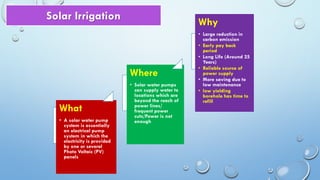
- Solar powered irrigation systems use photovoltaic (PV) solar panels to generate electricity to power water pumps for irrigation. The electricity is provided without fuel costs and the systems can operate indefinitely as long as there is sunlight.
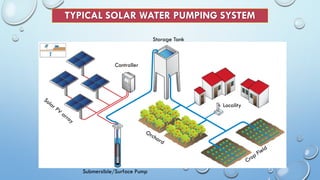
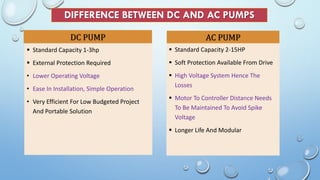
- The key components are solar panels, a controller, storage tank, and submersible or surface pump. Solar pumps can supply water to remote locations not reachable by power lines and provide a reliable source of power with low maintenance costs compared to diesel pumps.
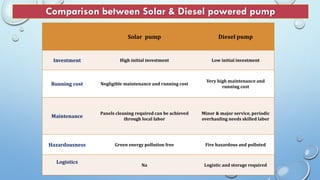
- Advantages include saving on energy costs, no dependence on electricity grids or rain, and enabling increased crop yields. Disadvantages are higher upfront costs and pumps not operating at night. Larger solar arrays are needed for high power