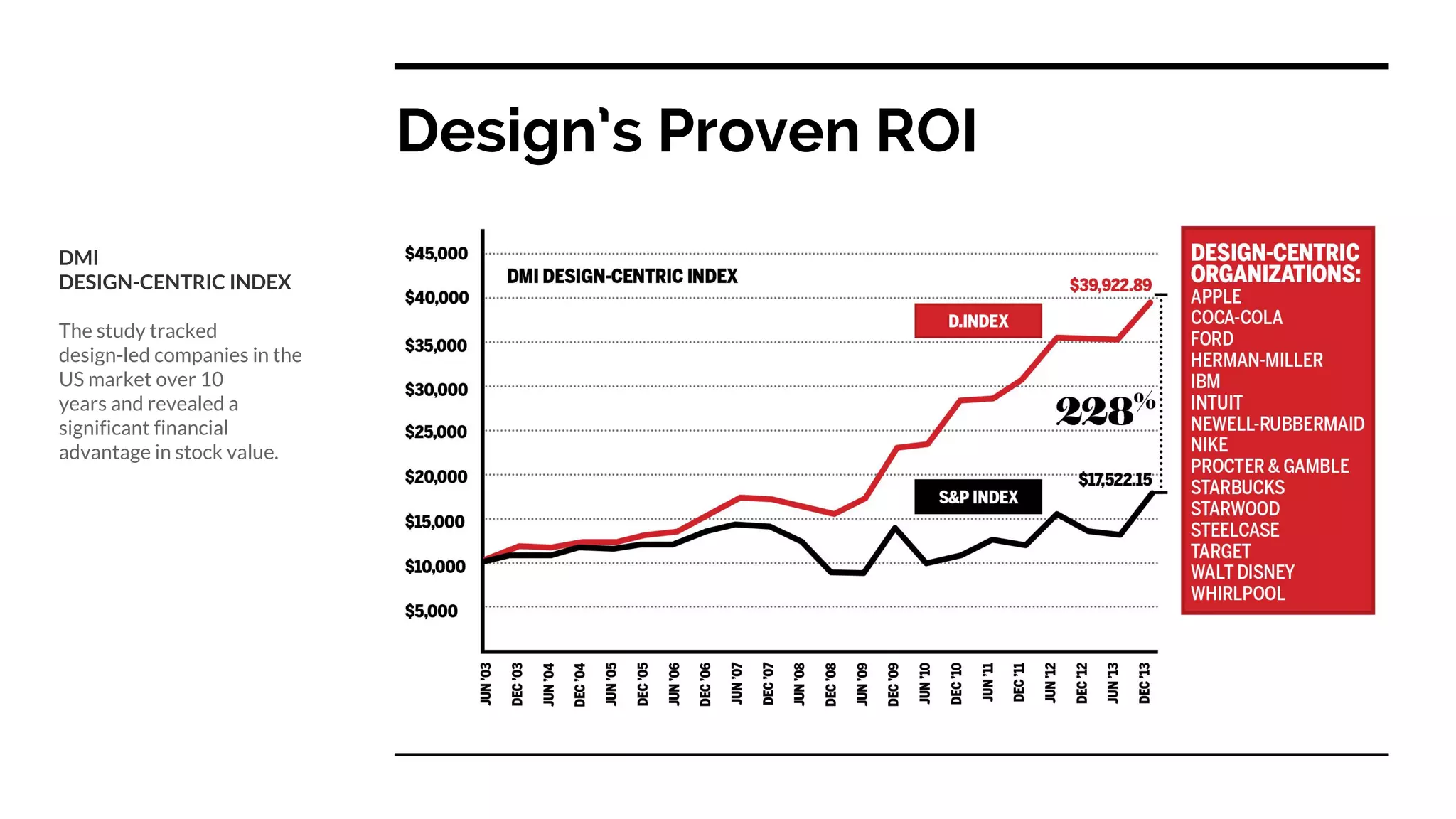
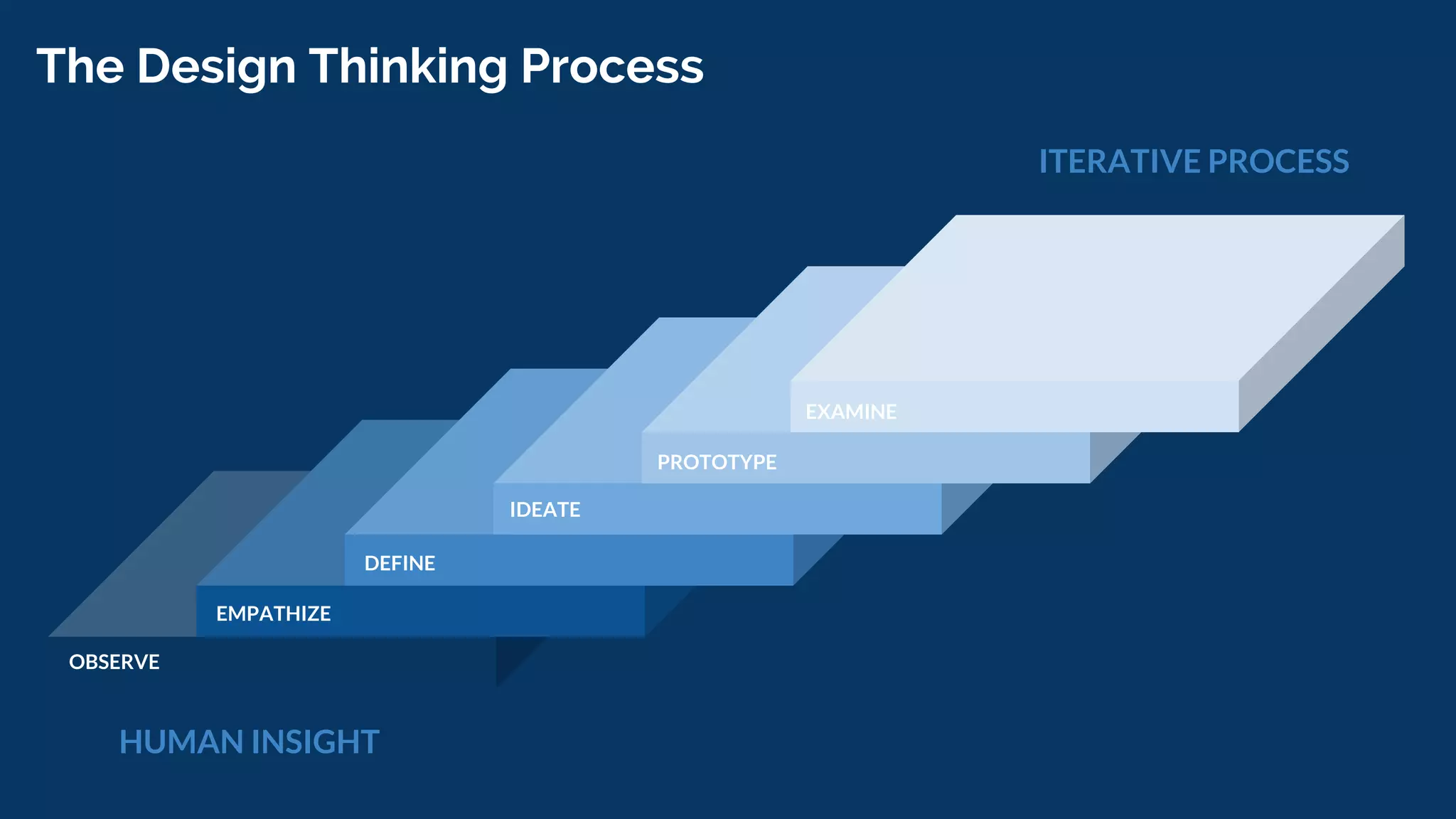
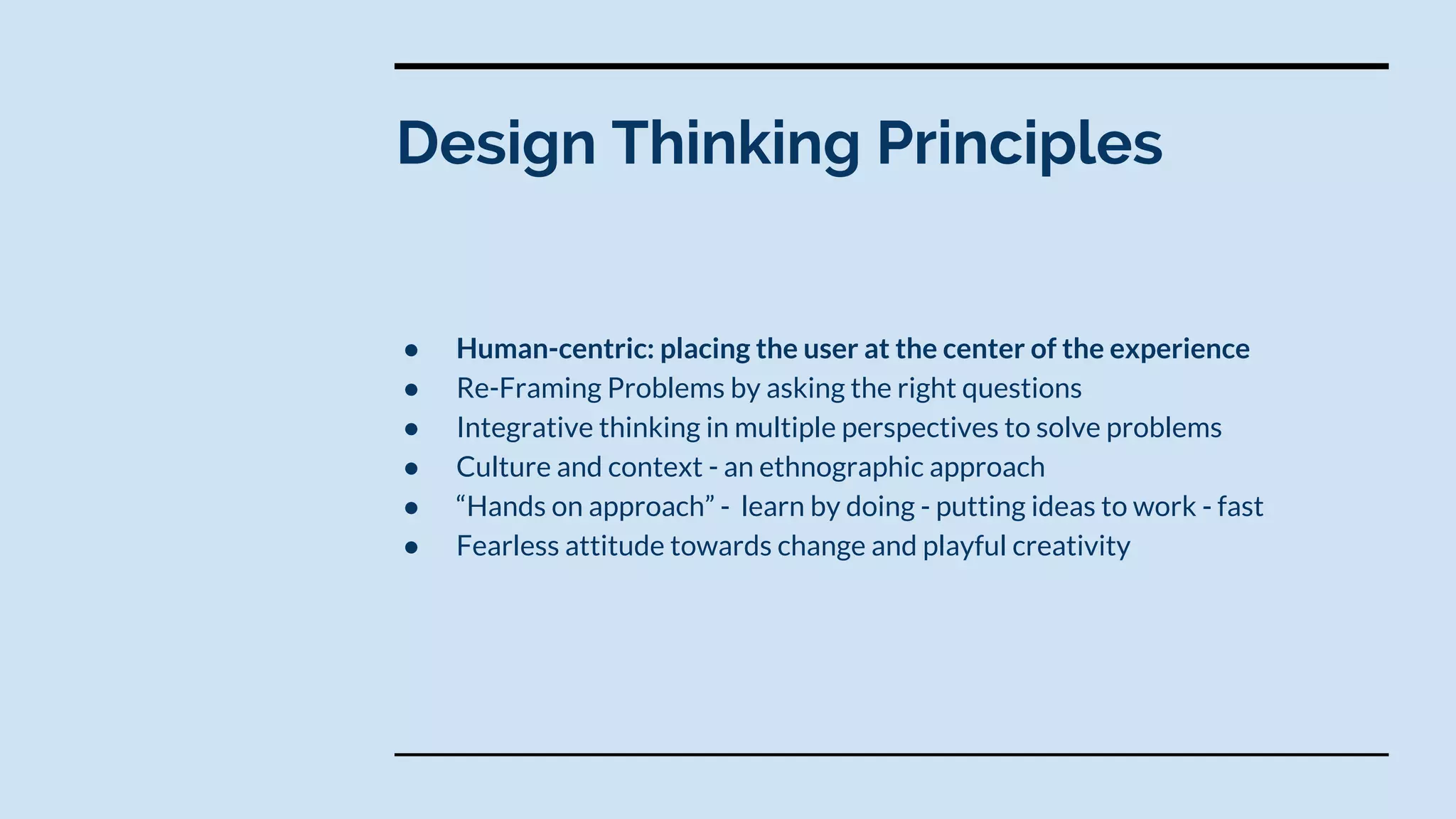
