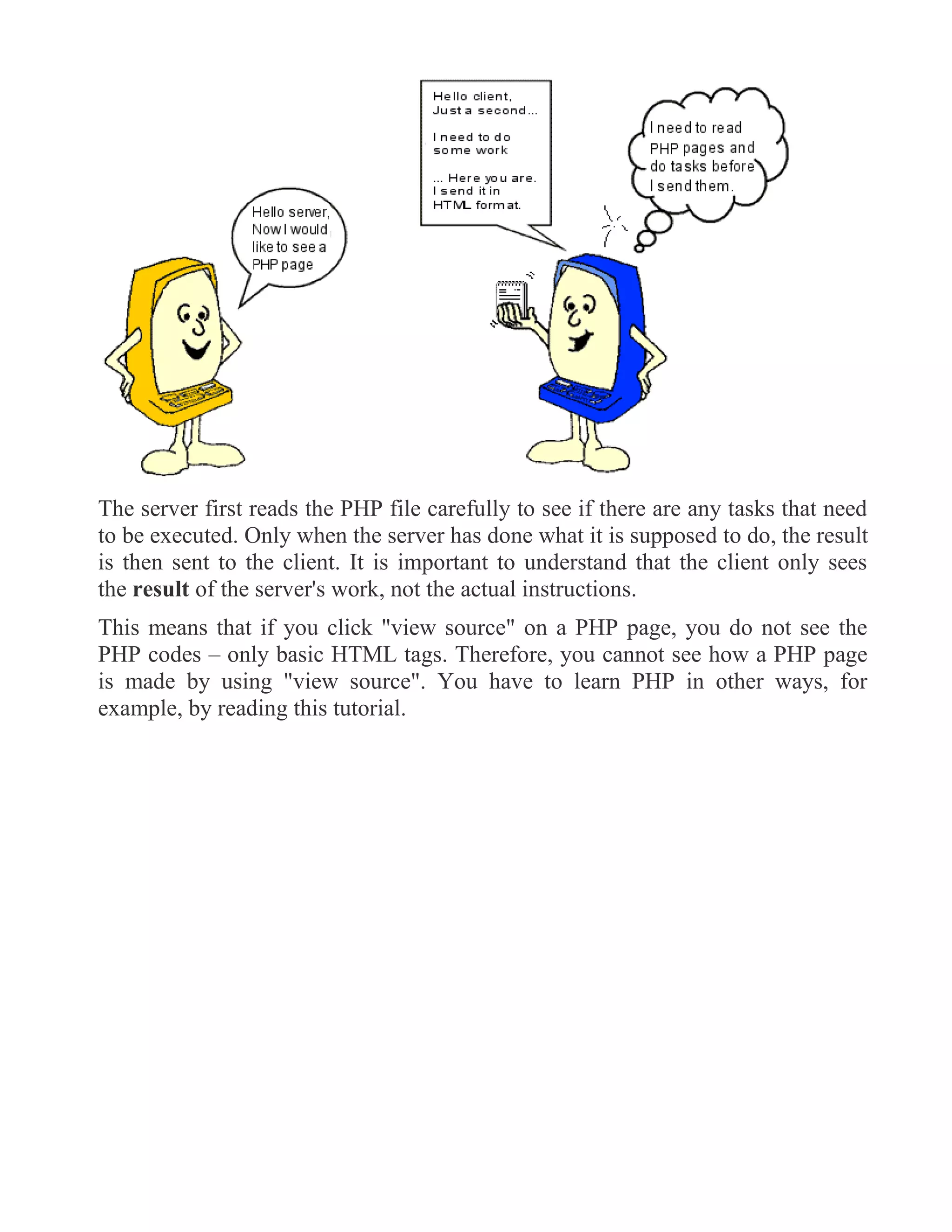
The document provides an introduction to web design and PHP. It defines key concepts like the World Wide Web, web browsers, URLs, and domain names. It explains that the web uses a client-server model where web servers store files and web clients (browsers) access them. PHP is introduced as a widely-used scripting language that allows dynamic content generation and interaction with databases on the server-side. PHP code is executed on the server and the results are returned as HTML to the client.