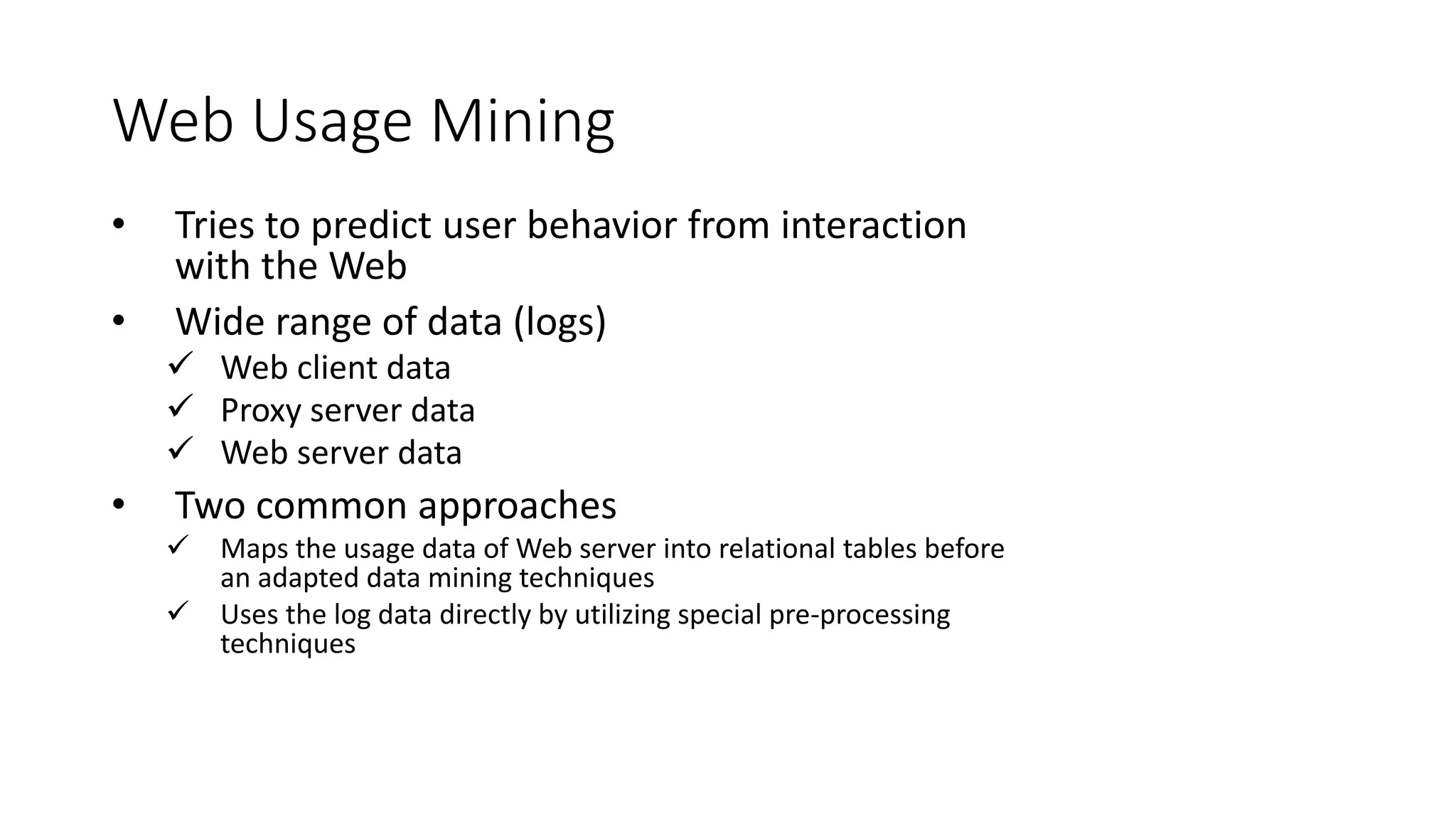
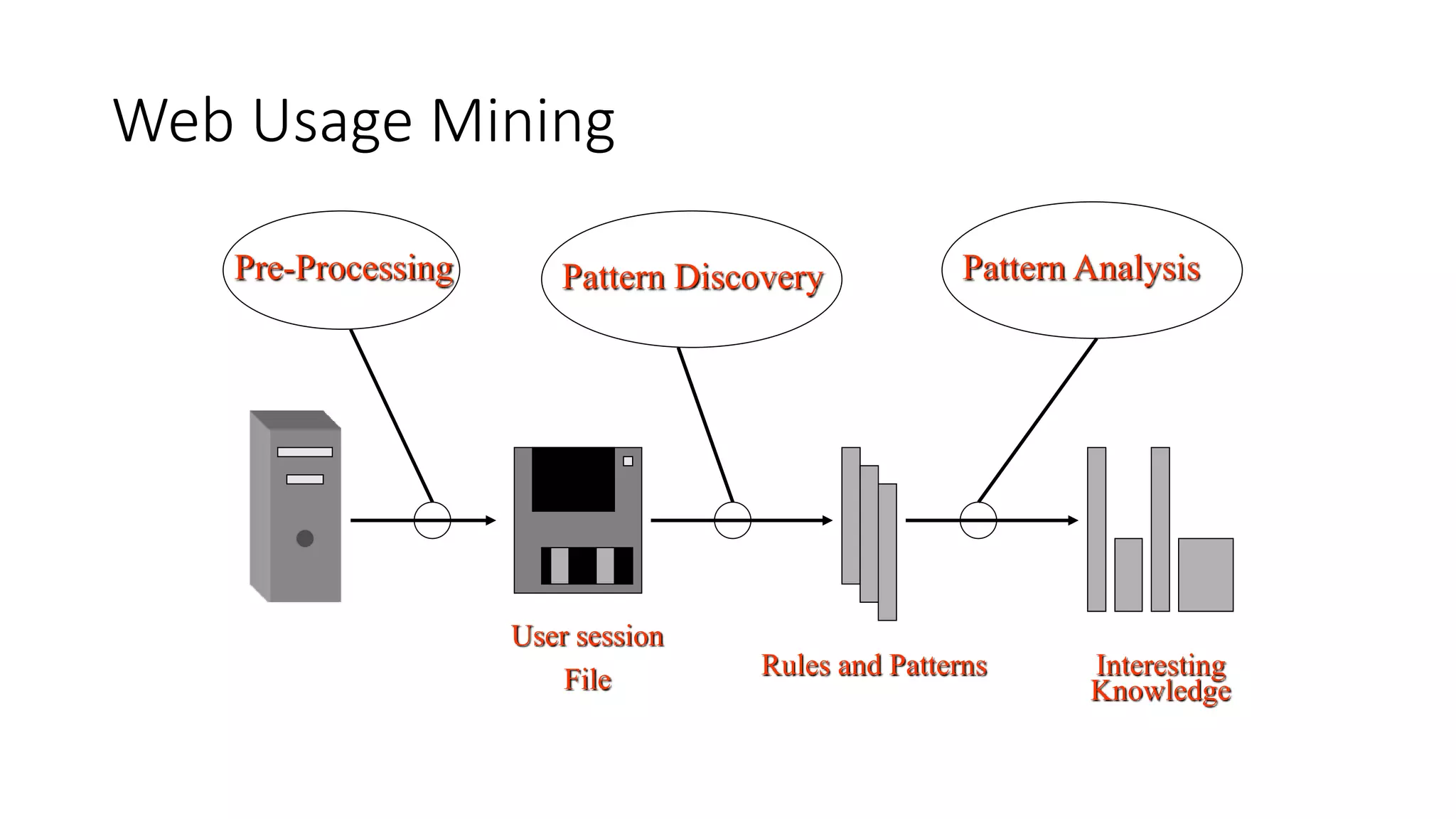
This document provides an overview of web mining. It defines web mining as using data mining techniques to automatically discover and extract information from web documents and services. It discusses the differences between web mining and data mining, and covers the main topics in web mining including web graph analysis, structured data extraction, and web advertising. It also describes the different approaches of web content mining, web structure mining, and web usage mining.
















