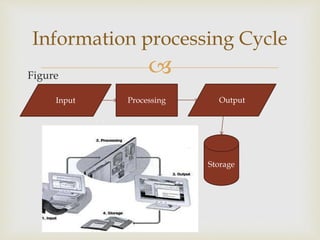
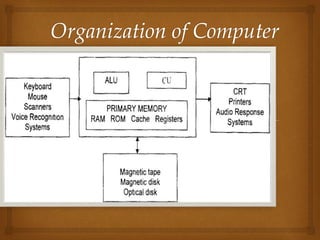
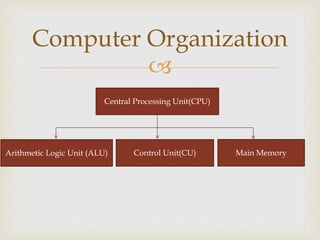
A computer is defined as an electronic device that can perform calculations at enormous speeds and generate output from input data according to programmed instructions. It consists of hardware, software, data, and users. The hardware is the physical machinery including input devices like keyboards, output devices like monitors, storage devices, communication devices, and the central processing unit. Software includes system software that controls the hardware and application software that allows users to perform tasks. Data are the individual facts and pieces of information processed by the computer. Users are people who operate the computer and provide it with instructions and data.