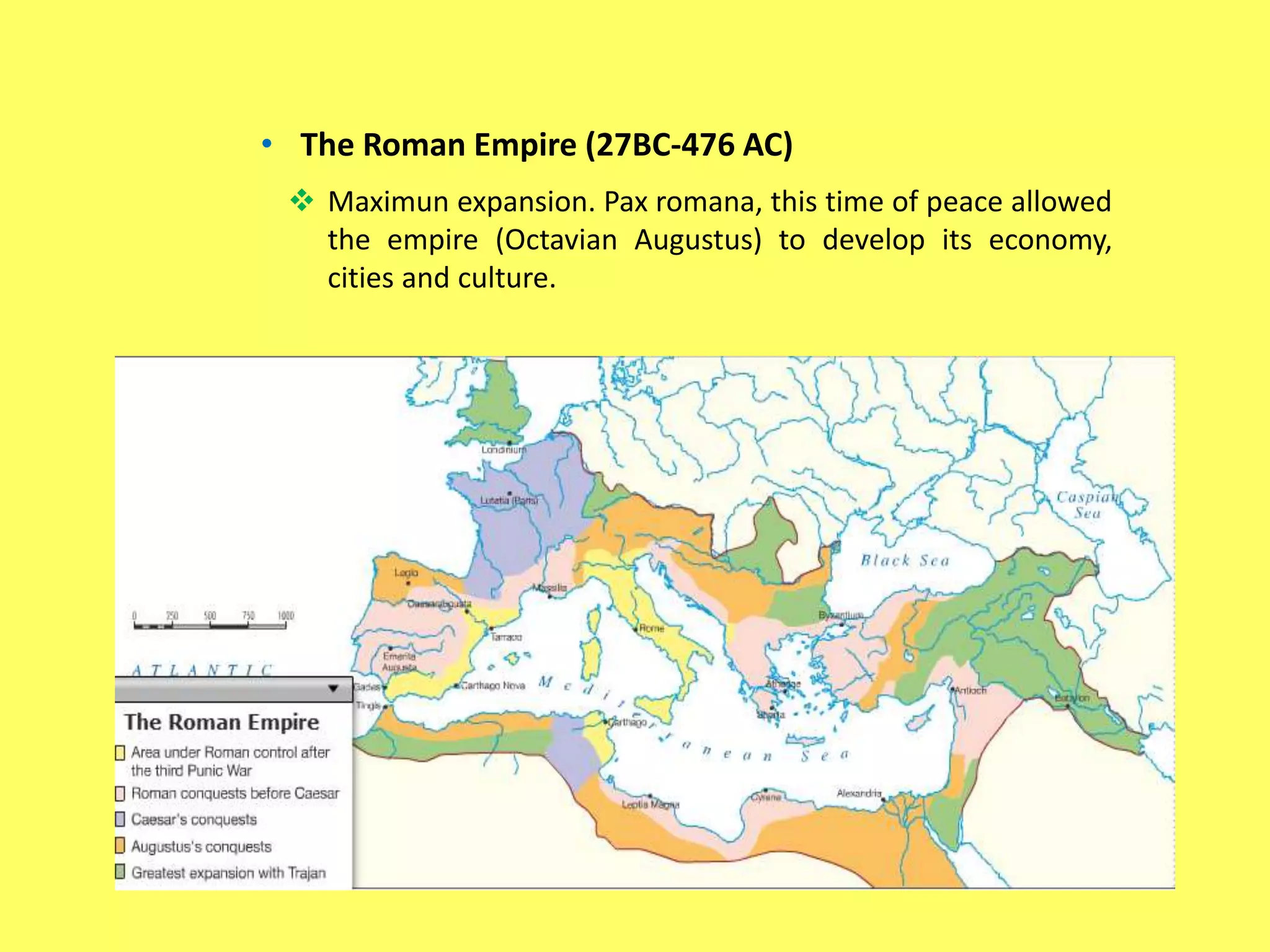
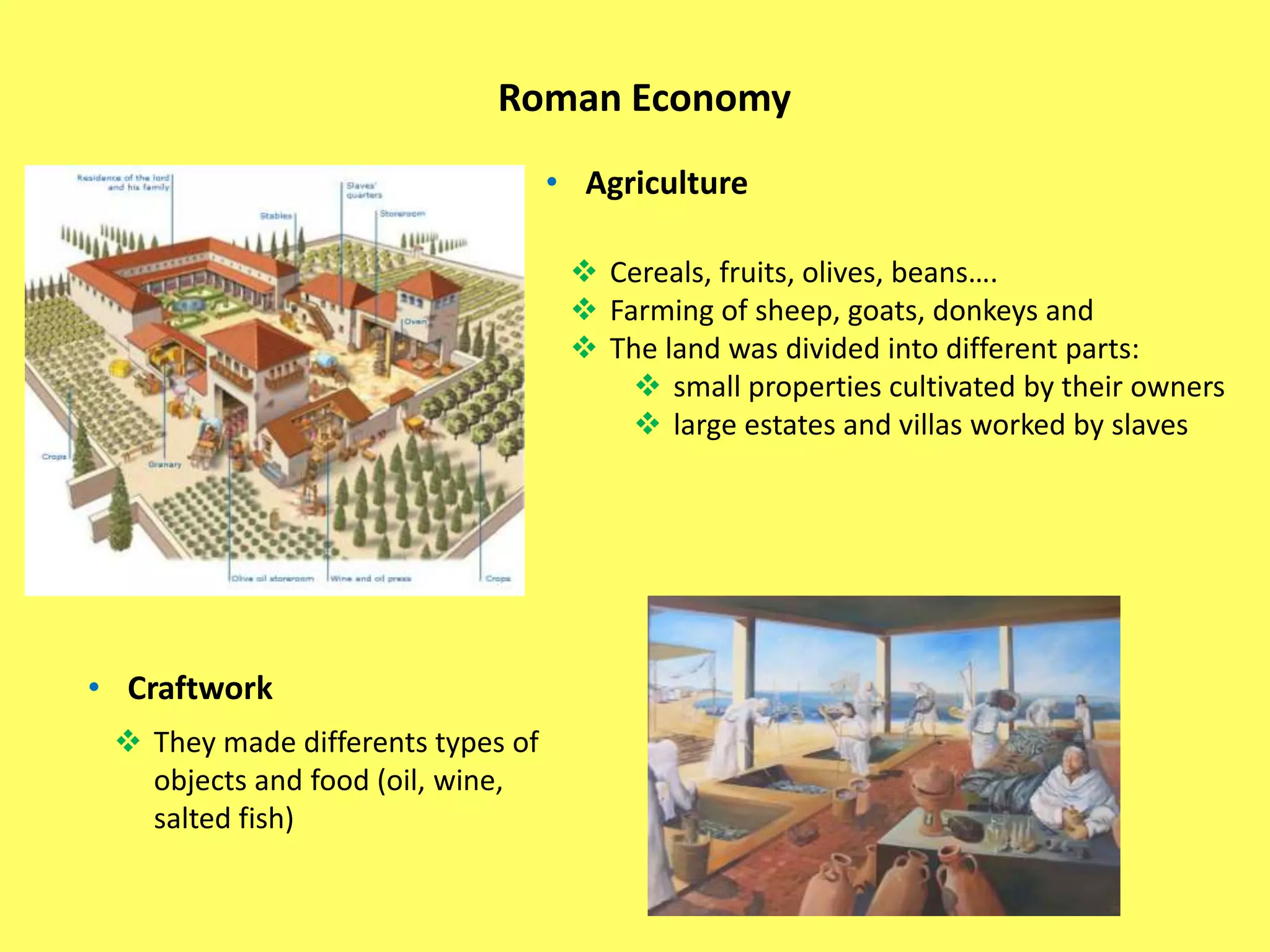
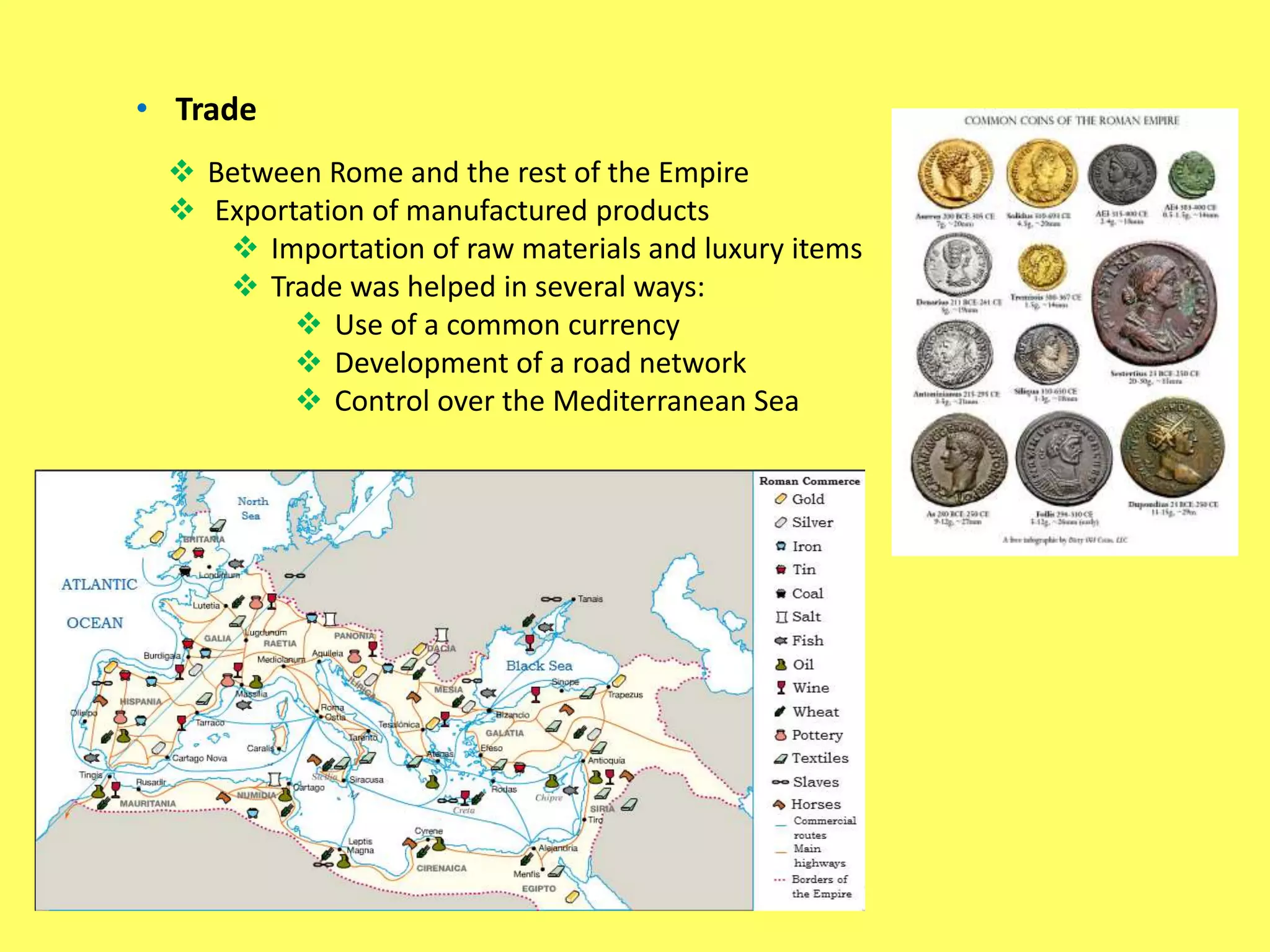
