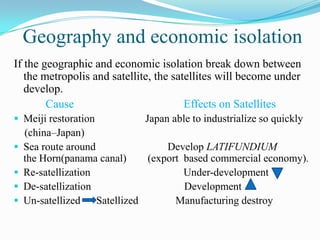
1. Andre Gunder Frank's dependency theory argues that underdeveloped countries are kept in a state of underdevelopment due to their economic dependence on developed "metropolis" countries, which extract economic surplus from satellite underdeveloped countries through trade.
2. The theory posits that underdeveloped countries experience the most development when their ties to the metropolis are weakest, such as during wars or economic crises, or due to geographic isolation.
3. Regions with the closest past ties to metropolis countries, through the export of primary commodities, are now the most underdeveloped, while regions that were able to industrialize saw a decline in dependence on the metropolis.