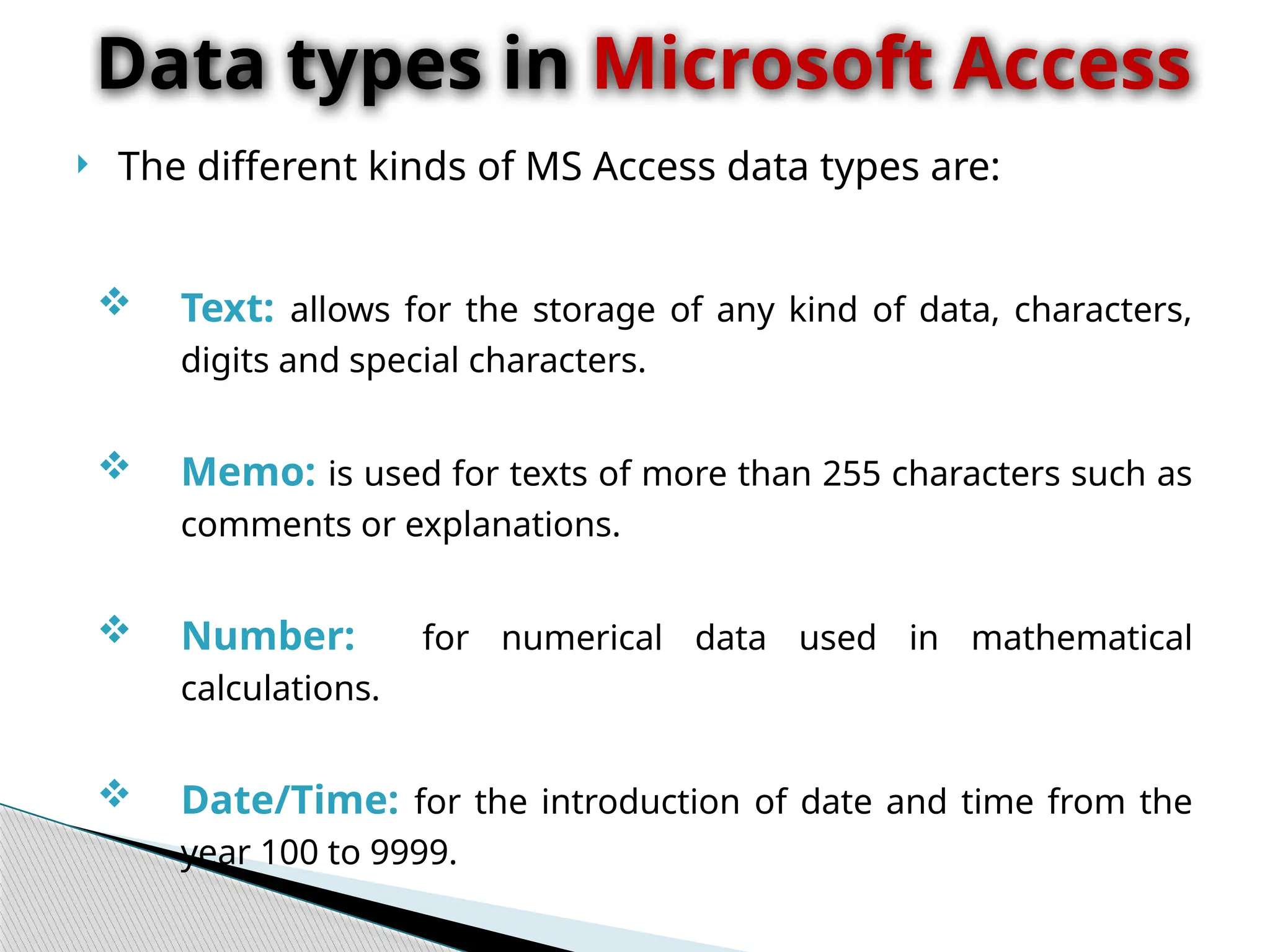
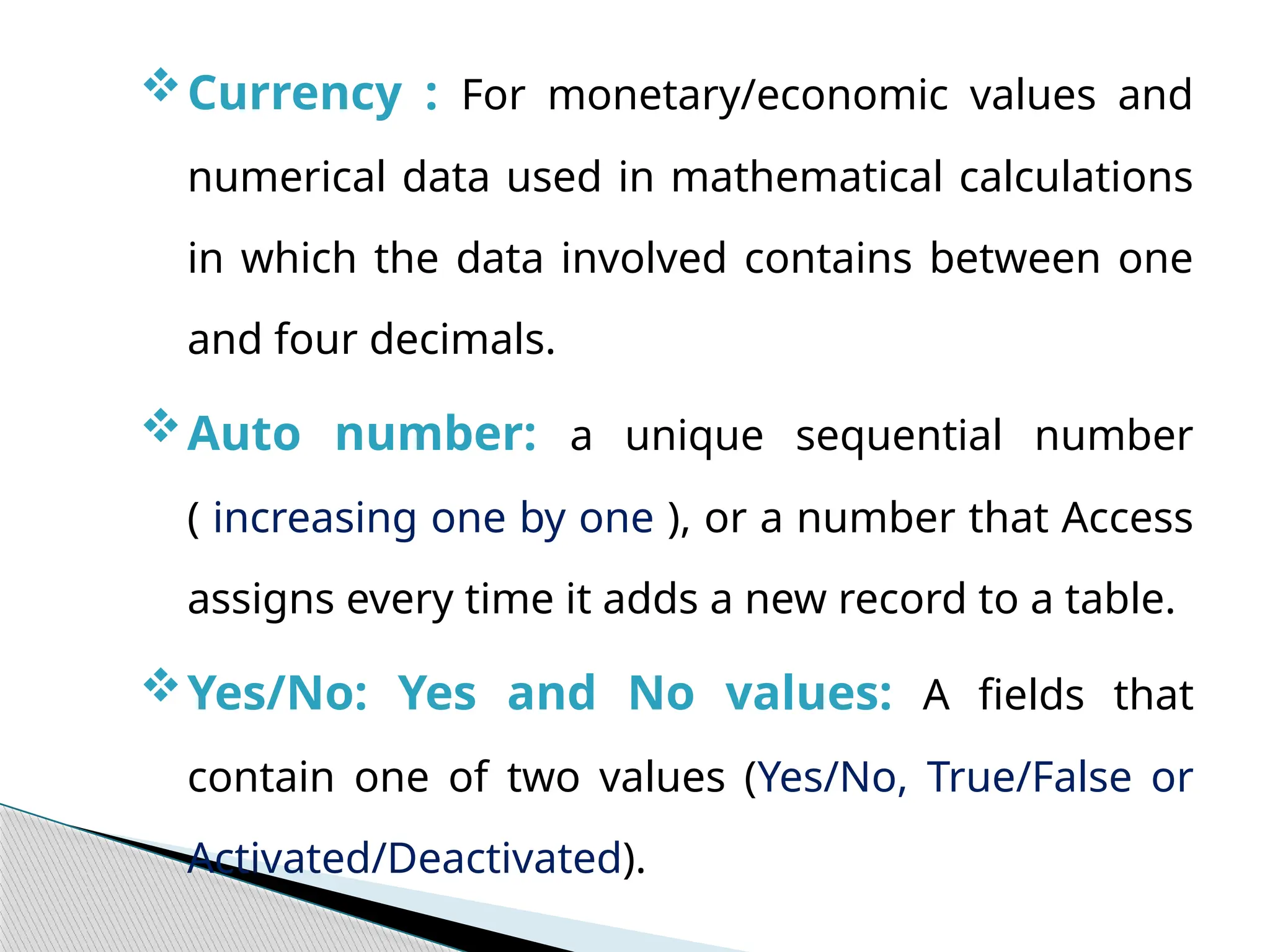
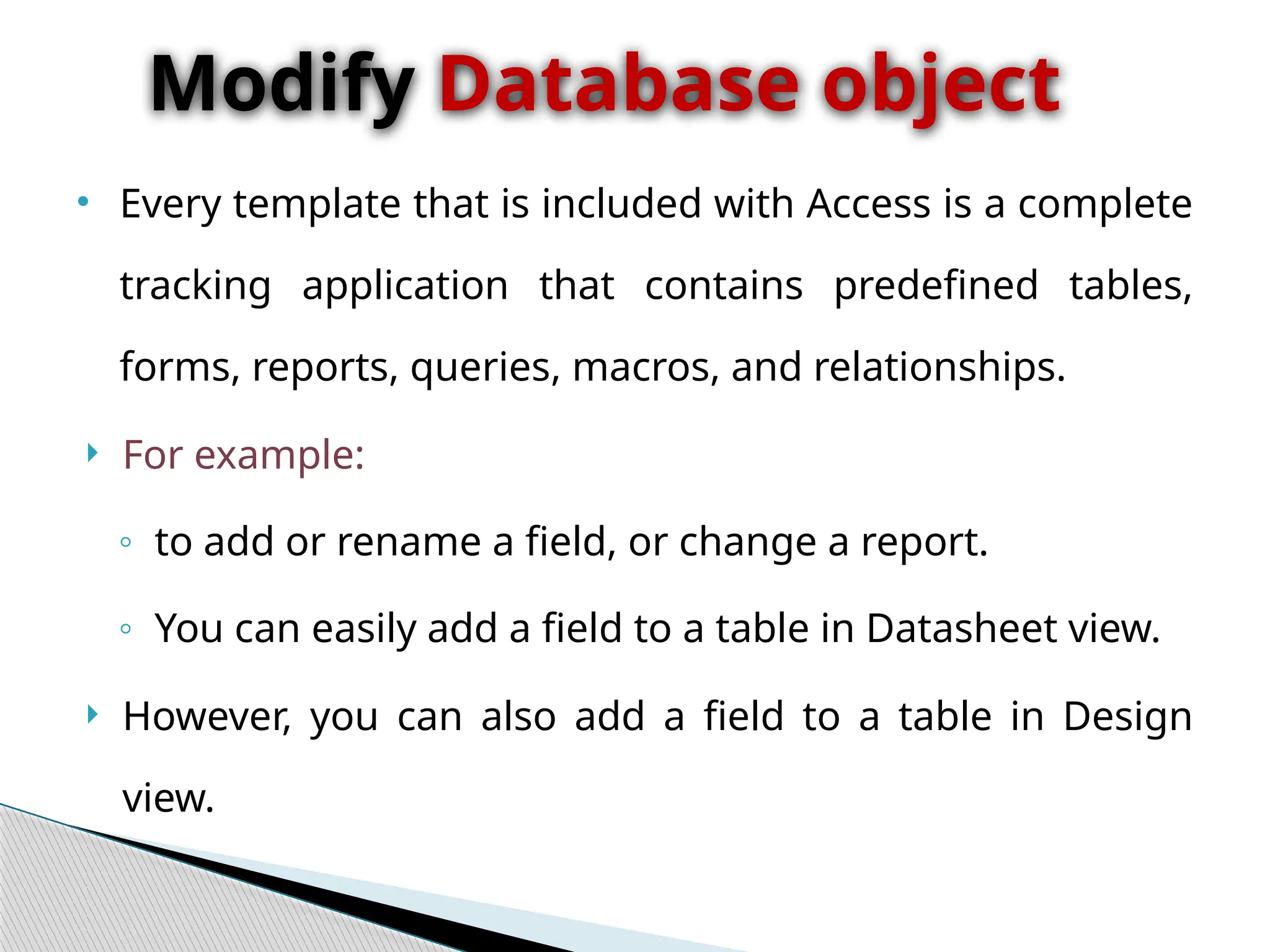
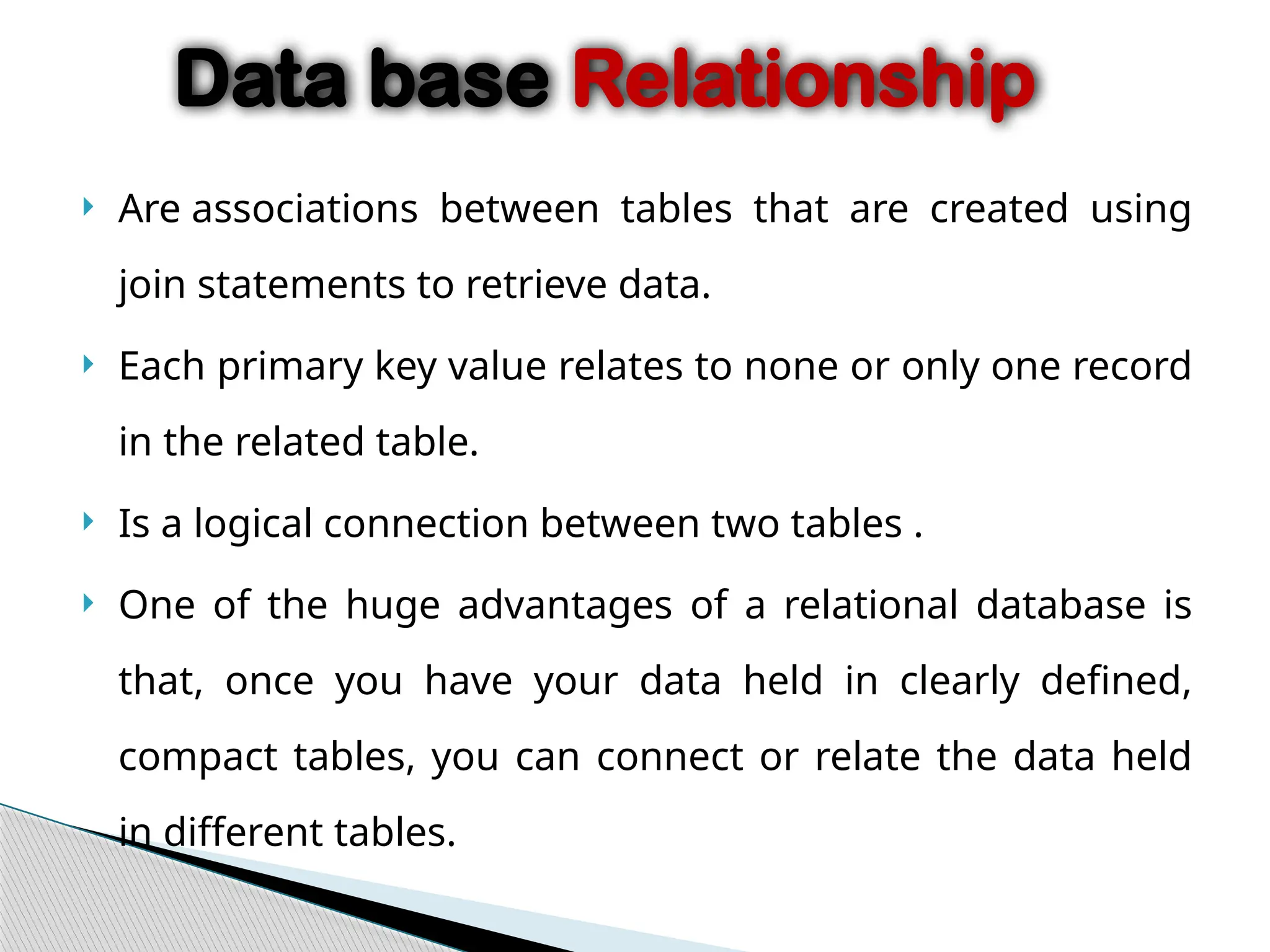
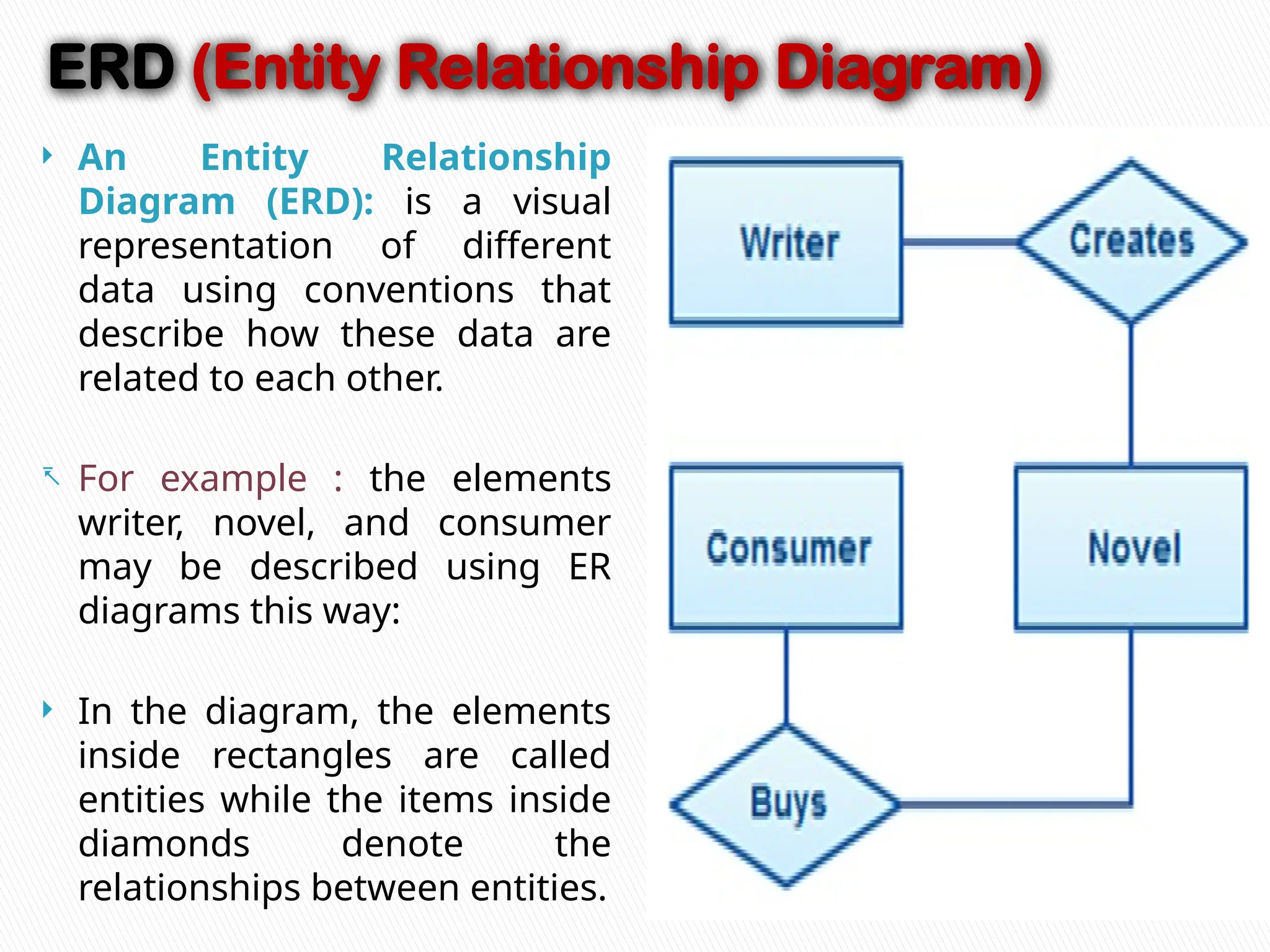