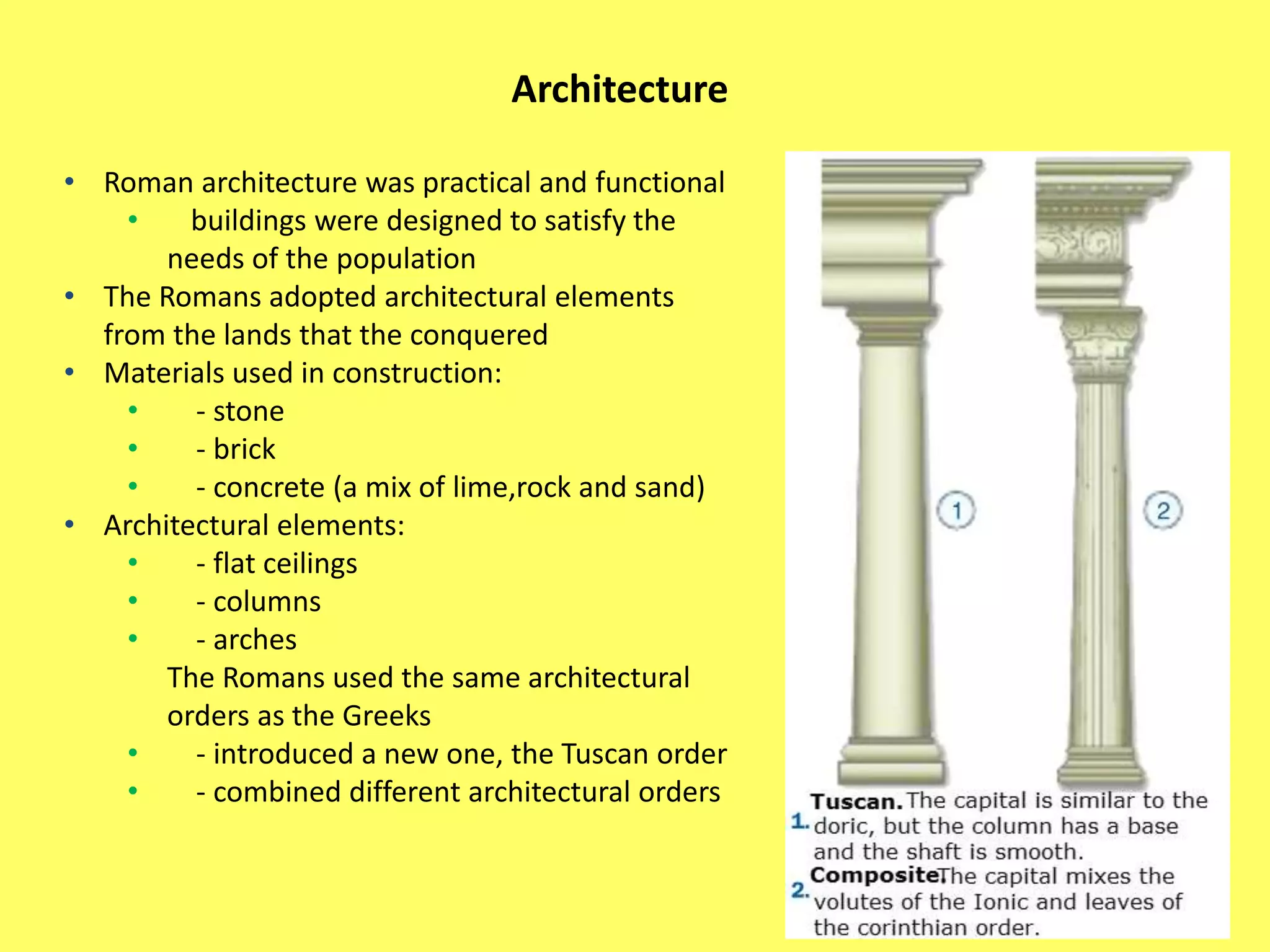
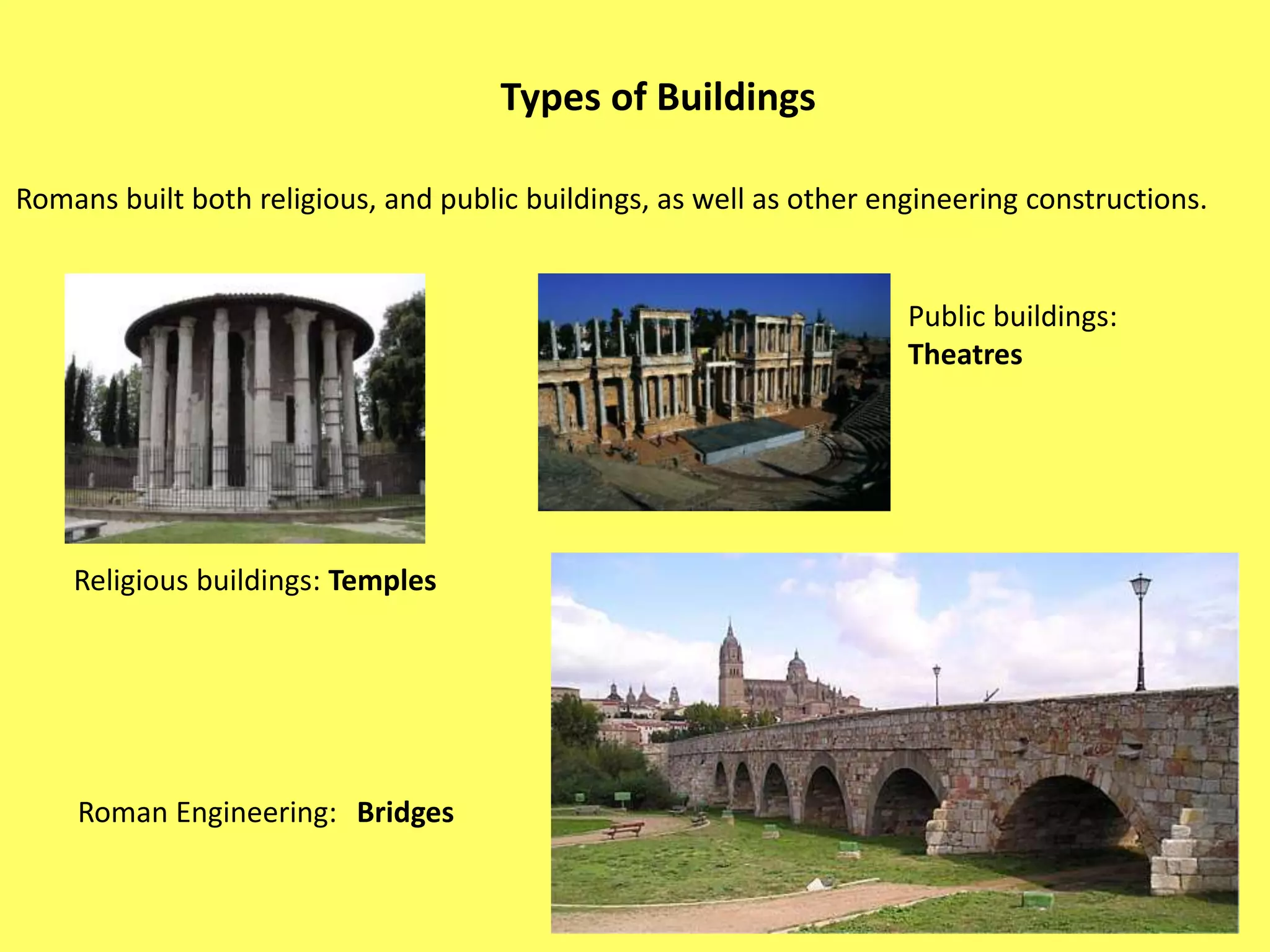
This document provides information about Ancient Rome in three main sections. It begins with the political organization of Rome from the monarchy period starting in 753 BC through the Roman Republic and Empire. Next it discusses the Roman economy, including agriculture, crafts, and trade. Finally, it covers aspects of Roman society such as social classes, religion, architecture, and engineering. The document was created by five Spanish students as a school assignment on the topic of Ancient Rome.