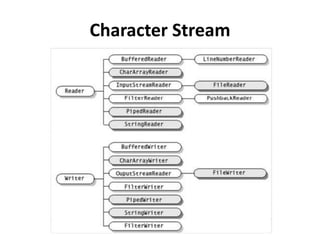
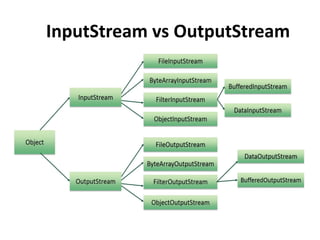
A data stream is a process that reads or sends data from/to one resource or location. There are two types of streams: byte streams for binary data and character streams for Unicode text data. Java's IO package provides classes for input and output streams to read from and write to various sources like files, networks, and memory. Reader and Writer classes handle text data while InputStream and OutputStream classes handle bytes. Buffered streams improve performance by using buffering. To read/write files, FileReader/FileWriter or FileInputStream/FileOutputStream are used.