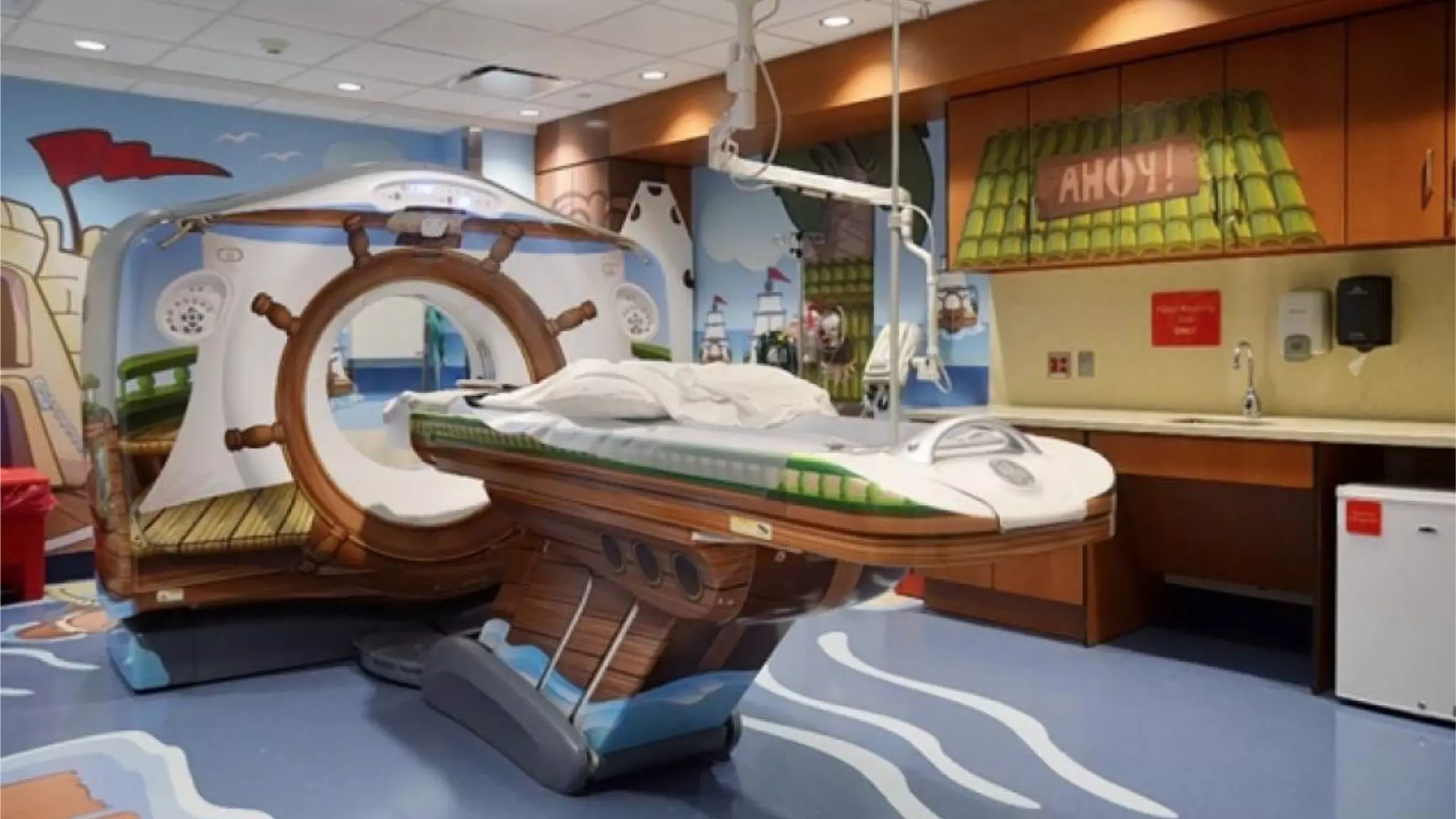
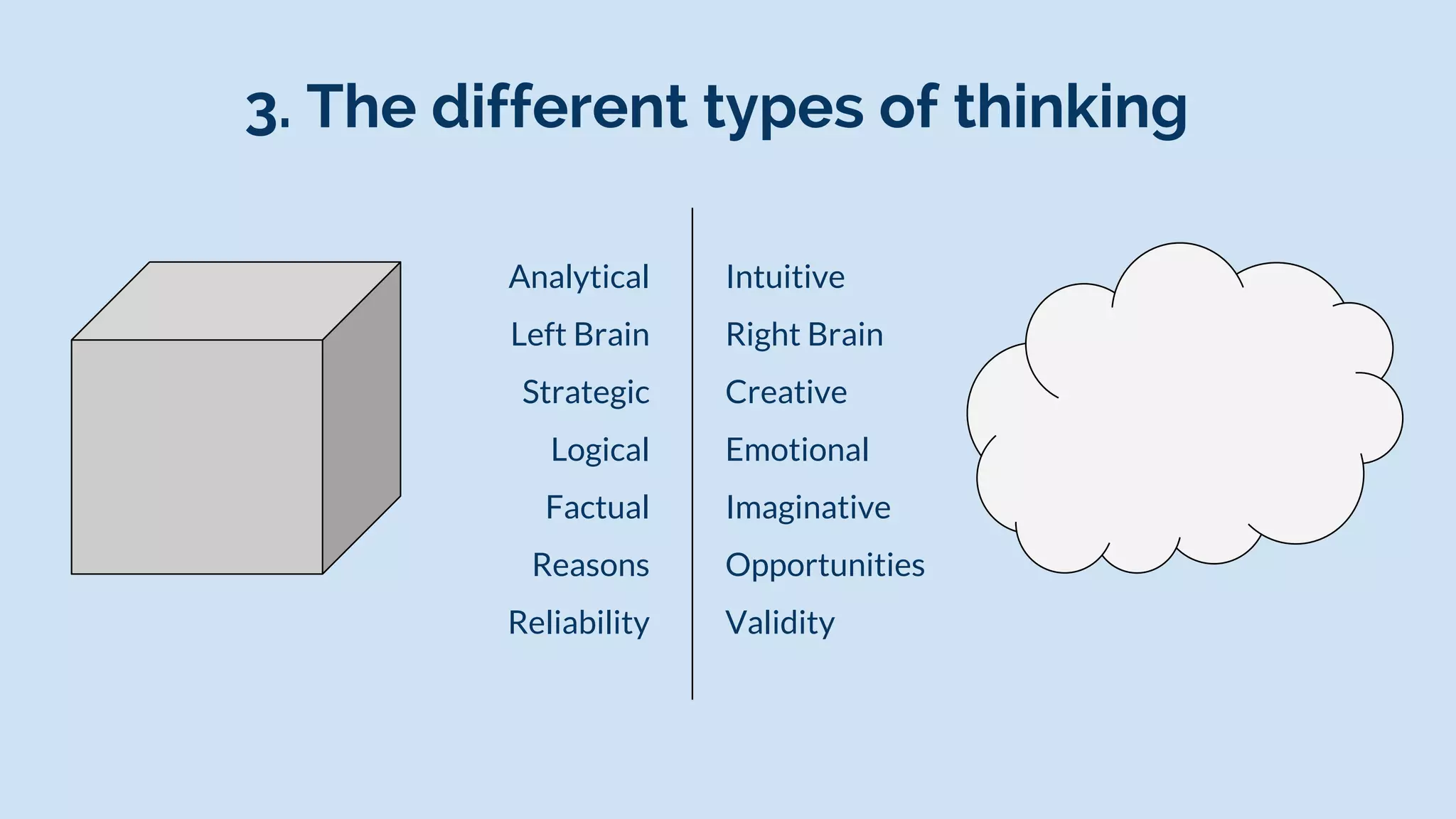
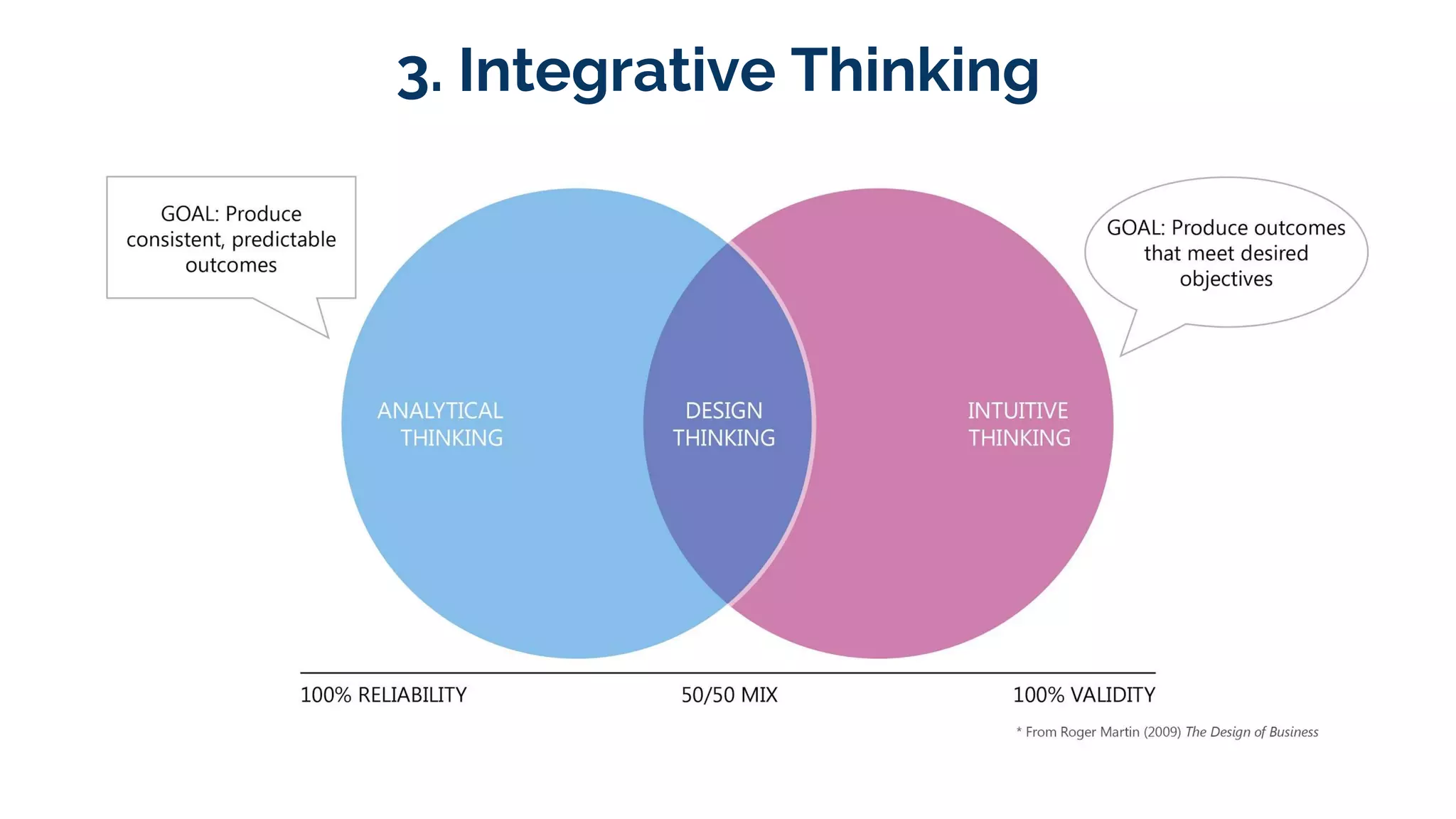
Design thinking is a human-centered problem-solving process that uses creative and analytical approaches to generate value. It involves empathizing with users to understand problems, defining the specific problem to address, ideating potential solutions, prototyping ideas, and getting feedback to examine how well a solution works. Design thinking focuses on reframing problems by asking the right questions and using integrative thinking across different perspectives. It has helped companies like Tesla, Airbnb, and TED solve problems and drive innovation through a fearless and hands-on approach.