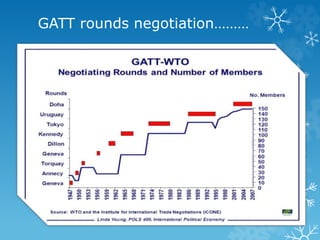
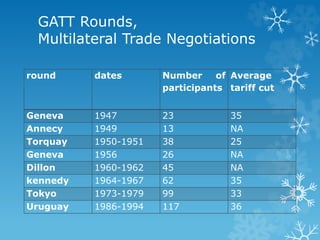
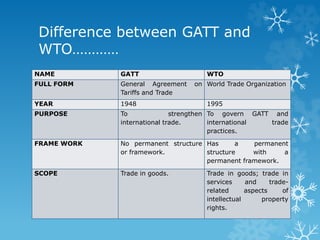
The World Trade Organization (WTO), established on January 1, 1995, succeeded the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) to oversee and liberalize international trade. The WTO has a formal structure and governs trade in goods, services, and intellectual property, contrasting with GATT's limited scope and framework. For Bangladesh, which is classified as a least developed country, the WTO's regulations significantly influence its economy, particularly concerning market access and external trade factors.