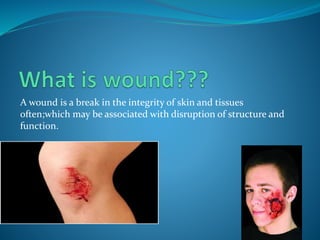
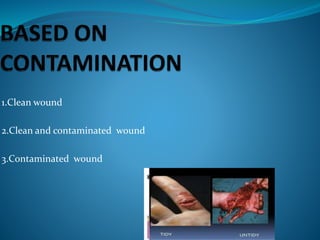
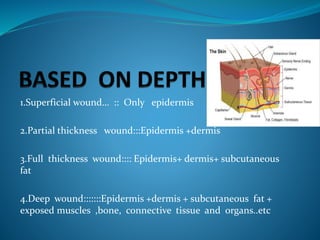
1. A wound is a break in the skin or tissues that disrupts structure and function. Wounds can be classified based on origin, contamination, and depth.
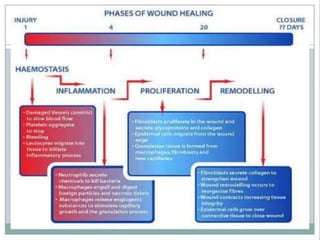
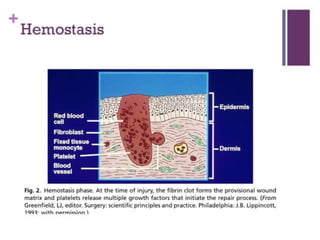
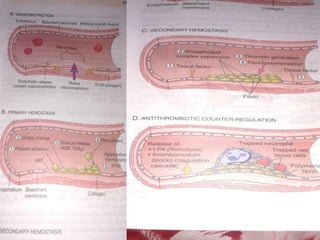
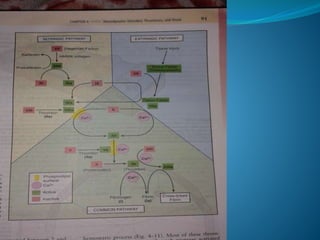
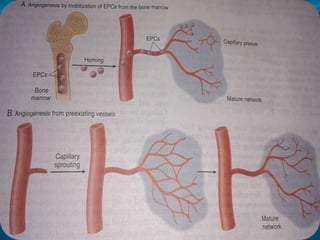
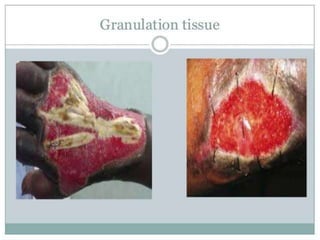
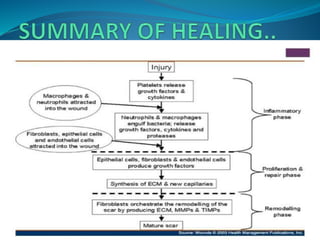
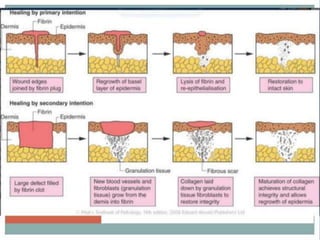
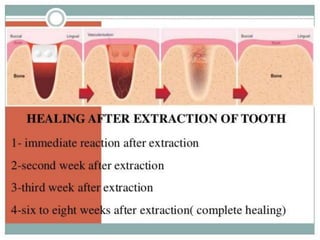
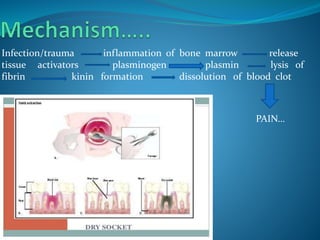
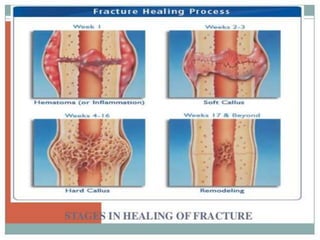
2. Healing is the body's response to injury that attempts to restore normal structure and function. It involves inflammation, tissue formation, cell migration, angiogenesis and tissue remodeling.
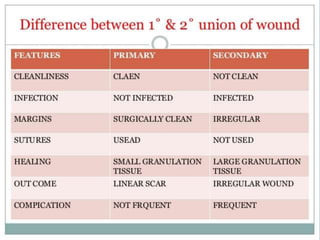
3. Many local and systemic factors can affect wound healing, including infection, poor blood supply, age, nutrition, medications and underlying illnesses. Proper wound care and management of patient health can support optimal healing.