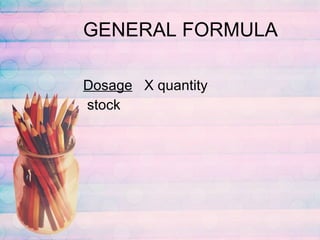
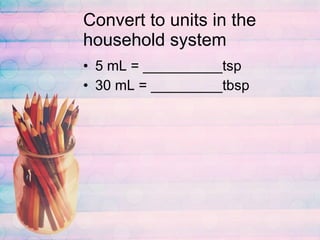
This document discusses proper drug administration including the rights of patients, nursing process, assessment, planning, interventions, evaluation and calculations. It covers the key elements of patient education and outlines Clark's rule, Fried's rule and Young's rule for calculating pediatric dosages based on weight, age and age plus 12 respectively. Examples of converting between measurement systems and dosage calculations are also provided.