![Web Content Mining: DB View
• DB view mainly uses the Object Exchange Model (OEM)
Represents semi-structured data by a labeled graph
The data in the OEM is viewed as a graph, with objects as the vertices
and labels on the edges
Each object is identified by an object identifier [oid] and
Value is either atomic or complex
• Process typically starts with manual selection of Web sites for
doing Web content mining
• Main application:
• The task of finding frequent substructures in semi-structured data
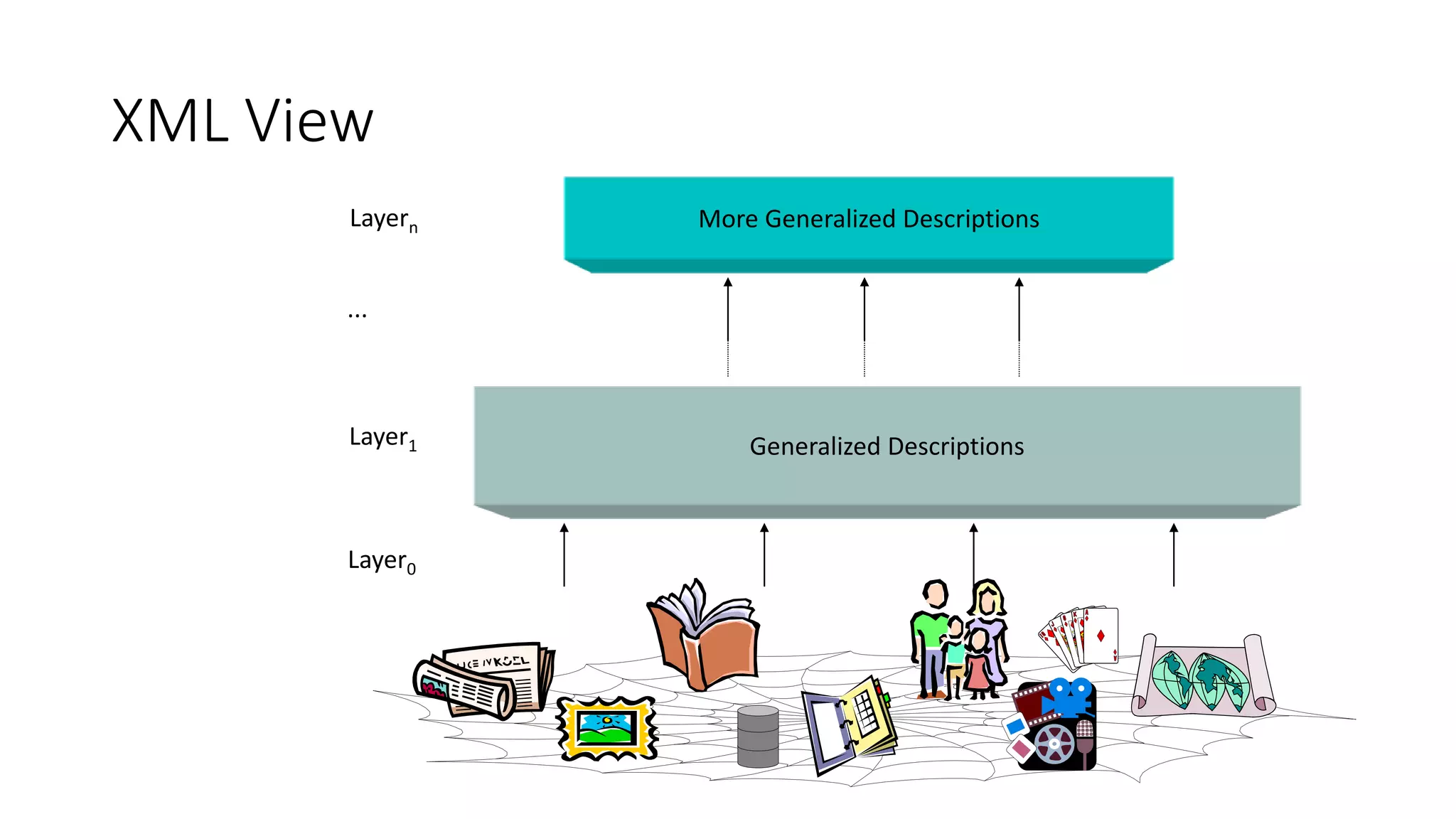
• The task of creating multi-layered database](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/d6a9d68a-e6e3-45dc-a248-fd6a5dd7476d-150504014409-conversion-gate01/75/Web-Mining-26-2048.jpg)