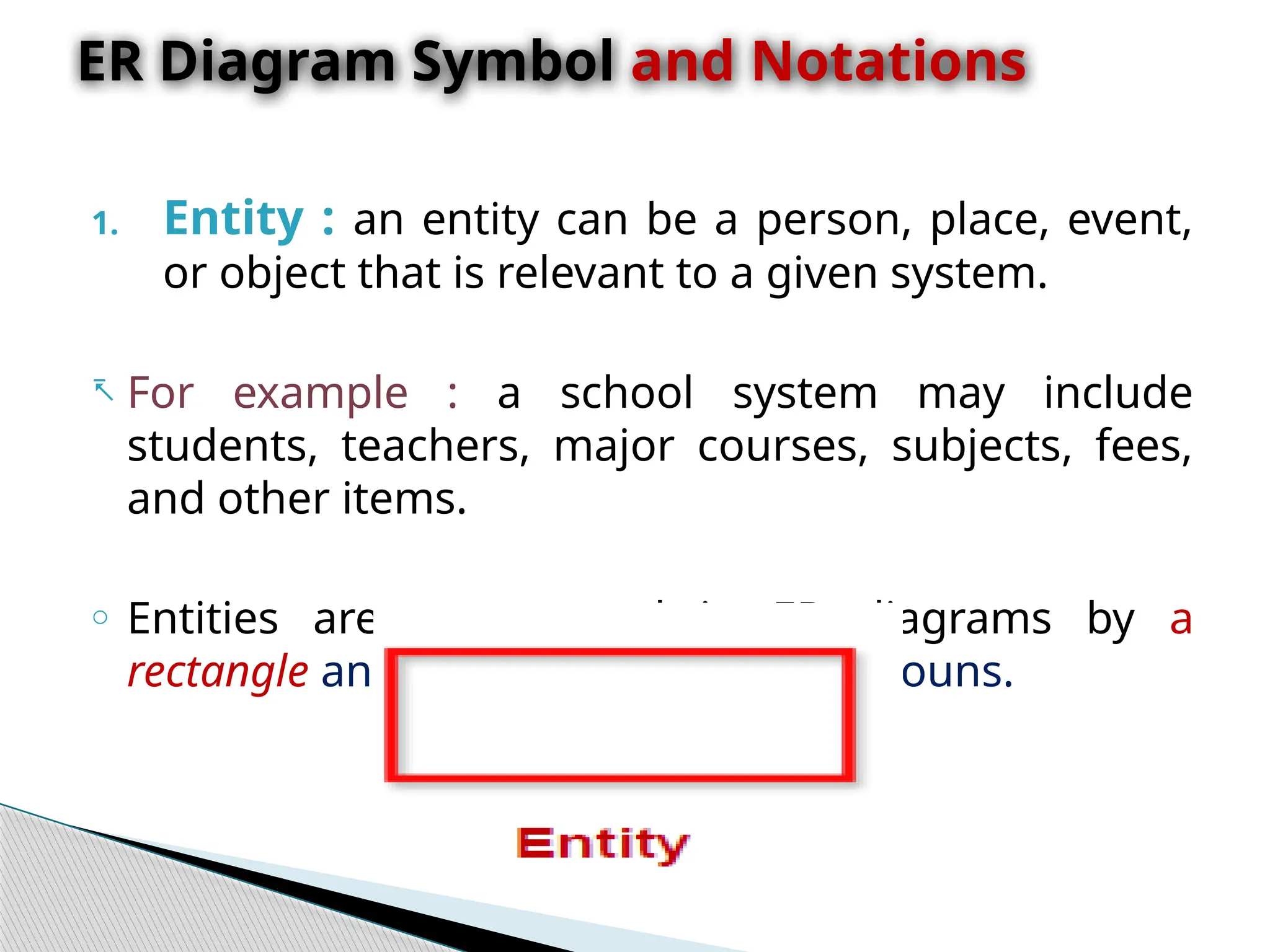
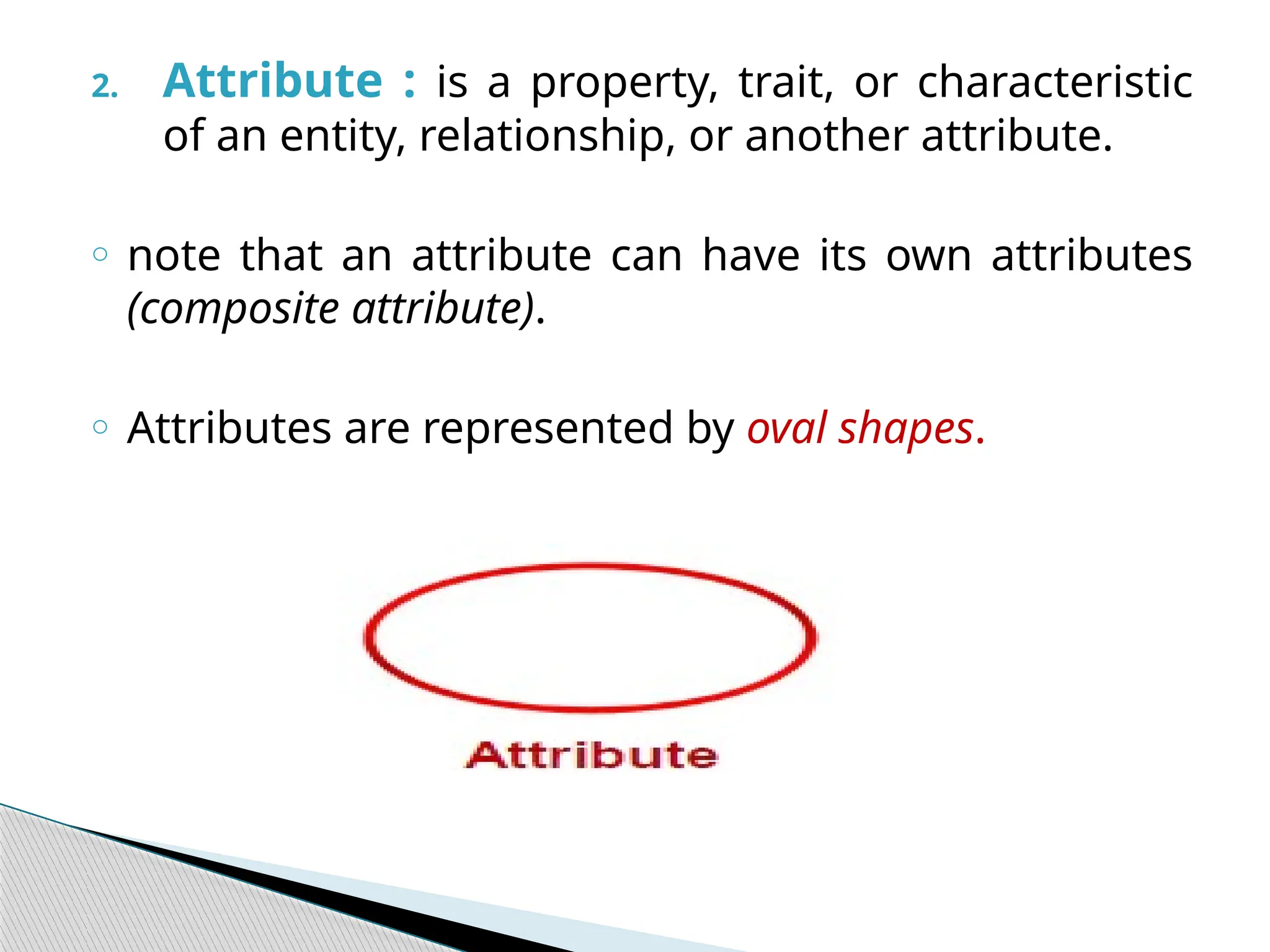
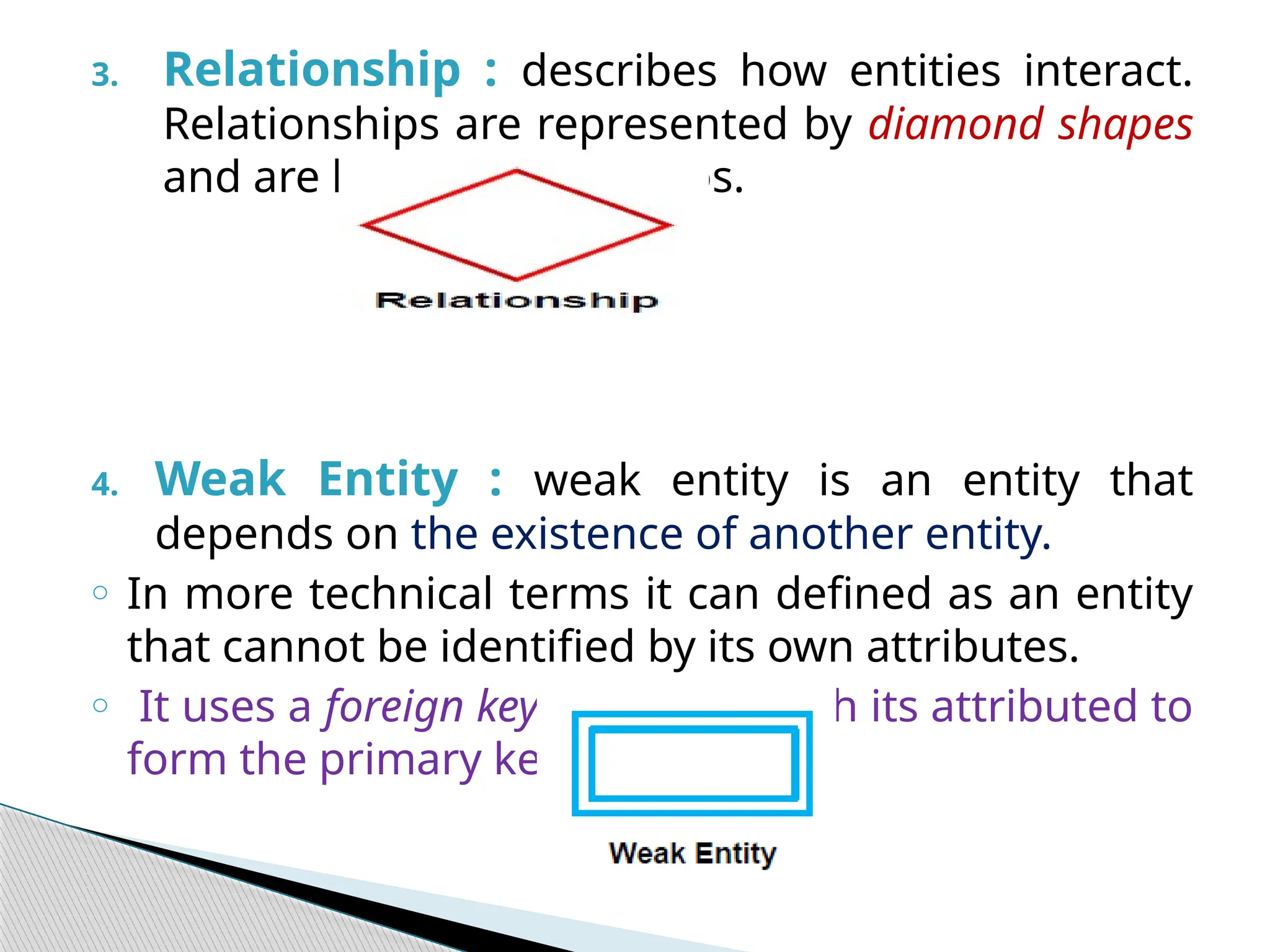
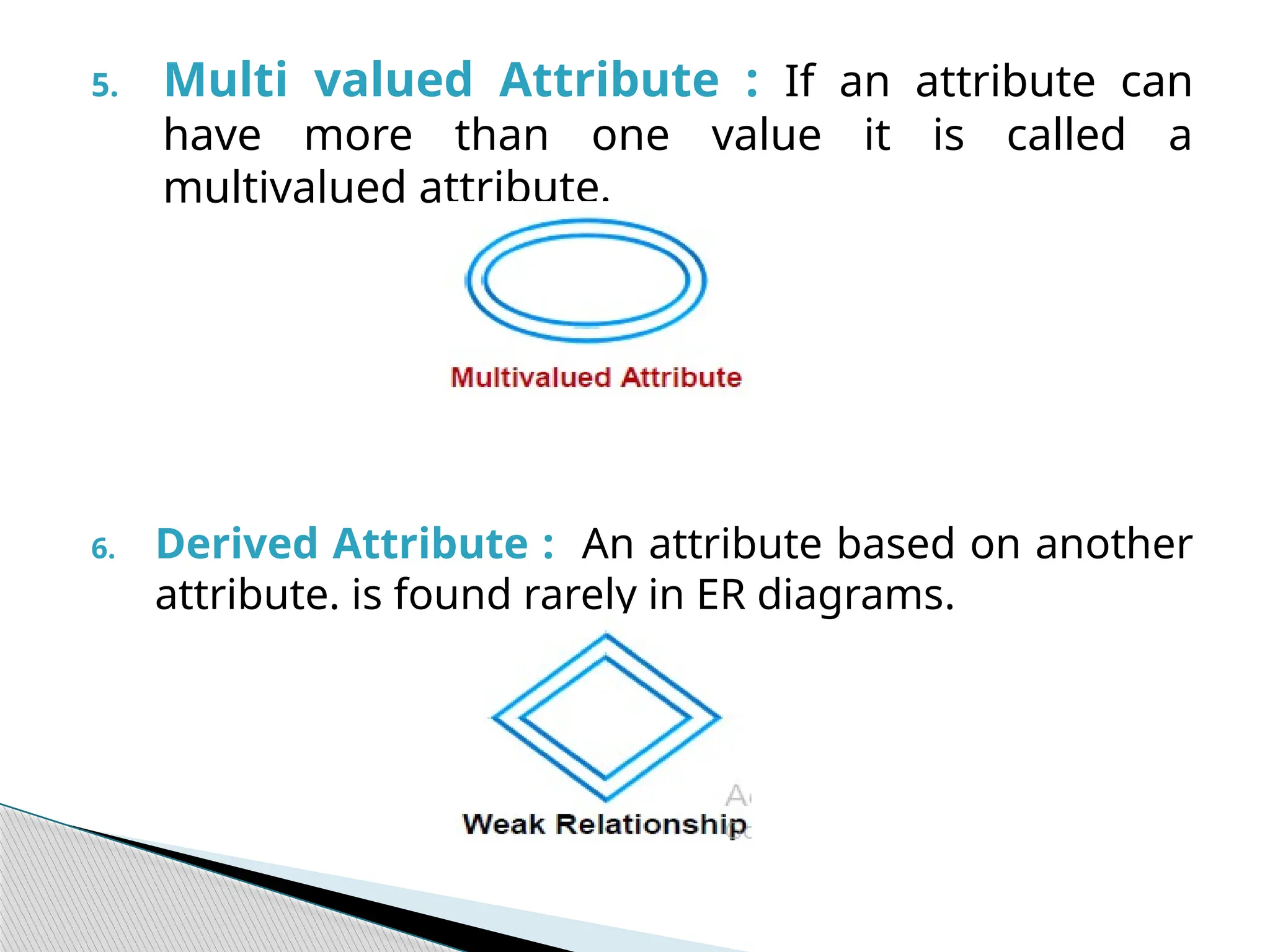
