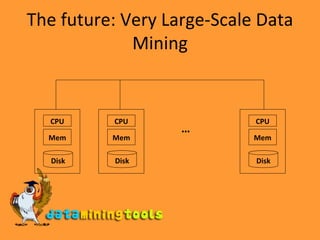
Web mining involves analyzing textual and link structure data from the world wide web to discover useful information. It deals with petabytes of data generated daily and needs to adapt to evolving usage patterns in real-time. Topics related to web mining include web graph analysis, power laws, structured data extraction, web advertising, user analysis, social networks, and blog analysis. The future will involve very large-scale data mining of datasets too big to fit in memory or even on a single disk.