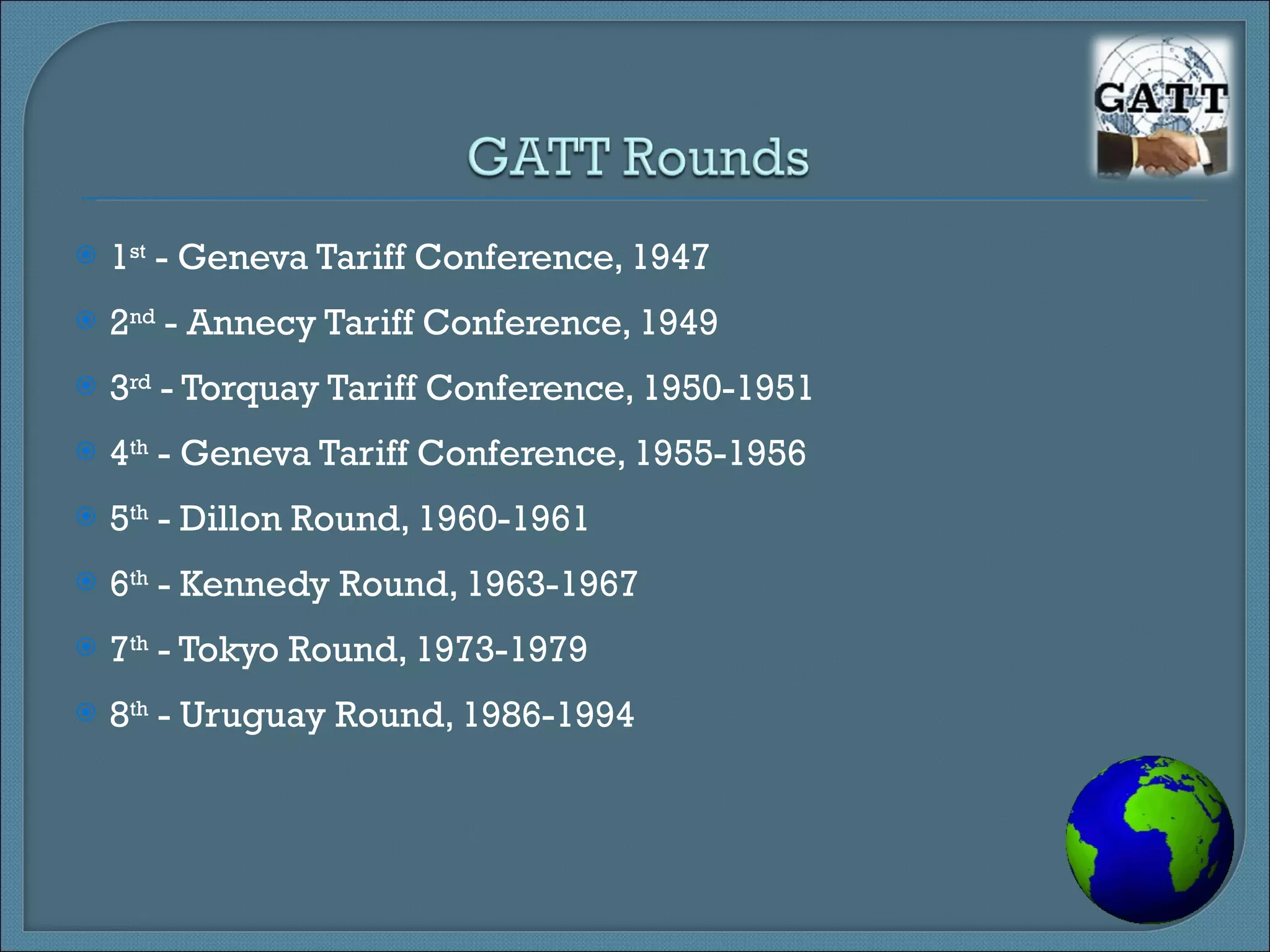
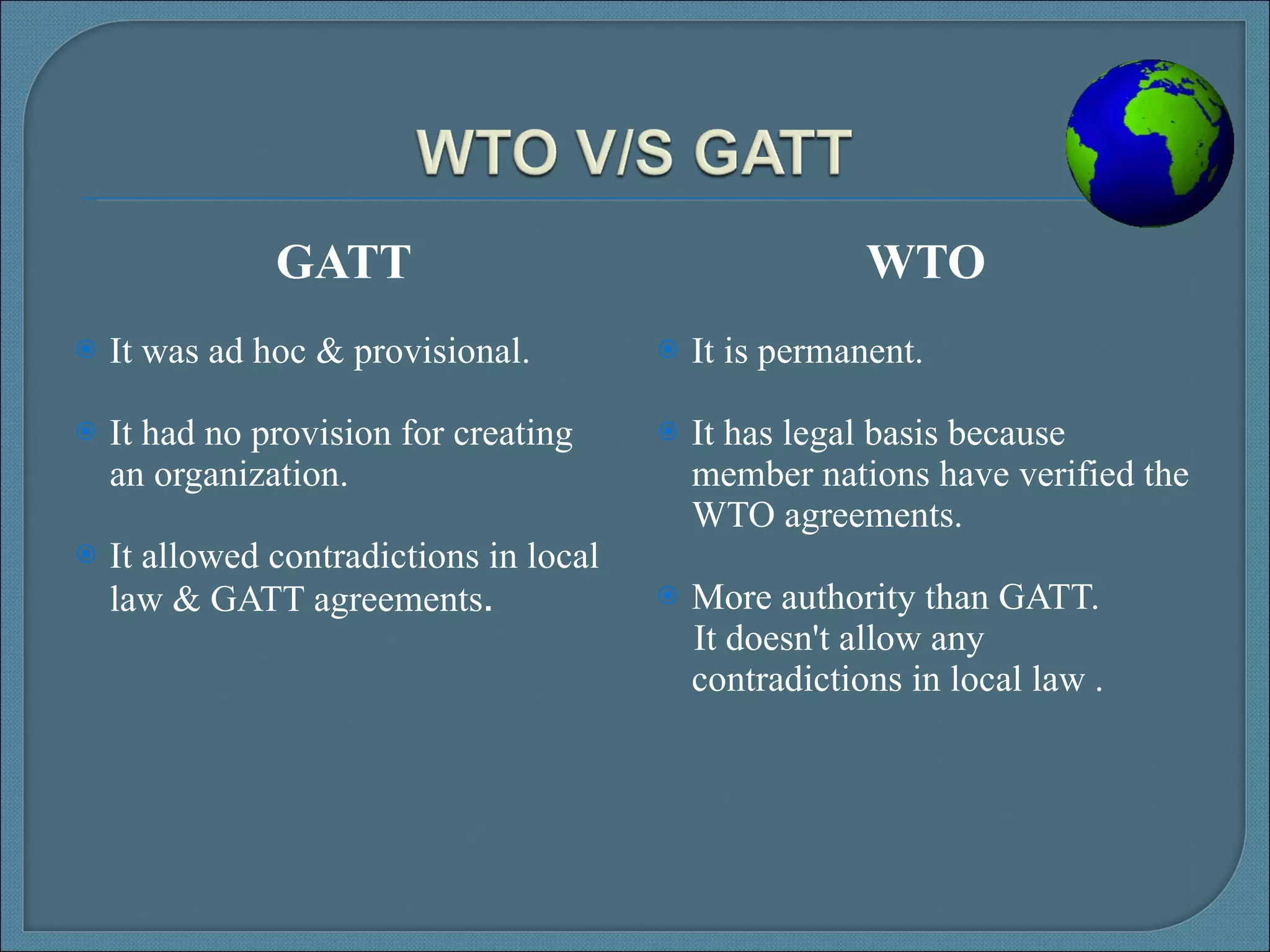
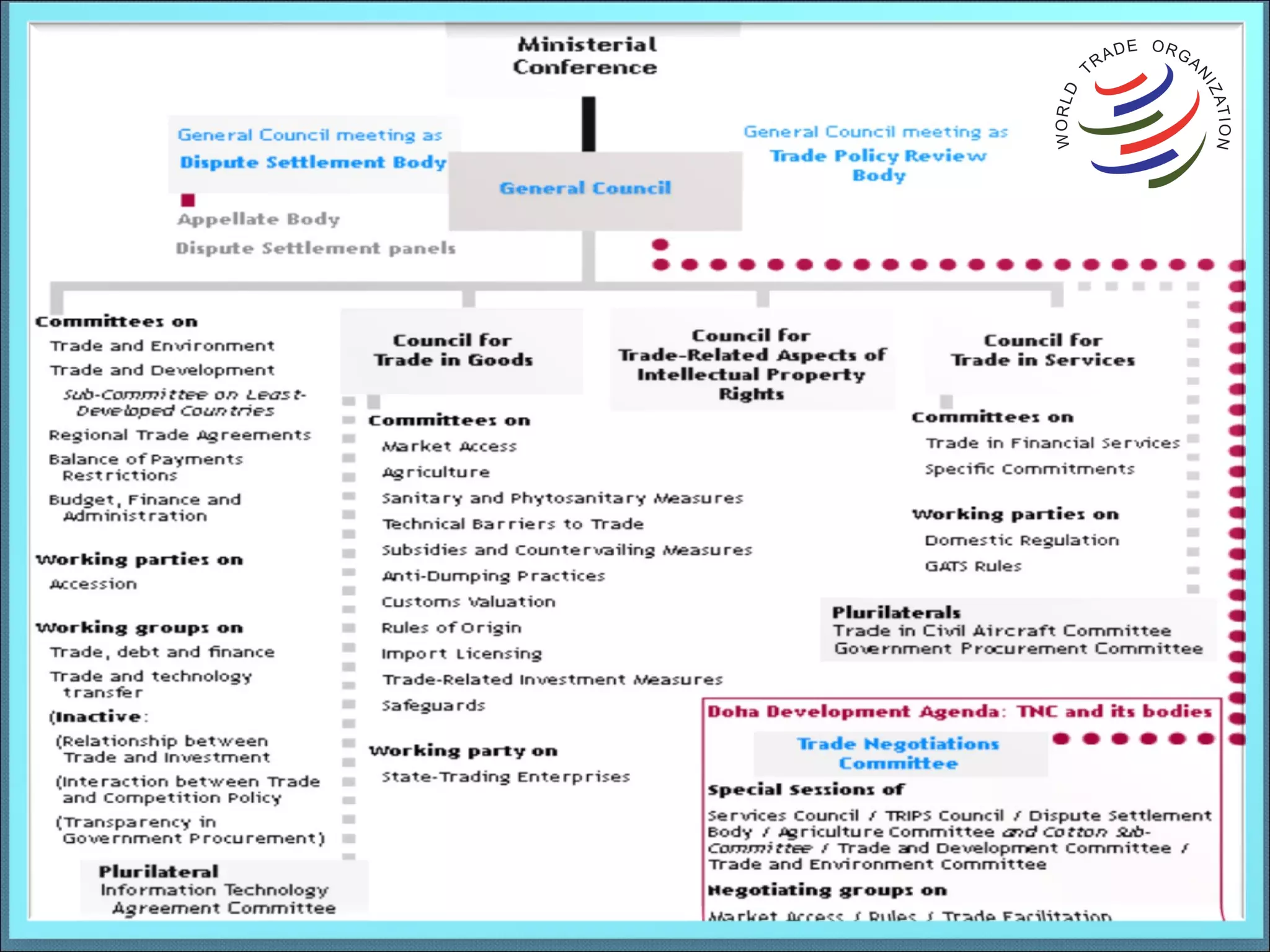
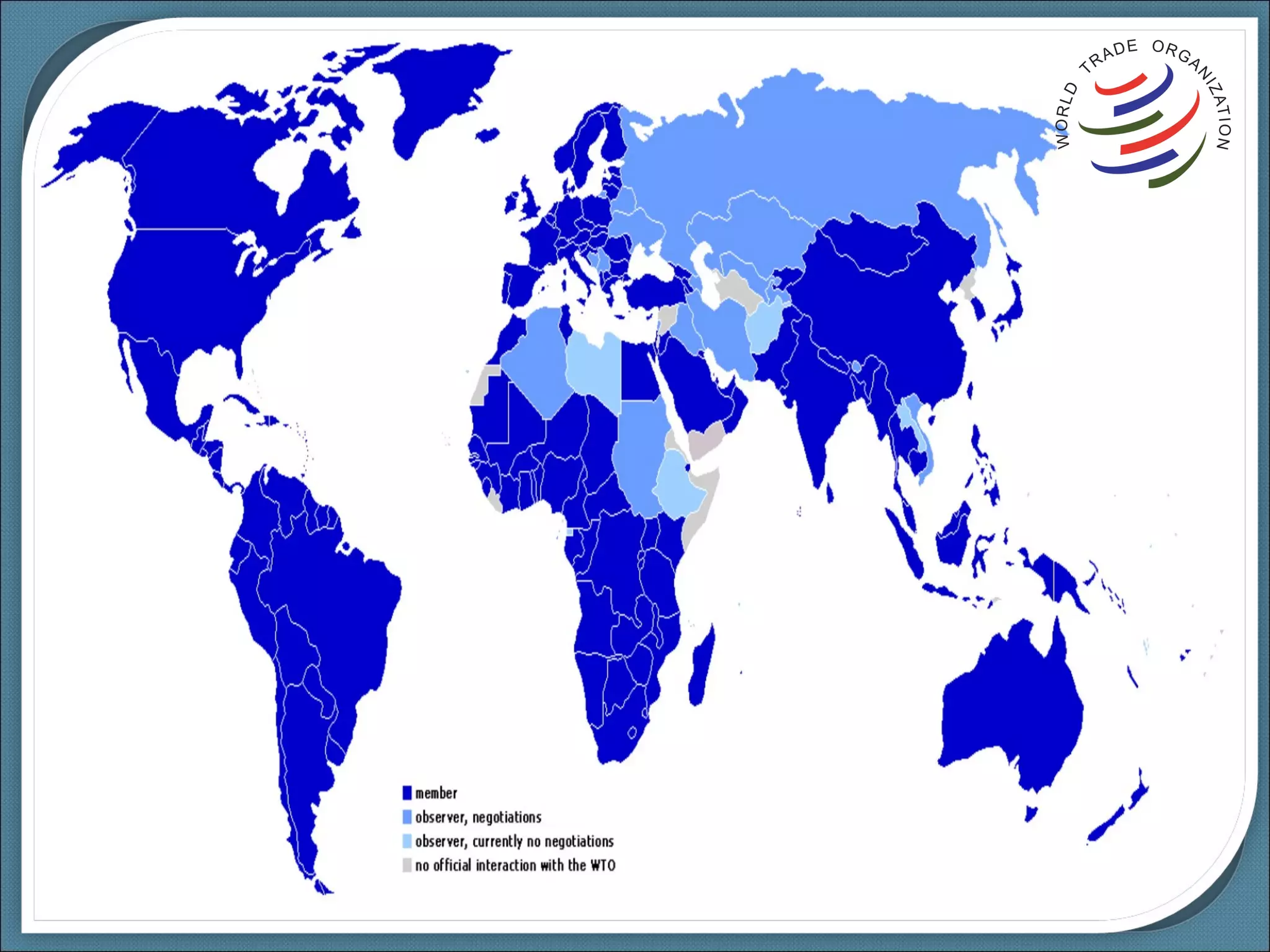
The World Trade Organization (WTO) was established in 1995 to oversee and liberalize international trade. It originated from negotiations and agreements under the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) established in 1947. The WTO has 153 member countries and governs global trade through multilateral agreements aimed at reducing trade barriers to promote economic growth. It provides a framework and dispute resolution process to ensure fair and predictable international trade.