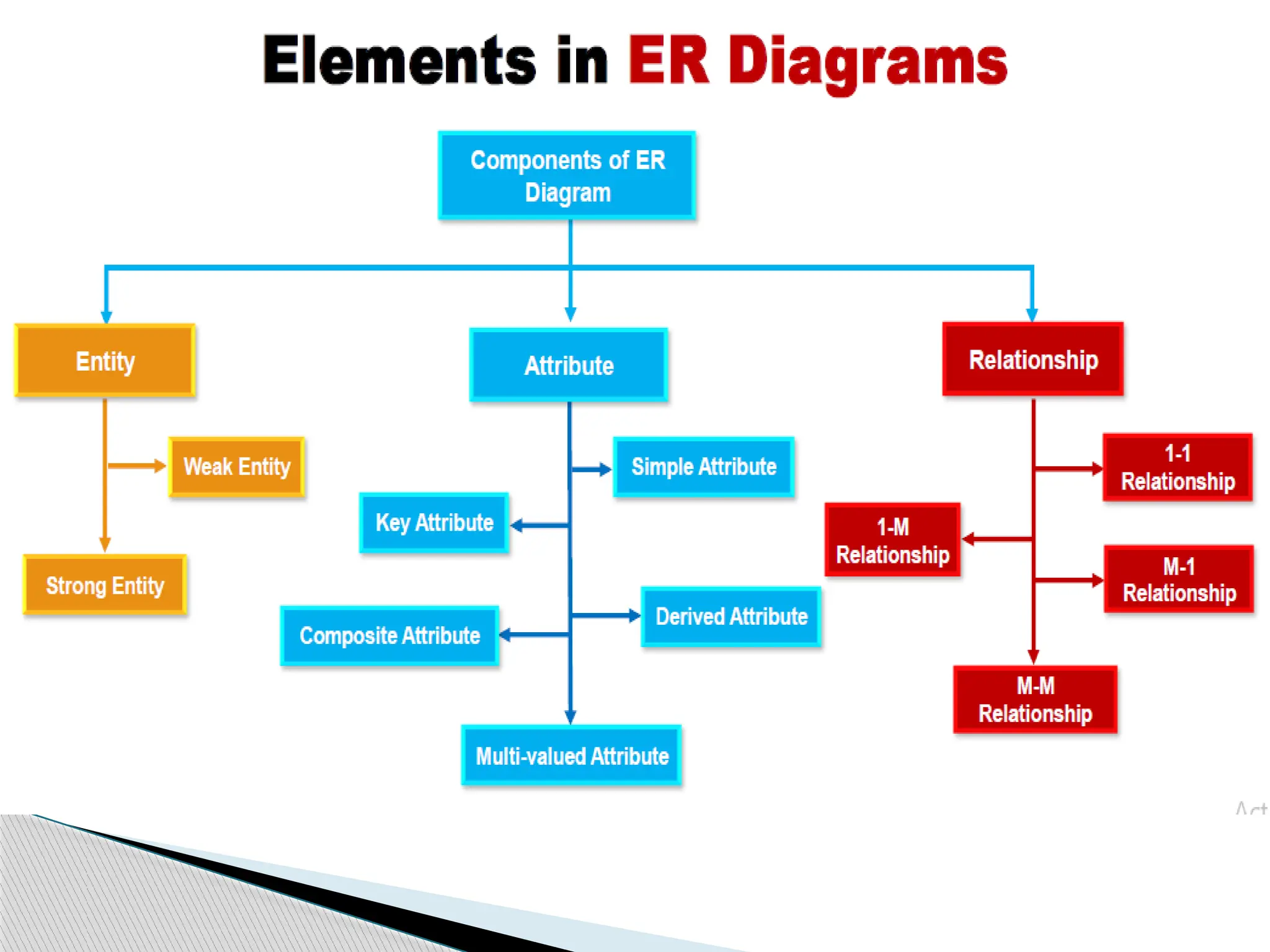
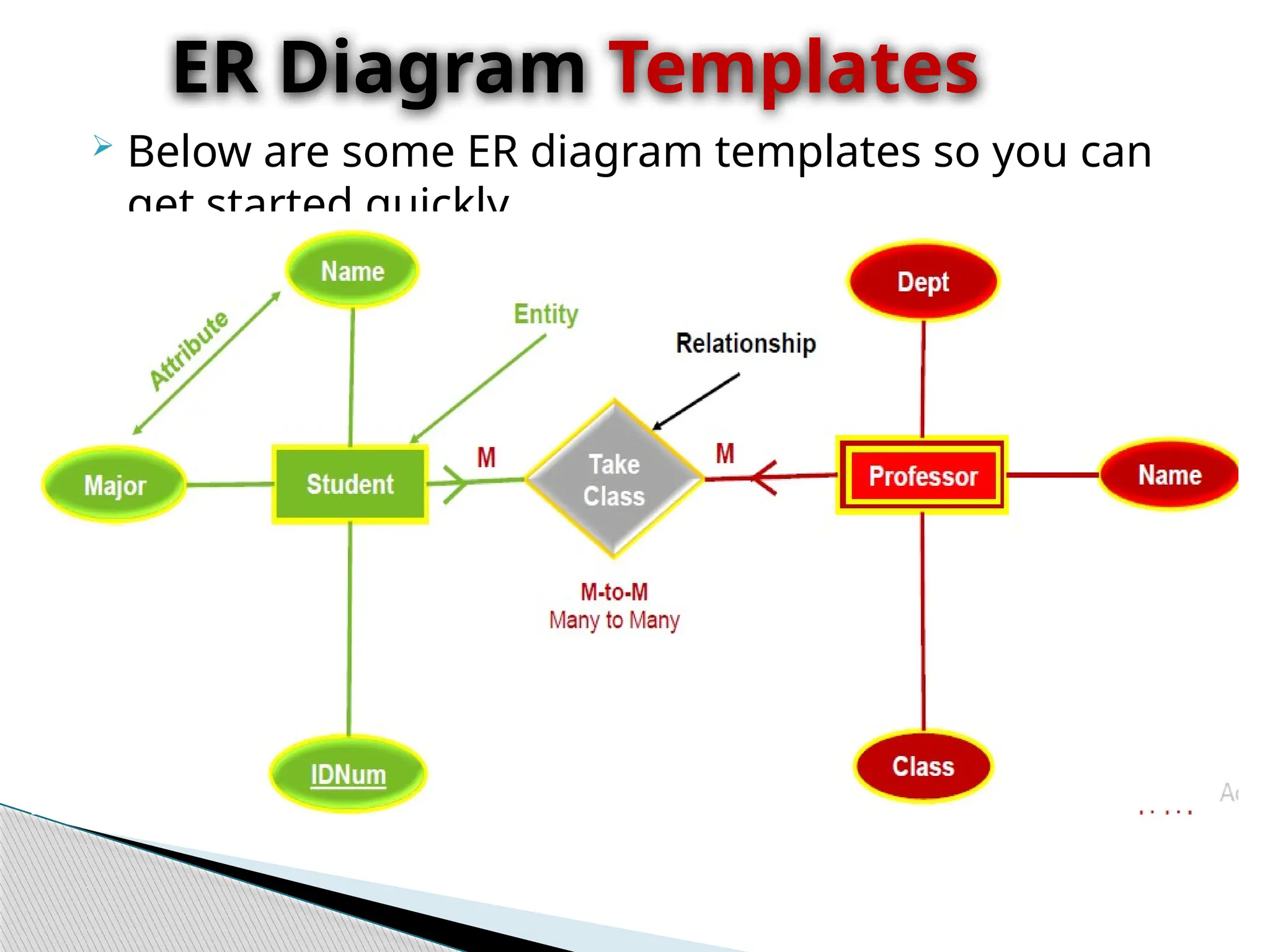
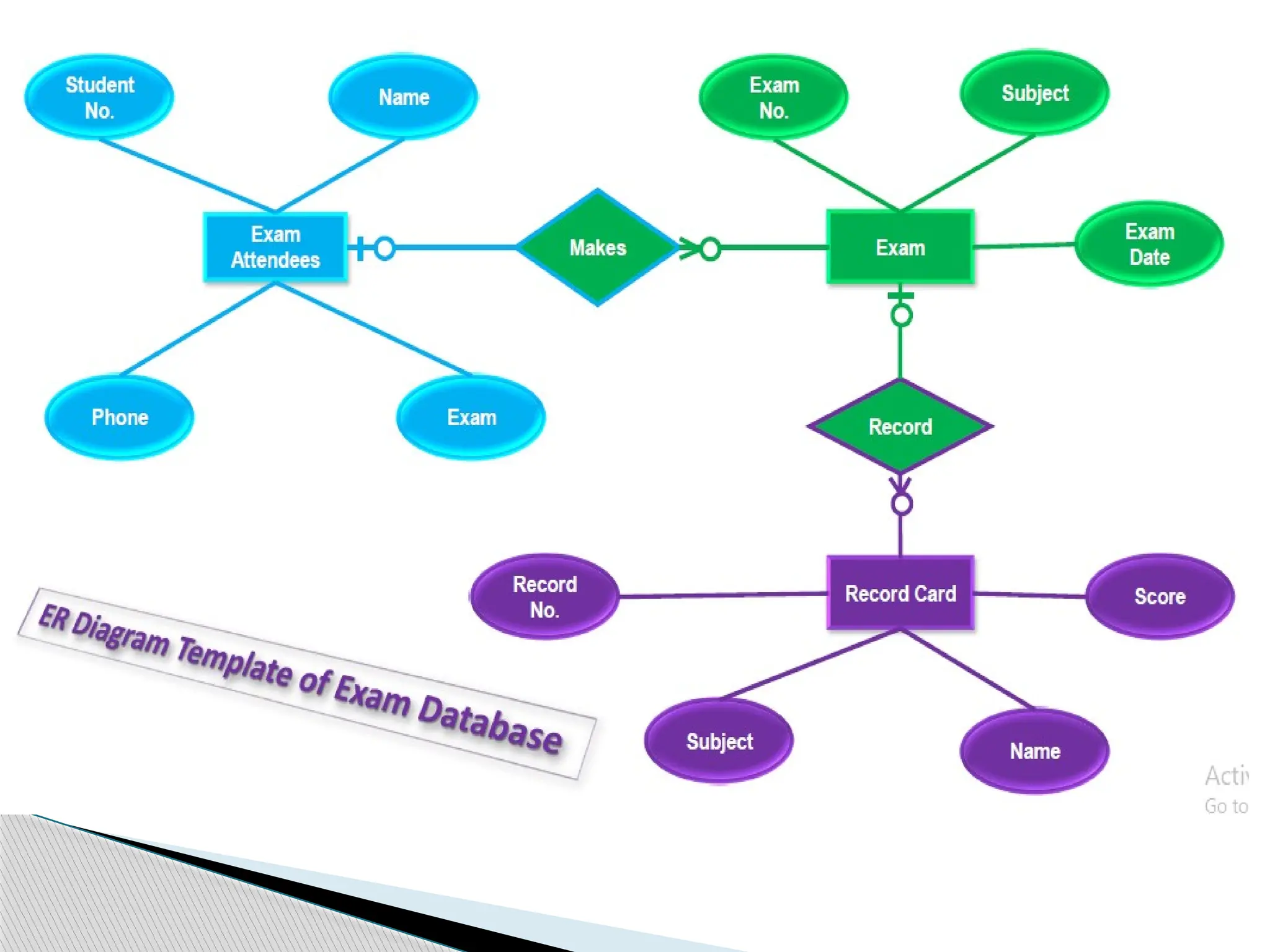
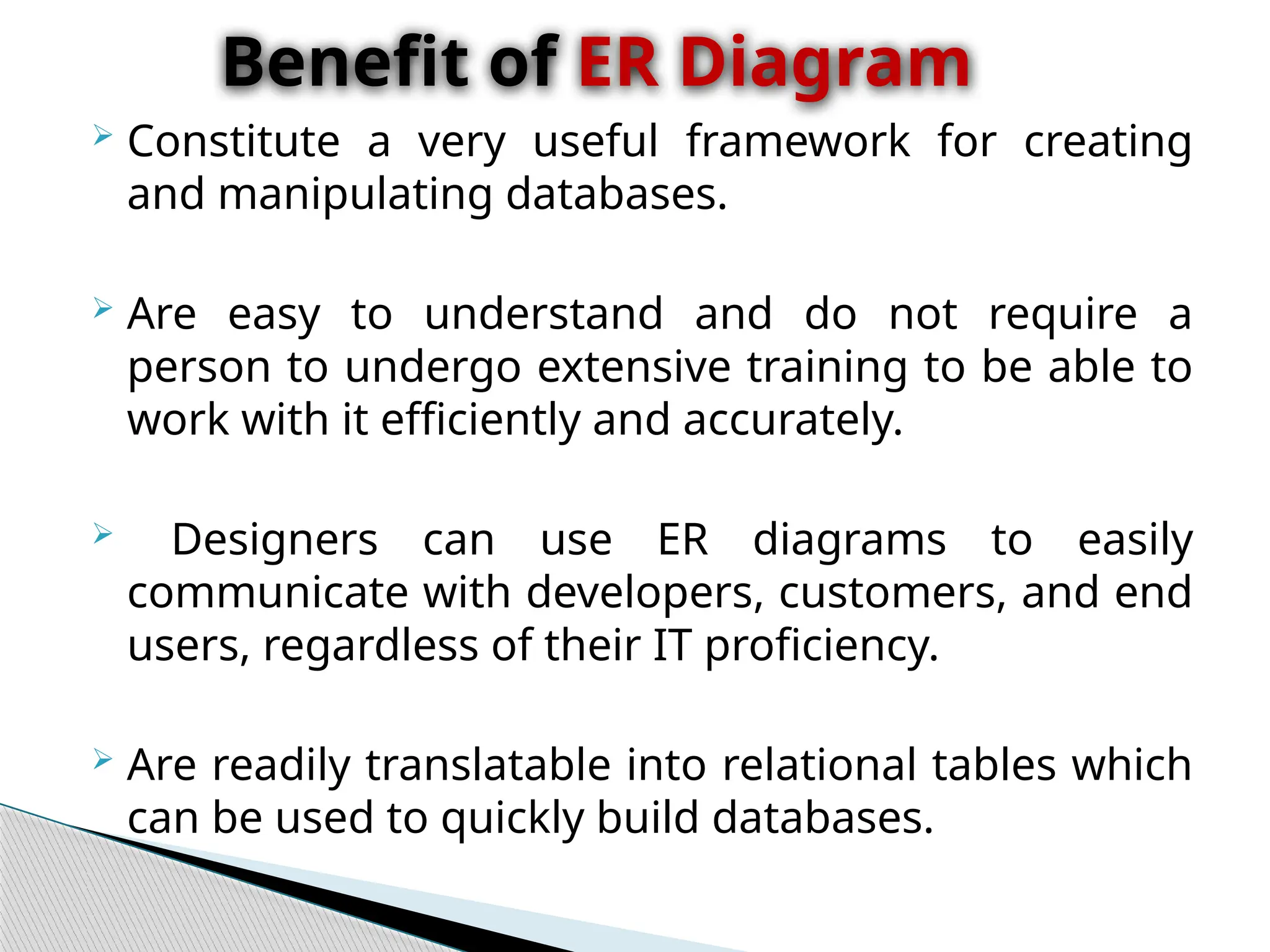
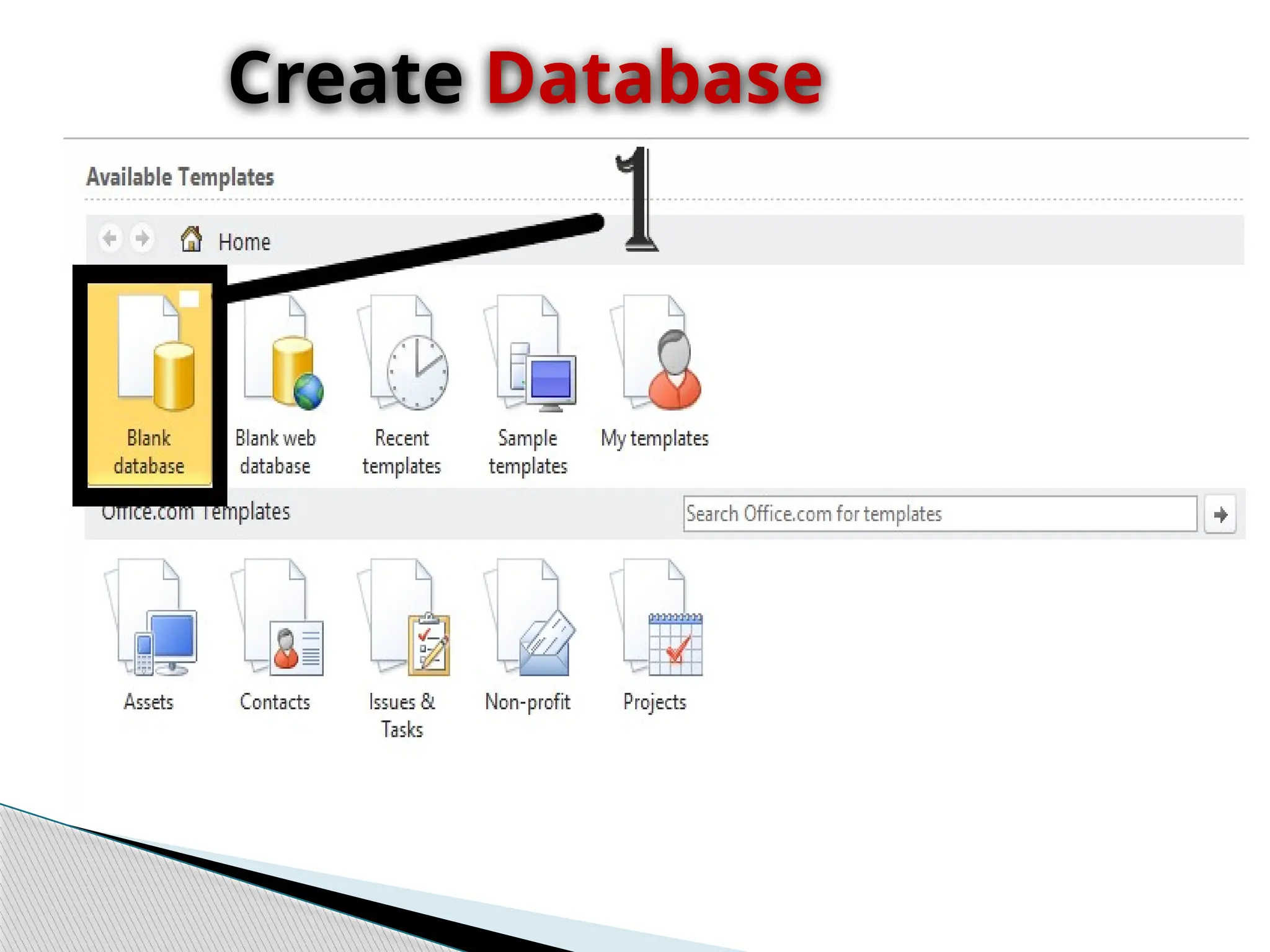
