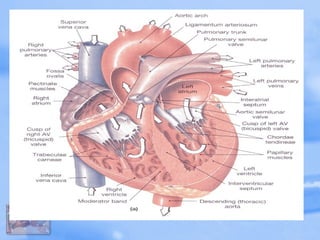
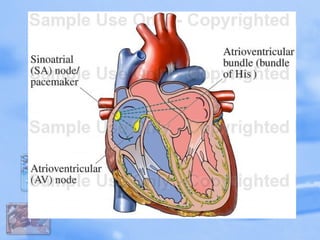
The document discusses the cardiovascular system and drugs that affect blood pressure. It covers the heart and circulation, factors that determine heart oxygen use and blood pressure, hypertension treatment approaches, and classes of antihypertensive drugs like diuretics, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, vasodilators, and drugs that treat hypotension. It also briefly mentions cardiotonic drugs.