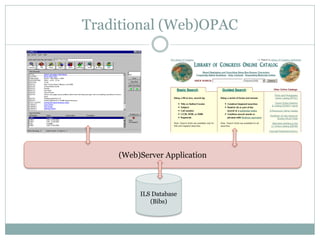
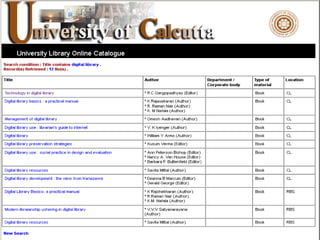
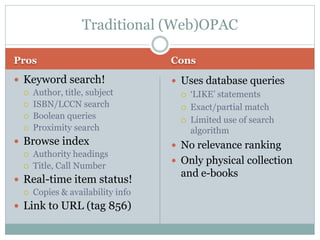
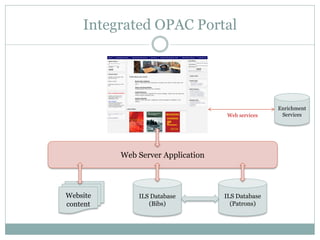
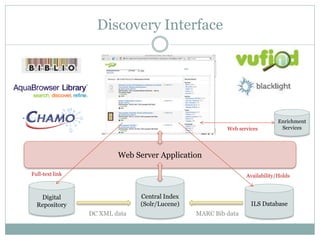
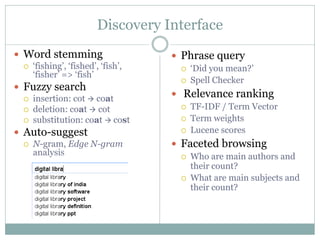
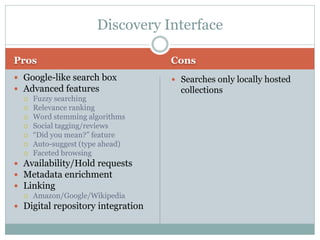
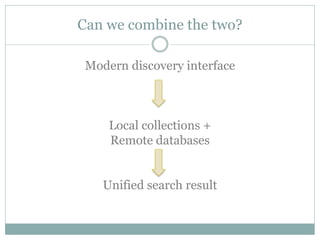
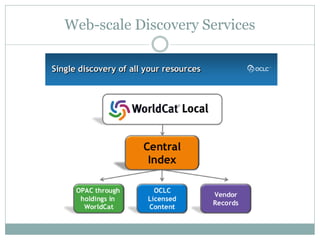
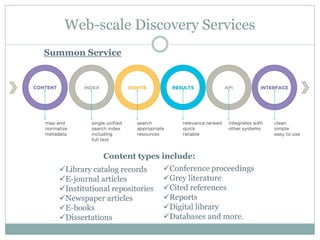
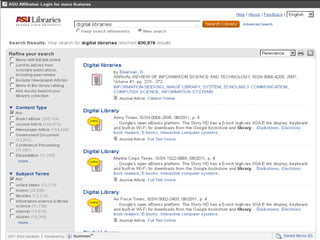
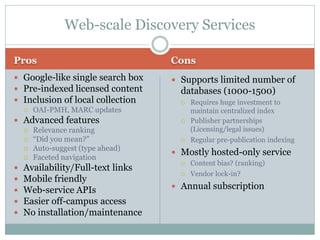
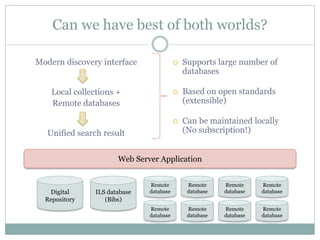
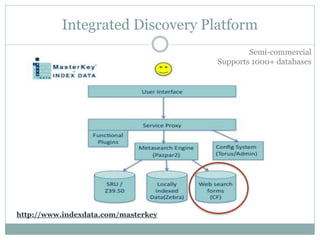
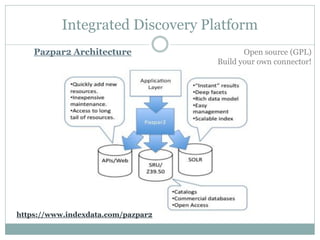
This document discusses the evolution of discovery tools from printed catalogues to modern integrated discovery platforms. It outlines the key features and limitations of traditional OPACs, federated search services, discovery interfaces, and web-scale discovery services. The conclusion emphasizes that no single system is perfect, and that as content becomes more open, discovery solutions should focus on open and extensible platforms that are also affordable.