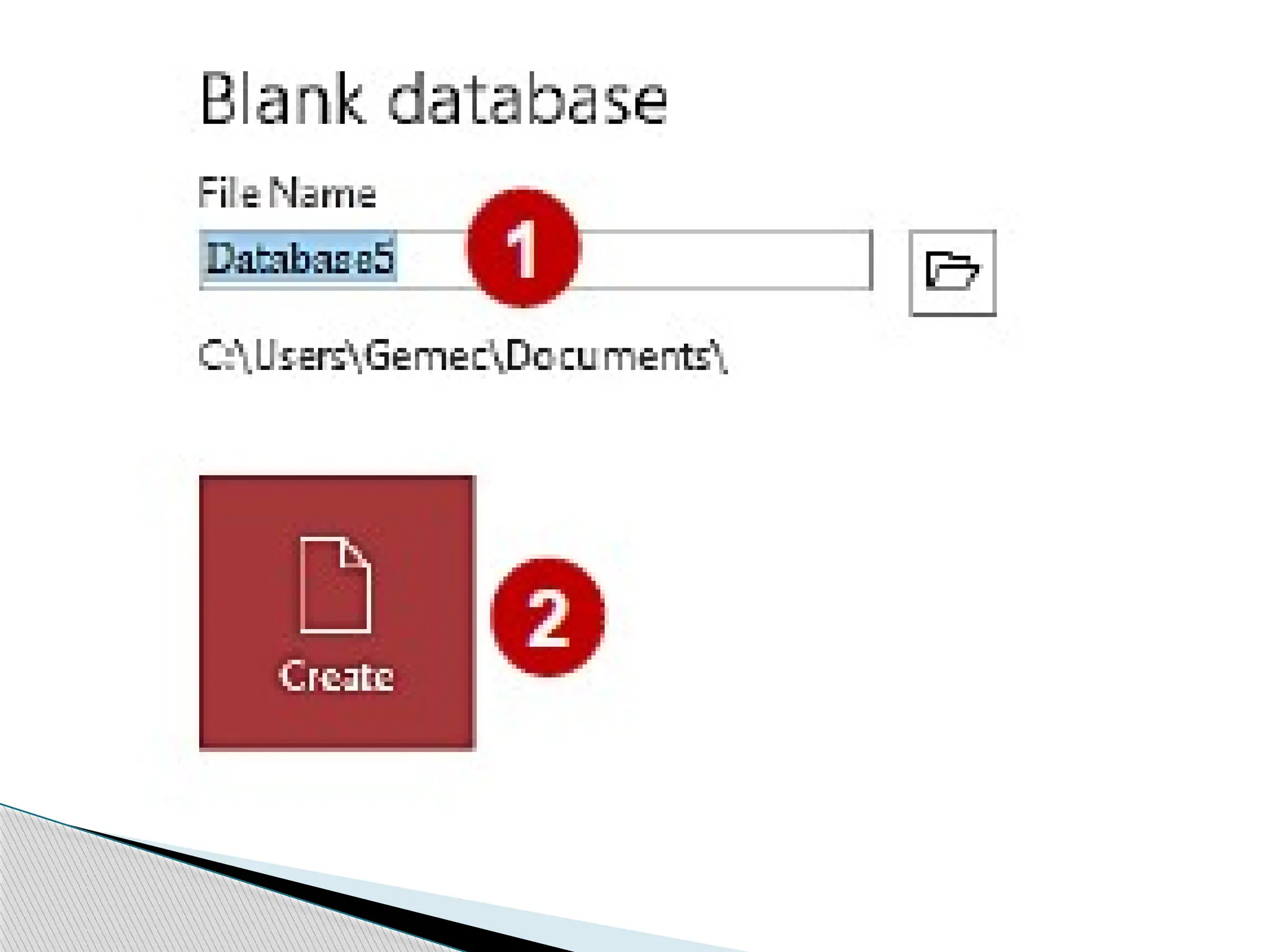
The document discusses database design principles, focusing on usability, extensibility, data integrity, and security within a database management system. It outlines the processes for creating and managing databases using Microsoft Access, including table design, data normalization, and establishing relationships between data elements. Additionally, it explains the significance of entity relationship diagrams (ERDs) and how they visualize the relationships among different data entities.







