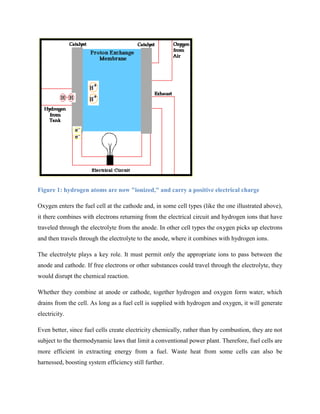
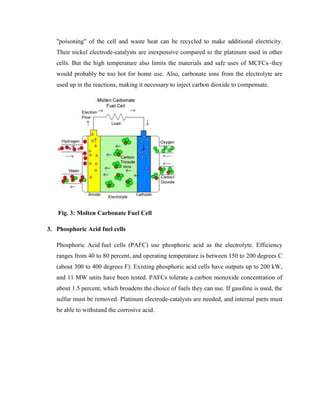
Fuel cells generate electricity through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen. There are several types of fuel cells that differ in their electrolyte material and operating temperatures. Alkali fuel cells use a potassium hydroxide electrolyte and operate at 150-200°C. Molten carbonate fuel cells use salt carbonate electrolytes and operate at 650°C. Phosphoric acid fuel cells use phosphoric acid and operate at 150-200°C. Proton exchange membrane fuel cells use a solid polymer electrolyte and operate at around 80°C. Solid oxide fuel cells use a ceramic electrolyte and operate at around 1000°C. Fuel cells can be powered by renewable hydrogen sources like water electrolysis or nonrenewable