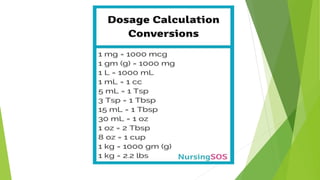
This document discusses pediatric drug dose calculations. It provides definitions of key terms like dose, dosage regimen, and dosage calculation terms. It explains that drug doses for children are typically based on weight and outlines several common formulas used to calculate appropriate doses for infants, toddlers, and children up to 12 years old based on either age or weight. These include formulas to calculate doses up to 2 years old based on age in months, doses for children 2-12 based on Clark's rule using weight in pounds, and formulas for calculating amounts in milliliters when a dose is known or vice versa. The purposes, rights, and approaches to drug administration in pediatrics are also summarized.