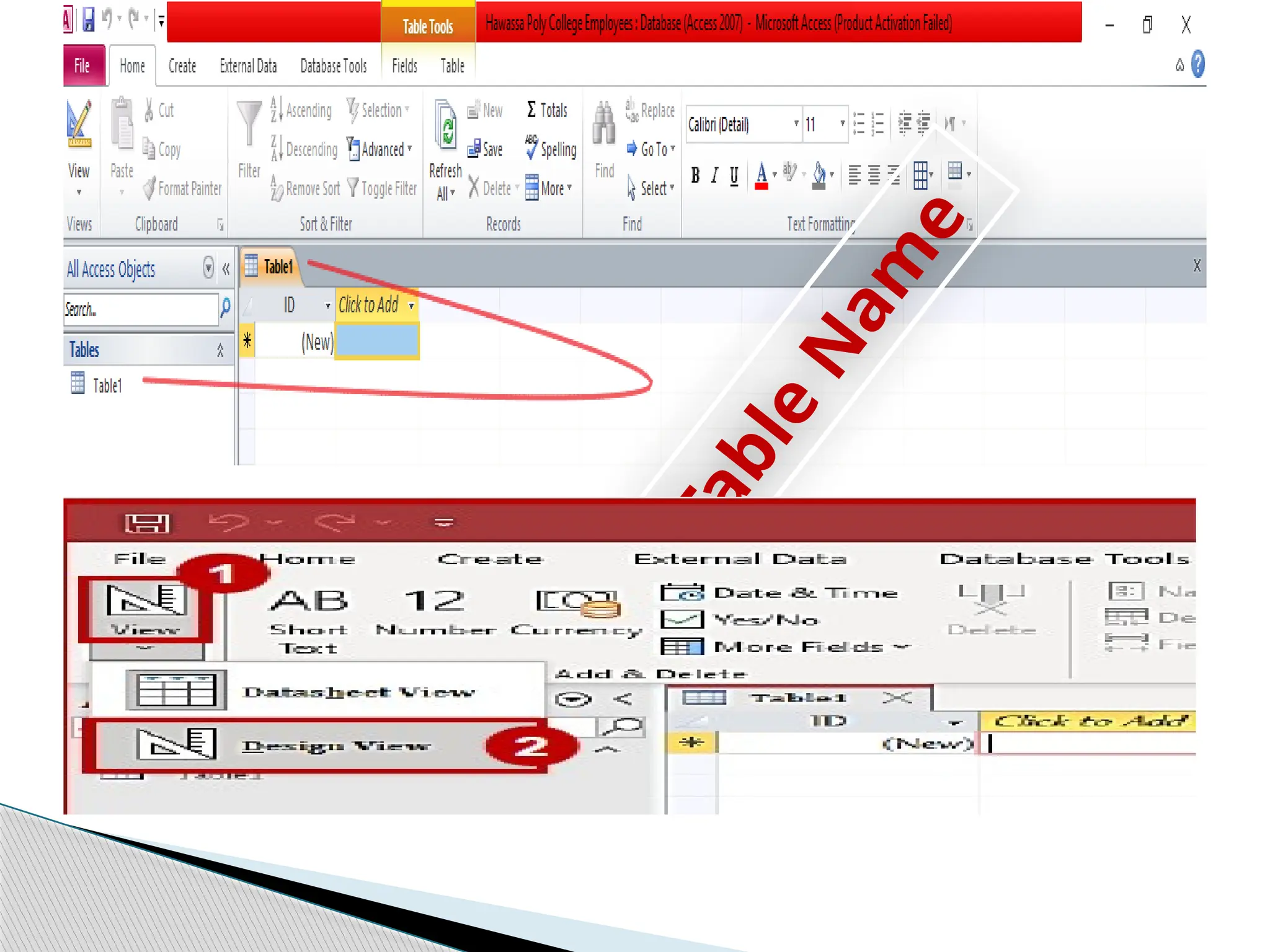
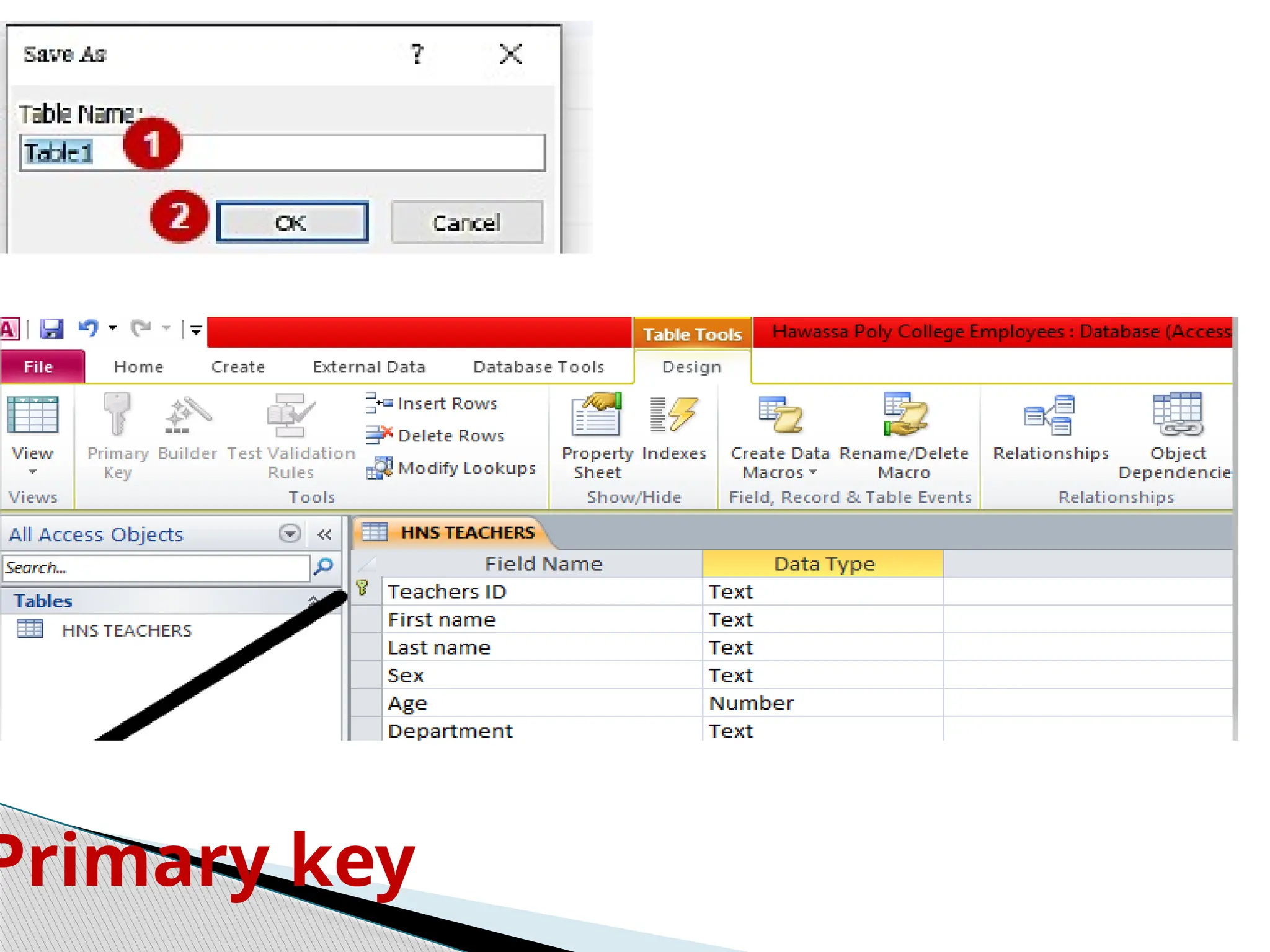
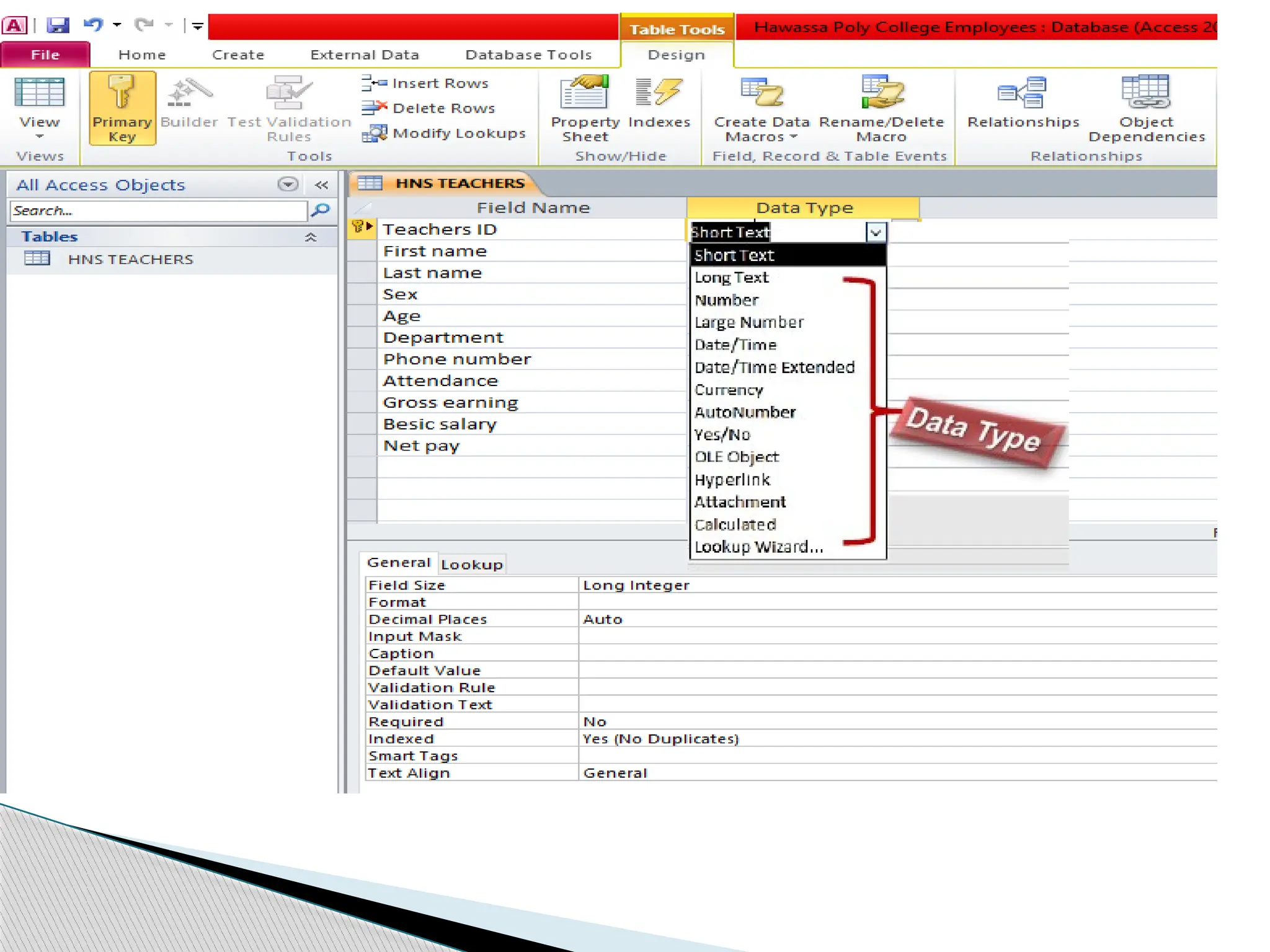
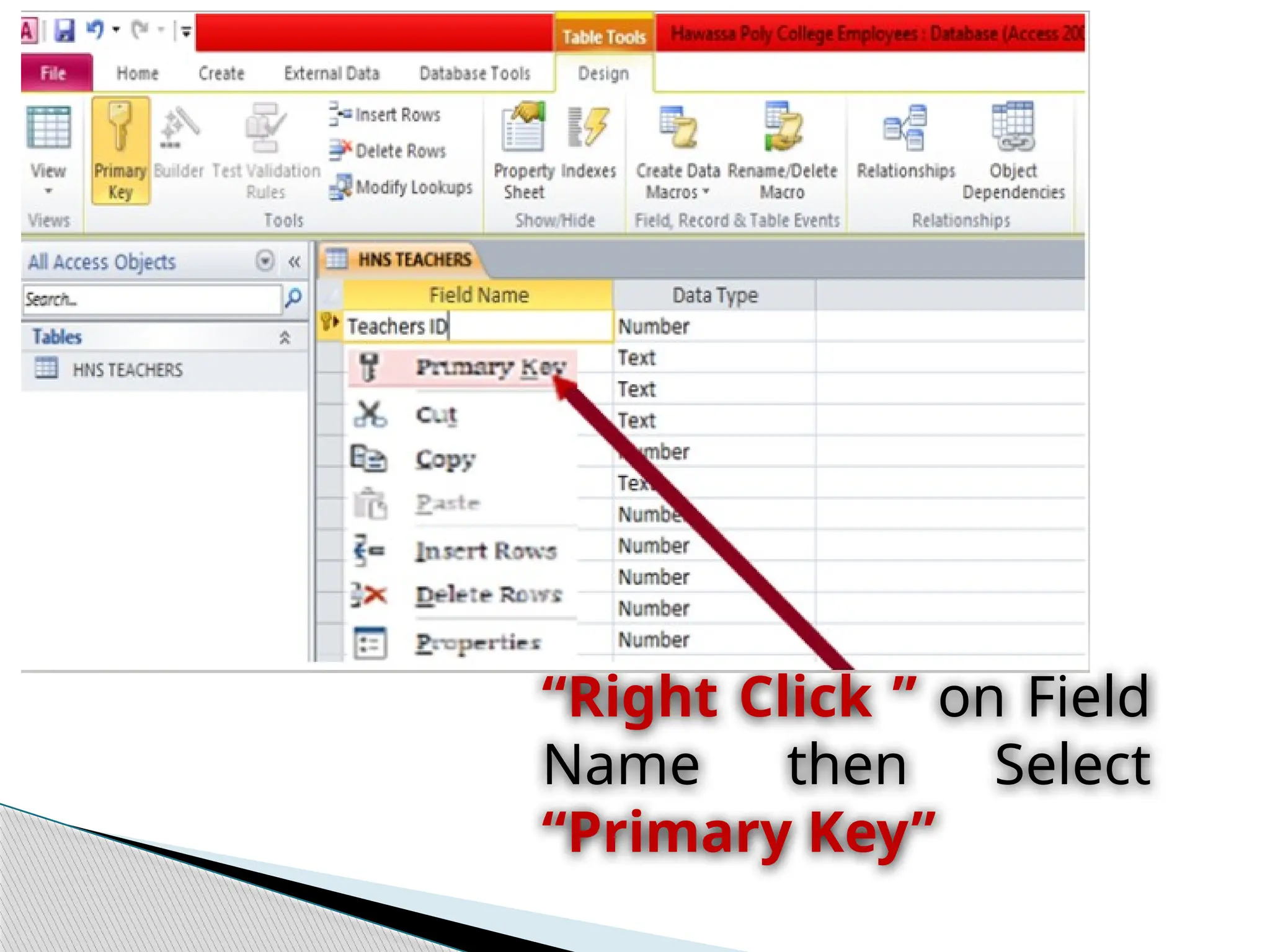
![ Entering unique names of the columns of the table in the
“field name” column of the design view.
Names of fields and objects in Microsoft Access can be up
to 64characters long.
They can include any combination of letters, numbers,
spaces, and special characters except a period (.), an
exclamation point (!), an accent grave (`), and brackets ([ ]).
They also can't begin with leading spaces
Designing table involves](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/operatedatabaseapplication-241224113551-866d8292/75/Operate-Database-Applicationidentify-ntrk-handtools-pptx-18-2048.jpg)