This document discusses web-scale discovery services (WDS), including what they are, their key features and benefits, examples of major WDS providers, and considerations for implementation. Specifically:
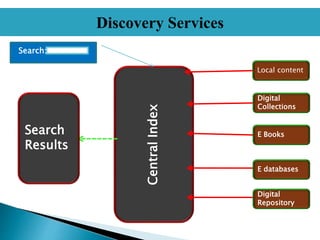
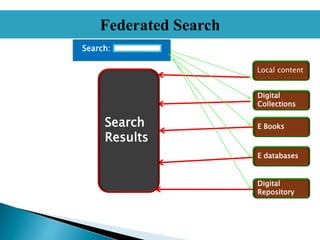
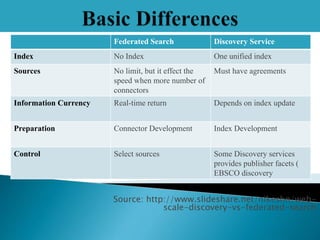
- WDS allows users to search a library's entire collection through a single search box, ranking results based on relevancy across sources. This is presented as an improvement over federated search.
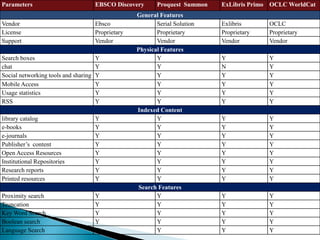
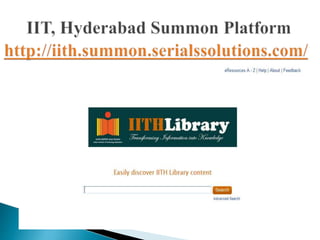
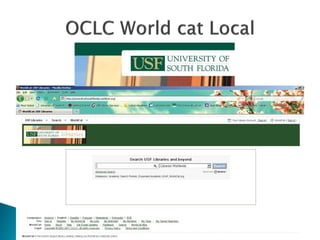
- Major WDS providers discussed include EBSCO Discovery Service, Ex Libris Primo, Serials Solutions Summon, and OCLC's WorldCat Local.
- A comparison of these providers shows they index a variety of content like the library catalog, e-books, journals, and more.
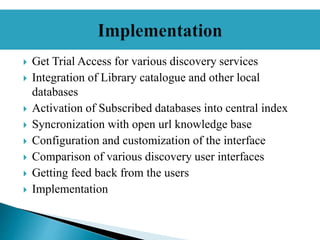
- The